CARVONE
- CAS NO.:99-49-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H14O
- Molecular Weight: 150.22
- MDL number: MFCD00062996
- EINECS: 202-759-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
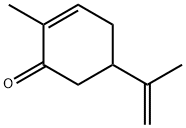
What is CARVONE?
Chemical properties
Pale-yellowish or colorless liquid with a strong characteristic odor. Soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, propylene glycol, and mineral oils; insoluble in glycerol and water. Combustible.
Chemical properties
Carvone occurs as (S)-(+)-
carvone ([α]18
D +64.3°,), (R)-(?)-carvone ([α]20
D ?62.5°),
or racemic carvone. The optical isomers differ considerably in their
sensory properties. They occur in high percentages in a number of essential oils.
(+)-Carvone is the main component of caraway oil (about 60%) and dill oil; (?)-
carvone occurs in spearmint oil at a concentration of 70–80%.
Both (+)- and (?)-carvone are used to flavor a number of foods and beverages.
(?)-Carvone is produced in much larger quantities and is mainly used in
oral hygiene products.
Chemical properties
Caravone occurs in different forms. l-Carvone exhibits odor of spearmint, while d-carvone exhibits odor reminiscent of caraway.
Physical properties
The carvones are colorless to slightly yellow liquids.(+)-Carvone has a herbaceous odor reminiscent of caraway and dill seeds, whereas (?)-carvone has a herbaceous odor reminiscent of spearmint. Depending on the reaction conditions, hydrogenation of carvone yields either carveol or dihydrocarvone, which are also used as flavor compounds. When treated with strong acids, carvone isomerizes to carvacrol.
Occurrence
The optically active and inactive forms have been reported among the constituents of about 70 essential oils. The dextro form is present in carvi, Antheum graveolens, Antheum sowa, Lippia carviodora, Mentha arvensis, etc. The levo form is present in Metha vifidis var. crispa, Mentha longifolia from South Africa, Eucalyptus globules and several mint species. The racemic form is present in ginger grass, Litsea gutalemaleusis, lavender and Artemisia ferganensis. Reported found in citrus oil and juice (lemon, lime, orange), celery seed, anise, clove, coriander seed, calamus, caraway herb and dill seed.
The Uses of CARVONE
Carvone is useful for the treatment of various metabolic disorders and GI related disorders.
The Uses of CARVONE
Flavoring, liqueurs, perfumery, soaps.
Definition
A ketone derived from the terpene dipentene. It is optically active, occurring naturally in both d- and l-forms.
Preparation
In the past, (+)- and (?)-carvones were isolated by fractional distillation
of caraway oil and spearmint oil, respectively. However, these carvones are
now prepared synthetically, the preferred starting materials being (+)- and (?)-
limonenes, which are converted into the corresponding optically active carvones.
Since optical rotation is reversed in the process, (+)-limonene is the startingmaterial
for (?)-carvone.
Thepreferred industrialmethod of carvone synthesis utilizes the selective addition
of nitrosyl chloride to the endocyclic double bond of limonene. If a lower
aliphatic alcohol is used as solvent, limonene nitrosochloride is obtained in high
yield. It is converted into carvone oxime by elimination of hydrogen chloride in
the presence of a weak base. Acid hydrolysis in the presence of a hydroxylamine
acceptor, such as acetone, yields carvone.
An alternative process for the production of (?)-carvone has recently been commercialized.
Starting from (+)-limonene 1,2-epoxide, a regioselective rearrangement
of the epoxide leads to (?)-carveol (trans- :[2102-58-1]; cis- :[2102-59-2]).
Thereaction is effected by the use of a catalyst consisting of a combination of metal
salts and phenolic compounds.
(?)-Carveol is subsequently oxidized to (?)-carvone by anOppenauer oxidation
or by dehydrogenation in the presence of special catalysts.The reaction may also
be performed as a one-pot reaction.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: d-Carvone: 6.7 to 820 ppb; l-carvone: 2.7 to 600 ppb
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 49, p. 3435, 1984 DOI: 10.1021/jo00192a054
Synthesis, p. 223, 1980 DOI: 10.1055/s-1980-28975
Synthesis
Carvone occurs in the dextro, levo and racemic form; l-carvone can be isolated from the essential oil of spearmint or is commercially synthesized from d-limonene; d-carvone is usually prepared by fractional distillation of oil of caraway, also from dillseed and dillweed oils, but this type differs in odor and flavors.
Properties of CARVONE
| Melting point: | 230℃ |
| Boiling point: | 232℃ (760.0 Torr) |
| Density | 0.963 g/cm3 (15℃) |
| refractive index | 1.710 |
| FEMA | 2249 | CARVONE |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Light Orange to Light Brown |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. minty licorice |
| JECFA Number | 380 |
| Dielectric constant | 11.0(22℃) |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-49-0 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Cyclohexen-1-one, 2-methyl-5-(1-methylethenyl)- (99-49-0) |
Safety information for CARVONE
Computed Descriptors for CARVONE
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
