Carisoprodol
Synonym(s):2-Methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol carbamate isopropylcarbamate
- CAS NO.:78-44-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H24N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 260.33
- MDL number: MFCD00057661
- EINECS: 201-118-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-20 19:50:36
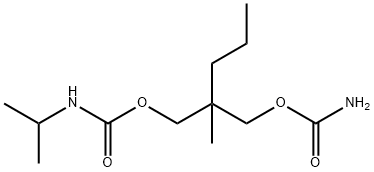
What is Carisoprodol?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of carisoprodol has not yet been established. The mean time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) of this drug was about 1.5-2 hours in clinical studies . Co-administration of a fatty meal with carisoprodol (350 mg tablet) had no impact on carisoprodol pharmacokinetics .
Toxicity
LD50 values
The LD50 values of carisoprodol for rats are 450 mg/kg for intravenous (IV) and intraperitoneal injection, and 1,320 mg/kg for gavage dosing. In mice, the LD50 values are 165 mg/kg for intravenous injection, 980 mg/kg for intraperitoneal injection, and 2,340 mg/kg for gavage dosing. The LD50 value for rabbits given carisoprodol by intravenous injection is 124 mg/kg .
Overdose
An overdose of carisoprodol leads to CNS depression, and in severe cases, induction of a coma. Shock, depression of respiratory function, seizures and death have also been reported in rare cases. Several symptoms may be associated with carisoprodol overdose, such as horizontal and vertical nystagmus, blurred vision, mydriasis, mild tachycardia and hypotension, respiratory depression, euphoria, CNS stimulation, muscular incoordination, and/or rigidity, confusion, headache, hallucinations, and dystonic reactions. Alcohol or other CNS depressants or psychotropic agents can exert additive effects on carisoprodol even when one of the agents has been ingested at the normal, therapeutic dose. Fatal accidental and non-accidental overdoses have both been reported with carisoprodol ingestion alone or ingestion of carisoprodol in combination with alcohol or psychotropic drugs .
A note on dependence and withdrawal
In the postmarketing reports after carisoprodol use, cases of dependence, withdrawal, and abuse have been reported with long-term use. The majority of dependence and withdrawal cases, as well as abuse, have occurred in patients with a history of addiction or who have used this drug in combination with other drugs having abuse potential. However, multiple post-marketing adverse event reports have been made of carisodopril-associated abuse when used without other drugs possessing abuse potential. Withdrawal symptoms have been observed and reported following sudden abrupt cessation after long-term carisodoprol use. To reduce the chance of carisodopril dependence, withdrawal, or abuse, carisodopril should be used with caution in addiction-prone patients and in patients taking other CNS depressants including alcohol. This drug should not be taken for longer than 2 to 3 weeks for symptomatic relief of acute musculoskeletal discomfort .
Use in pregnancy
This drug has been classified as Pregnancy Category C. There are no clinical trial data on the use of carisoprodol during human pregnancy. Animal studies show that carisoprodol crosses the placenta and leads to adverse effects on fetal growth and postnatal survival. In postmarketing reports, the main metabolite, meprobamate, has not demonstrated a consistent association between maternal use and an increased risk for specific congenital malformations .
Use in nursing
Limited data in humans demonstrate that this is found excreted in breast milk and may reach concentrations in breast milk of 2-4 times the maternal plasma concentrations . It is therefore advisable to exercise caution when this drug is used during breastfeeding .
Description
Carisoprodol (Item No. 30778) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a skeletal muscle relaxant. It also has sedative properties. Carisoprodol is regulated as a Schedule IV compound in the United States. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Description
Carisoprodol (CRM) (Item No. ISO60206) is a certified reference material categorized as a skeletal muscle relaxant. It also has sedative properties. Carisoprodol is regulated as a Schedule IV compound in the United States. Carisoprodol (CRM) (Item No. ISO60206) is provided as a DEA exempt preparation. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Soma,Wallace,US,1959
The Uses of Carisoprodol
Muscle relaxant (skeletal)
Carisoprodol has an onset of action of ca. 30min and a duration of 4–6h. It is administered orally. Presumably, it acts by inhibiting interneuronal activity in the spinal cord and the brainstem reticular formation. Clinically effective doses are accompanied by drowsiness or dizziness; its mechanism may involve sedation.Its CNS depressant effects are additive with those of ethanol and other psychotropic agents. Carisoprodol has a low potential for drug dependence.

The Uses of Carisoprodol
For the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful, musculoskeletal conditions.
The Uses of Carisoprodol
Carisoprodol suppresses interneuronal action of reticular formation of the spinal cord. It is used as an adjuvant drug for loss of flexibility of skeletal muscle as well as for relieving pain caused therein. Synonyms of this drug are rela, soma, carisoma, and sanoma.
Background
Originally approved by the FDA in 1959 , carisoprodol is a centrally acting muscle relaxant used in painful musculoskeletal conditions in conjunction with physical therapy and other medications . This drug is available by itself in an oral tablet or combined with aspirin, or in a fixed-dose combination with both aspirin and codeine .
In January 2012, this drug was classified as a Schedule IV substance under the controlled substances act in several US states due to alarming rates of abuse despite having a low potential for abuse in addition to a low risk of dependence .
Indications
Carisoprodol is indicated for the relief of discomfort related to acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions .
Important limitations of use :
? Should only be used for acute treatment periods up to two or three weeks
? Adequate evidence of effectiveness for more prolonged use has not been established
? Not recommended in pediatric patients less than 16 years of age
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is the mono-N-isopropyl derivative of meprobamate (which is a significant metabolite). Carisoprodol interrupts neuronal communication within the reticular formation and spinal cord, resulting in sedation and alter tion in pain perception. It is used as a muscle relaxant in the symptomatic treatment of musculoskeletal conditions associated with painful muscle spasm.
