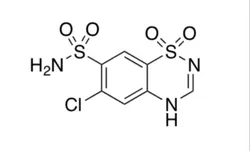
Chlorothiazide
Synonym(s):6-Chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
- CAS NO.:58-94-6
- Empirical Formula: C7H6ClN3O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 295.72
- MDL number: MFCD00058576
- EINECS: 200-404-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-20 16:56:22
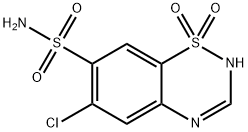
What is Chlorothiazide?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration.
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50: > 10 g/kg. Signs of overdose include those caused by electrolyte depletion (hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hyponatremia) and dehydration resulting from excessive diuresis. If digitalis has also been administered hypokalemia may accentuate cardiac arrhythmias.
Description
Chlorothiazide is a first-in-class thiazide diuretic initially discovered from its ability to inhibit carbonic anhydrase in vitro. As an antihypertensive agent, this thiazide increases renal excretion of sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate ions by inhibiting tubular reabsorptive mechanisms.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Diuril,Merck Sharp and,US,1957
The Uses of Chlorothiazide
Diuretic; antihypertensive. Hydrochlorothiazide EP Impurity A.
The Uses of Chlorothiazide
Chlorthiazide is a diuretic that causes the body to excrete excess fluid. This drug exhibits strong diuretic action during both acidosis and alkalosis. It is used for arterial hypertension, in edematous syndromes of various genesis, congestive effects in cardiovascular insufficiency, nephrosis and nephritis, and toxicosis. It is especially recommended for hypertonic illnesses. It lowers intraocular pressure in a number of cases.
Background
A thiazide diuretic with actions and uses similar to those of hydrochlorothiazide. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p812)
Indications
Chlorothiazide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. It is also indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
What are the applications of Application
Chlorothiazide is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase
Definition
ChEBI: Chlorothiazide is 4H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide in which the hydrogen at position is substituted by chlorine and that at position 7 is substituted by a sulfonamide group. A diuretic, it is used for treatment of oedema and hypertension. It has a role as a diuretic and an antihypertensive agent.
Manufacturing Process
(A) m-Chloroaniline (64 g, 0.5 mol) was added dropwise with stirring to 375
ml of chlorosulfonic acid in a 3-liter round bottom, 3-necked flask cooled in an
ice bath. Sodium chloride (350 g) was added portionwise over a period of 1 to2 hours and the mixture then heated gradually in an oil bath to 150°C. After 3
hours at 150° to 160°C, the flask was cooled thoroughly in an ice bath and
the contents treated with a liter of cold water. The product was extracted with
ether and the extract washed with water and dried over sodium sulfate.
After removal of ether on the steam bath, the residual 5-chloroaniline-2,4-
disulfonyl chloride, which may be crystallized from benzene-hexane MP 130°
to 132°C, was cooled in an ice bath and treated with 150 ml of 28%
ammonium hydroxide in a 2-liter Erlenmeyer flask. The mixture was heated
on the steam bath for 1 hour, cooled and the product collected on the filter,
washed with water and dried. Upon crystallization from dilute alcohol 5-
chloro-2,4-disulfamylaniline was obtained as colorless needles, MP 251° to
252°C.
(B) A solution of 88 g of 5-chloro-2,4-disulfamylaniline in 1.1 liters of 88%
formic acid was heated under reflux for 2 hours. After removal of 200 ml of
solvent by distillation, one liter of water was added and the product collected,
washed with water and dried. Crystallization from dilute alcohol afforded 6-
chloro-7-sulfamyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide as colorless needles, MP
342.5° to 343°C, as described in US Patent 2,809,194.
brand name
Diuril (Ovation).
General Description
Crystals; white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Alkaline aqueous solutions will decompose on standing or heating .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Chlorothiazide are not available; however, Chlorothiazide is probably combustible.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of Chlorothiazide is an interference with the renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. The diuretic action of chlorothiazide, like other drugs of this series, is caused by reduced absorption of sodium and chloride ions by the kidneys during their simultaneous, intense excretion from the organism.
Pharmacokinetics
Like other thiazides, chlorothiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). It inhibits Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue. Chlorothiazide affects the distal renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. At maximal therapeutic dosages, all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic efficacy. Chlorothiazide increases excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Natriuresis may be accompanied by some loss of potassium and bicarbonate. After oral doses, 10-15 percent of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Chlorothiazide crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Safety Profile
Moderately_toxic by intraperitoneal and intravenous routes. Mddly toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. Has been implicated in aplastic anemia. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx NOx and Cl-.
Synthesis
Chlorothiazide, 1,1-dioxide 6-chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazin-7-sulfonamide (21.3.3) is synthesized in the exact same manner, is all thiazide diuretics. 3- Chloroaniline (or 3-trifluoromethylaniline) undergoes sulfoylchlorination by chlorosulfonic acid, forming 4,6-sulfonochloride-3-chloroaniline (21.3.1), the reaction of which with ammonia gives 4,6-sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline (21.3.2). Heating this with formamide leads to formation of chlorothiazide (21.3.3).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, furosemide has largely supplanted the use
of thiazides as a general diuretic (edema treatment). Thiazides are
still used for the treatment of systemic hypertension,
nephrogenic
diabetes insipidus, and to help prevent the recurrence of calcium
oxalate uroliths in dogs.
Chlorothiazide is approved for use in dairy cattle for the treatment
of post parturient udder edema, but the veterinary labeled
product has been discontinued in the USA.
Metabolism
Chlorothiazide is not metabolized but is eliminated rapidly by the kidney.
Properties of Chlorothiazide
| Melting point: | 342-343°C |
| Boiling point: | 608.8±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.7303 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6100 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly, Heated) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 6.85, 9.45(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 19.5 ºC |
| Merck | 14,2168 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58-94-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Chlorothiazide(58-94-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorothiazide (58-94-6) |
Safety information for Chlorothiazide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Chlorothiazide
Chlorothiazide manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 58-94-6 99%View Details
58-94-6 99%View Details
58-94-6 -
 Chlorothiazide 99%View Details
Chlorothiazide 99%View Details
58-94-6 -
 Chlorothiazide 58-94-6 98%View Details
Chlorothiazide 58-94-6 98%View Details
58-94-6 -
 Chlorothiazide 58-94-6 98%View Details
Chlorothiazide 58-94-6 98%View Details
58-94-6 -
 Chlorothiazide 95% CAS 58-94-6View Details
Chlorothiazide 95% CAS 58-94-6View Details
58-94-6 -
 Chlorothiazide CAS 58-94-6View Details
Chlorothiazide CAS 58-94-6View Details
58-94-6 -
 58-94-6 90 % AboveView Details
58-94-6 90 % AboveView Details
58-94-6 -
 Nlt 95% Powder Hydrochlorothiazide EP Impurity A, 58-94-6View Details
Nlt 95% Powder Hydrochlorothiazide EP Impurity A, 58-94-6View Details
58-94-6
