CHLOROBENZILATE
Synonym(s):Ethyl 4,4′-dichlorobenzilate
- CAS NO.:510-15-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H14Cl2O3
- Molecular Weight: 325.19
- MDL number: MFCD00055312
- EINECS: 208-110-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
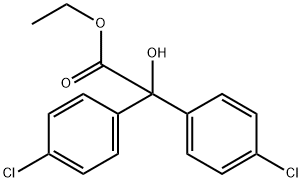
What is CHLOROBENZILATE?
Description
Chlorobenzilate is an organochlorine pesticide belonging to the same class as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). It was originally developed by Ciba–Geigy and introduced in 1952.
Chemical properties
viscous yellow liquid or pale yellow crystals
Chemical properties
Ethyl 4,40 -dichlorobenzilate is a yellow solid when pure. The technical product is a brownish liquid.
The Uses of CHLOROBENZILATE
Acaricide in spider-mite control; synergist for DDT.
The Uses of CHLOROBENZILATE
Nonsystemic pesticide and acaricide.
The Uses of CHLOROBENZILATE
The primary use of chlorobenzilate is as an acaricide for mite control on citrus crops and in beehives. It has a narrow insecticidal action, killing only mites and ticks. Historically, chlorobenzilate was used as a synergist for DDT. Although now banned for use in the United States and Europe, it is believed to be used on crops other than citrus in other countries.
Definition
ChEBI: Chlorobenzilate is a diarylmethane.
General Description
Viscous yellow liquid or pale yellow crystals. Light brown crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
CHLOROBENZILATE is hydrolyzed by alkalis and strong acids. Incompatible with lime .
Health Hazard
Moderately toxic by oral route; toxic symptoms similar to DDT and Perthane; ingestionof large dose can produce nausea, vomiting,tremor and convulsions; skin or eye contactcan cause irritation; application of 25 mgproduced moderate irritation of eye inrabbits; adequate evidence of carcinogenicityin experimental animals; produced tumors inrats and mice; evidence of carcinogenicity inhumans remains unknown.
LD50 oral (rat): 700 mg/kg
LD50 oral (mouse): 729 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for CHLOROBENZILATE are not available; however, CHLOROBENZILATE is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin and eye irritant. A pesticide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.
Potential Exposure
It is a buffer in many chemical intermediates; an organochlorine miticide; to kill mites, ticks, and other insects; as a synergist for DDT. Incompatibilities: Strong acids, strong bases; lime.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, removefrom exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal prestopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Rhodotorula gracilis, a yeast isolated from an insecticide-treated soil,
degraded chlorobenzilate in a basal medium supplemented by sucrose. Metabolites identified by this decarboxylation process were 4,4′-dichlorobenzilic acid, 4,4′-dichlorobenzophenone and carbon dioxide (Miyazaki et al., 1969, 1970).
Soil. Though no products were identified, the half-life of chlorobenzilate in two fine
sandy soils was estimated to be 1.5–5 weeks (Wheeler, 1973).
Photolytic. Chlorobenzilate should not undergo direct photolysis since it does not
absorb UV light at wavelengths greater than 290 nm (Gore et al., 1971).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from strong acids, strong bases. Wherepossible, automatically pump liquid from drums or otherstorage containers to process containers. Sources of ignitionare prohibited where this chemical is used, handled, orstored. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2996 Organochlorine pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.UN2761 Organochlorine pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Toxicity evaluation
The historical use of chlorobenzilate resulted in its release into the environment. It has low water solubility (log Kow = 4.74) and adsorbs strongly to sediment and suspended particulate matter in aquatic environments. Chlorobenzilate has low soil mobility due to an estimated Koc of 1500 and thus is not expected to leach into groundwater. Decomposition via photolysis or hydrolysis is not considered significant. The halflife of chlorobenzilate in fine sandy soils was estimated to be 10–35 days, with degradation being primarily microbial. In silty clay loam and clay soils, the half-life of chlorobenzilate was estimated to be 10.8–15.1 and 29.5–169.1 days, respectively. Volatilization from water or soil is not appreciable due to an estimated Henry’s law constant of 7.2 atmm3 mol-1. If released into air, chlorobenzilate will exist in both vapor and particulate phases. The half-life of vapor-phase chlorobenzilate in ambient air was estimated to be 3.2 days. Chlorobenzilate in the particulate phase is expected to be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. There is no evidence for long-range transport of chlorobenzilate. Bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms is moderate to high due to a reported bioconcentration factor range of 224–709 in fish.
Incompatibilities
Strong acids, strong bases, lime
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of CHLOROBENZILATE
| Melting point: | 37-38℃ |
| Boiling point: | bp0.04 146-148° |
| Density | 1.332 |
| refractive index | 1.5727 |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| pka | 11.11±0.29(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 13mg/L(20 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,2141 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, alkalies, lime. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 510-15-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorobenzilate (510-15-6) |
Safety information for CHLOROBENZILATE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for CHLOROBENZILATE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1