BROMUCONAZOLE
- CAS NO.:116255-48-2
- Empirical Formula: C13H12BrCl2N3O
- Molecular Weight: 377.06
- MDL number: MFCD01678688
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
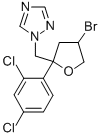
What is BROMUCONAZOLE?
The Uses of BROMUCONAZOLE
Bromuconazole is used on winter wheat and barley for the control of foliar mildews, rusts and other diseases.
The Uses of BROMUCONAZOLE
Agricultural fungicide.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of oxolanes carrying 1,2,4-triazol-ylmethyl and 2,4-dichlorophenyl substituents at position 2 as well as a bromo substituent at position 4. A foliar applied conazole fungicide for a range of crops including cereals, fruit, vegetables and vines.
Metabolic pathway
Bromuconazole is a relatively stable compound which is not readily
hydrolysed, is quite persistent in soil and is subject to relatively slow
photodegradation. It is metabolised in plants but the parent compound
tends to be the major residue. However, bromuconazole is almost completely
metabolised in animals and birds (chickens) and its metabolites
are rapidly eliminated.
As with many other triazole fungicides, metabolism is very complex.
Bromuconazole exists in four forms (two diastereoisomeric pairs). There
are numerous sites available for biotransformation (lack of regioselectivity)
and there is also a lack of stereoselectivity at most sites. For example,
there are also four forms of metabolite 5 (4-hydroxybromuconazole) (two
diastereoisomeric pairs as with bromuconazole itself). Oxidation of
secondary alcohols to ketones and the thiolation of certain sites further
complicate the picture. Thiolation presumably occurs via the involvement
of glutathione but mercapturic acid conjugates (N-acetylcysteines)
do not appear to have been isolated.
Bromuconazole has been the subject of an evaluation by the Pesticide
Safety Directorate of UK MAFF. All of the information presented below is
derived from this source (PSD, 1996). All reported radiolabelled studies
were conducted using [14C-phenyl]bromuconazole.
Degradation
Bromuconazole was found to be stable in buffer at pH 5,7 and 9 at 25 °C
over 30 days.
Aqueous photolysis using filtered light to simulate mid-summer sun at
50" N conducted at 25 °C and pH 4 caused slow photodegradation. The
DT50 of bromuconazole was 18.2 days. Over 28 days a 10% yield of CO2
was obtained and six or more photoproducts were detected with none
accounting for more than 8% of the total. No degradation occurred in dark
controls.
Properties of BROMUCONAZOLE
| Melting point: | 84℃ |
| Boiling point: | 504.3±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.71 |
| vapor pressure | 50 mg 1-1 |
| refractive index | 1.6110 (estimate) |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 2.75±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| BRN | 8393967 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bromuconazole (116255-48-2) |
Safety information for BROMUCONAZOLE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for BROMUCONAZOLE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Bromuconazole CAS 116255-48-2View Details
Bromuconazole CAS 116255-48-2View Details
116255-48-2 -
 Bromuconazole CAS 116255-48-2View Details
Bromuconazole CAS 116255-48-2View Details
116255-48-2 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1