Preparation
Carisoprodol is Prepared by reaction of 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-pro-panediol with phosgene and ammonium hydroxide, then with isopropyl isocyanate.
Manufacturing Process
A cooled 10% solution of 1 mol of phosgene in toluene was added with
stirring to a cooled solution of 1 mol of 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol and
2 mols of dimethylaniline also dissolved in toluene, at such a rate that the
temperature of the mixture was maintained at about 25°C. The mixture was
allowed to remain at this temperature for several hours, then cooled and
extracted with cold 5% hydrochloric acid solution to remove the
dimethylaniline. The toluene layer was dried using a suitable drying agent and
the 2-methyl-2-propyl-3-hydroxypropyl chlorocarbonate used in subsequent
reactions in the form of its solution in anhydrous toluene.
A quantity of solution obtained as described containing 0.1 mol of the
chlorocarbonate was treated with 0.2 mol of anhydrous isopropylamine and
allowed to react at ordinary room temperature. The solution was cooled,
extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid and the organic layer concentrated by
evaporation of the solvent. The crude monocarbamate was purified by
distilling at 86° to 88°C at about 0.01 mm. It was a clear, viscous liquid.
21.7 g (0.1 mol) of N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-3-hydroxypropylcarbamate
and 7.5 g (0.11 mol) of anhydrous sodium cyanate are stirred in 200 ml
anhydrous chloroform in a suitable vessel equipped with a gas inlet tube,stirrer and thermometer. While cooling the vessel, anhydrous hydrogen
chloride is passed into the stirred mixture slowly for 5 hours maintaining the
temperature between 0° and 5°C. Alternatively ethyl urethane in the presence
of aluminum isopropylate as a catalyst may be used in place of the sodium
cyanates and HCl. The mixture is then allowed to stand at room temperature
overnight.
The solid material is separated by filtration and the chloroform solution
concentrated to an oil under reduced pressure. The oil is dissolved in 50 ml of
trichloroethylene, the solution treated with charcoal, filtered and the filtrate
added to 125 ml of hexane. The crystalline material which forms on standing
at refrigerator temperature is removed by filtration, washed with light
petroleum ether and dried at about 50°C. Approximately 20 g of product are
obtained. On recrystallizing from trichloroethylene-hexane, 17.8 g of purified
compound are obtained, MP 89° to 91°C.
brand name
Rela (Schering); Soma (Medpointe).
Therapeutic Function
Muscle relaxant
General Description
Carisoprodol, N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate, 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol carbamate isopropylcarbamate(Soma), is the mono-N-isopropyl–substituted relative ofmeprobamate. The structure is given in the discussion ofmeprobamate. It is indicated in acute skeletomuscular conditionscharacterized by pain, stiffness, and spasm. As canbe expected, a major side effect of the drug is drowsiness.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Carisoprodol is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: The most common symptoms of exposure to Carisoprodol are drowsiness and hives. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, vertigo, ataxia, tremors, agitation, irritability, headache, insomnia, fainting, hiccups, visual disturbances, asthma, fever, hypotension, excitement and paralysis.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Carisoprodol are not available, but Carisoprodol it probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Carisoprodol is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant that does not act directly on skeletal muscle but acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS). This drug relieves the painful effects of muscle spasm . A metabolite of carisoprodol, meprobamate, possesses both anxiolytic and sedative properties . Clinical studies have shown that this drug causes impairment of psychomotor performance in neuropsychological tests.
Synthesis
Carisoprodol, N-iso-propyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol (15.3.12), is synthesized by reacting 2-methyl-2-propylpropanediol-1,3 dicarbamate with 1 mol of phosgene, forming the chloroformate (15.3.10), from which carbamate (15.3.11) is formed by reacting it with isopropylamine. Reacting this with either urethane or sodium cyanate gives carisoprodol (15.3.12).

Metabolism
The main pathway of carisoprodol is liver metabolism is by the cytochrome enzyme CYP2C19 to form meprobamate. This enzyme exhibits genetic polymorphism, which may affect the metabolism of this drug .
Properties of Carisoprodol
| Melting point: | 92-92°C |
| Boiling point: | 403.59°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1035 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4560 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in acetone, in alcohol and in methylene chloride. |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 4.2 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 19.5 ºC |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-44-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carisoprodol(78-44-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carisoprodol (78-44-4) |
Safety information for Carisoprodol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Carisoprodol
Carisoprodol manufacturer
Meenaakshi Molecules Pvt Ltd
Chemeca Drugs Private Limited (Vegesna Laboratories Pvt Ltd)
Verdant Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
PSN Medicare Private Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 78-44-4 Carisoprodol 99%View Details
78-44-4 Carisoprodol 99%View Details
78-44-4 -
 Carisoprodol 98%View Details
Carisoprodol 98%View Details -
 Carisoprodol CAS 78-44-4View Details
Carisoprodol CAS 78-44-4View Details
78-44-4 -
 Carisoprodol 78-44-4 98%View Details
Carisoprodol 78-44-4 98%View Details
78-44-4 -
 Carisoprodol 78-44-4 99%View Details
Carisoprodol 78-44-4 99%View Details
78-44-4 -
 78-44-4 Carisoprodol 98%View Details
78-44-4 Carisoprodol 98%View Details
78-44-4 -
 Anti-Phospho-NF-kB p65-S536 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-Phospho-NF-kB p65-S536 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 ANTI-PHOSPHO-NF KAPPA B(S536) antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
ANTI-PHOSPHO-NF KAPPA B(S536) antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details