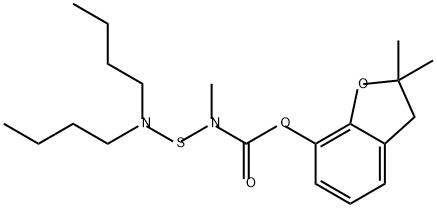
Carbosulfan
Synonym(s):2,3-Dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran-7-yl (dibutylaminothio)methylcarbamate
- CAS NO.:55285-14-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H32N2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 380.54
- MDL number: MFCD00143930
- EINECS: 259-565-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
What is Carbosulfan?
Description
Carbosulfan (8),2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran- 7-yl(dibutylaminothio)methylcarbamate(IUPAC), is an orange to brown, clear viscous liquid (bp 124–128 ?C), miscible with organic solvents and solubility 0.3 ppm in water(25 ?C). It is closely related structurally to carbofuran,and like carbofuran, it is a cholinesterase inhibitor with systemic activity.
Chemical properties
Orange-yellow thick liquid.
The Uses of Carbosulfan
Carbosulfan is an insecticide with contact and stomach action. It is used to control a wide range of soil-dwelling and foliar pests in cotton, sugar beet, potato, rice, fruit, maize, vegetables, sugar cane and coffee.
Definition
ChEBI: Carbosulfan is a member of 1-benzofurans and a carbamate ester. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, a carbamate insecticide, an acaricide, an agrochemical and a nematicide.
General Description
Viscous brown liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Thio and dithiocarbamates slowly decompose in aqueous solution to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids.
Reactivity Profile
Carbosulfan is a thiocarbamate. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides.
Potential Exposure
Carbosulfan is a carbamate insecticide and a low toxic derivative from cabofuran. It is a broad spectrum insecticide, nematicide, miticide, effective against pests and mites. It is used to protect alfalfa, apple, citrus, corn, deciduous fruit, potato, rice, sorghum, soybean, sugar beets, sugarcane, and other vegetable, field, tree and orchard crops. It is used for seed treatments
Metabolic pathway
Carbosulfan is an N-sulfenyl-N-methylcarbamate which is effectively a pro-insecticide of carbofuran. The latter is formed in vivo by the biochemical or chemical thiolysis of carbosulfan. N-S Bond cleavage, oxidation, conjugation and hydrolysis are the main metabolic routes for carbosulfan in plants and animals. Carbosulfan is degraded via carbofuran in soil. In plants, carbosulfan is metabolised via carbofuran to 3-hydroxycarbofuran (PM).
Metabolism
Itsmetabolic patterns are similar to those of carbofuran. In rats, it rapidly undergoes hydrolytic and oxidative processes followed by conjugation. It is not persistent in soils, with DT50 ca. 2–5 days, and it was rapidly degraded to carbofuran in a sandy loam soil (4). Carbofuran was subsequently hydrolyzed at the carbamate ester group to form the phenol carbofuran or oxidized at the 3- position. Biscarbofuran disulfide and minor products were also detected. Carbofuran was also formed in soils by nonbiological degradation processes.
Shipping
UN2992 Carbamate pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials; UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Carbosulfan is hydrolysed in aqueous media most rapidly under acidic
conditions. Its DT50 values (25 °C) at pH 4,6 and 7 were <1 hour, 22 hours
and 7.6 days respectively (PM). In a variety of aqueous solvents there was
facile cleavage of the N-S carbamate bond of carbosulfan to yield carbofuran
(2) as the sole or major product (see Scheme 1) (Umetsu et al., 1980).
A solution of [14C]carbosulfanin propylene glycol was treated with 0.001
or 0.01 N aqueous HCl at 40 °C. Solutions were analysed at intervals up to
24 hours. Carbosulfan was relatively stable with more than 40% being
recovered after 24 hours in the solution of lower acidity. Carbofuran (2)
was the principal transformation product in hydrochloric acid. Biscarbofuran
disulfide (3) was present in only trace amounts and small
amounts of polysulfides of carbosulfan (4,n = 2-6) were detected (Umetsu
and Fukuto, 1982).
Carbosulfan was quite stable in neutral and alkaline media. [14C-carbonyl]-
or [14C-dibutylamino]Carbosulfan dissolved in dichloromethane:
acetic acid (9:l) converted to a range of products via N-S bond cleavage.
The principal products were carbofuran (2), dibutylamine and a mixture
of polysulfide derivatives: bis-carbofuran disulfide (3) and a mixture of
bis-carbofuran polysulfides (5). Structures of products were confirmed by
MS and NMR (Umetsu et al., 1981a,b).
Incompatibilities
Carbamates are incompatible with strong oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydro-peroxides; strong reducing agents such as hydrides; strong acids and bases. Contact with nitrides or chemically active metals (aluminum, copper, magnesium, neptunium, sodium, tin, titanium,zinc, etc.) causes the release of potentially explosive hydrogen gas and a metal salt.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Noncombustible containers should be crushed and buried under more than 40 cm of soil. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Carbosulfan
| Melting point: | <25 °C |
| Boiling point: | approximate 126℃ |
| Density | 1.0560 |
| vapor pressure | 3.1 x 10-5 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6360 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 96 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 3.15±0.70(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 0.3 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| form | neat |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Light brown to brown |
| Merck | 13,1836 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 55285-14-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carbamic acid, [(dibutylamino)thio]methyl-, 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl ester(55285-14-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbosulfan (55285-14-8) |
Safety information for Carbosulfan
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Carbosulfan
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Carbosulfan CAS 55285-14-8View Details
Carbosulfan CAS 55285-14-8View Details
55285-14-8 -
 Carbosulfan CAS 55285-14-8View Details
Carbosulfan CAS 55285-14-8View Details
55285-14-8 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1