Bromacil
Synonym(s):5-Bromo-3-sec.-butyl-6-methyluracil
- CAS NO.:314-40-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H13BrN2O2
- Molecular Weight: 261.12
- MDL number: MFCD00055364
- EINECS: 206-245-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-26 18:29:04
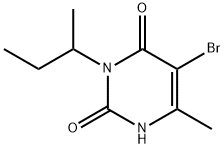
What is Bromacil?
Description
Bromacil (CAS 314-40-9) belongs to a class of herbicides known as uracils, first developed by DuPont in 1962. Its herbicidal activity is due to inhibition of photosynthesis in several species of weeds and brush. Since its introduction in 1962, farmers in North and South America and Asia have used bromacil-containing herbicides for crop protection.
Chemical properties
white to beige crystalline solid
Chemical properties
Bromacil is a noncombustible colorless, crystalline solid, which may be dissolved in a flammable liquid.
The Uses of Bromacil
Bromacil is a nonselective inhibitor of photosynthesis, absorbed mainly through the root and used for general weed control on uncropped land at 5–15 kg/ha (2–4 kg/ha annual maintenance). It is also used for weed control in citrus plantations and for perennial grass control and annual pineapple plantations.
The Uses of Bromacil
Herbicide.
The Uses of Bromacil
Uracil herbicide applied to soil to control a wide variety of annual and perennial grasses, broad-leaved weeds and general vegetation on uncropped land. It is also used for selective weed control in apple, asparagus, cane fruit, hops and citrus crops.
Definition
Substitute approved by EPA for some uses of 2,4,5-T.
General Description
Colorless to white odorless crystalline solid. Used as an herbicide. Commercially available as a wettable powder or in liquid formulations.
Reactivity Profile
Bromacil is incompatible with the following: Strong acids (decomposes slowly), oxidizers, heat, sparks, open flames .
Hazard
Possible carcinogen. Thyroid effects.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Agricultural Uses
Bromacil: Bromacil is used primarily for the control of annual and perennial grasses and broadleaf weeds, both nonselectively on noncrop lands and selectively for weed-control in citrus and pineapple crops. The top five applications in California for which this is used are oranges, lemons, grapefruit, and right-of-ways and landscapes. A limit of 0.1 mg/kg of agricultural products is set in several countries[35]. Not approved for use in EU countries.
Trade name
BOREA®; BOROCIL EXTRA®; α-BROMACIL 80 WP®; BROMAX®; CROPTEX ONYX®; CYNOGEN®; DuPontTM HERBICIDE 976®; EEREX®; FENOCIL®; HERBICIDE 976®; HIBOR; HYDON®; HYVAR®; HYVAR-X®; HYVAR X BROMACIL®; HYVAR X-L®; HYVAR X WEED KILLER®; HYVAR X-WS®; ISOCIL®; KROVAR®; NALKIL®; ROUT®; URAGAN®; URAGON®; UROX®; UROX B WATER SOLUBLE CONCENTRATE WEED KILLER®; UROX HX GRANULAR WEED KILLER®; WEED-BROOM® (mixture of DSMA, Bromacil & 2,4-D)
Potential Exposure
Used for general weed or brush control in noncrop areas and primarily for the control of annual and perennial grasses and broadleaf weeds, both nonselectively on noncrop lands and selectively for weed-control in a few crops (citrus and pineapple). A limit of 0.1 mg/kg of agricultural products is set in several countries. Those exposed will be those involved in manufacture, formulation, and application.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
No evidence of carcinogenic potential was seen in rats or dogs fed up to 1250 ppm bromacil for 2 years. Bromacil was not oncogenic in rats fed 50, 250, or 2500 ppm for 2 years. A marginal increase in the incidence of hepatocellular neoplasms was seen in mice fed 5000 ppm (but not 250 or 1250 ppm) for 18 months.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Metabolites tentatively identified in soil were 5-bromo-3-(3-hydroxy-1-methyl propyl)-6-methyluracil, 5-bromo-3-sec-butyl-6-hydroxymethyluracil, 5-bromo-3-(2-
hydroxy-1-methylpropyl)-6-methyluracil and carbon dioxide. The presence of uracil prod ucts suggests that bromacil was degraded via hydroxylation of the side chain alkyl groups.
In the laboratory, 25.3% of 14C-bromacil degraded in soil to carbon dioxide after 9 weeks
but mineralization in the field was not observed. The half-life of bromacil in a silt loam
was 5–6 months (Gardiner et al., 1969).
To a neutral sandy loam soil maintained at a soil water holding capacity of 60%, 2.88
ppm of 2-14C-bromacil was applied. After 600 days, 22.1% (0.64 ppm) of the applied
amount was converted to 14CO2 (Wolf and Martin, 1974). The evolution of 14CO2 was
sign
Residual activity in soil is limited to approximately 7 months (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
In California soils, bromacil was persistent for 30 months (Lange et al., 1968; Weber and
Best, 1972). The reported half-life in soil is 60 days (Alva and Singh, 1991
The average half-life for bromacil in soil incubated in the laboratory under aerobic
conditions was 132 days (Zimdahl et al., 1970). In field soils, the average disappearance
half-life was 349 days (Gardiner et al., 1969; Leistra et al., 1975). Under aerobic conditions,
the mineralization half-lives for bromacil in soil ranged from 151 days to 4.5 years
(Gardiner et al., 1969; Wolf and Martin, 1974).
Groundwater. According to the U.S. EPA (1986) bromacil has a high potential to leach
to groundwater.
Metabolic pathway
The microorganism, a Pseudomonas sp. isolated from soil by using bromacil as a sole source of carbon and energy, shows a potential to decontaminate soil samples fortified with bromacil under laboratory conditions. The degradation pathways of bromacil by the Pseudomonas sp. may include 5-bromouracil as an intermediate which leads to 5- bromodihydroxyluracil. Ozonization, UV photolysis, and sensitized sunlight photodegradation of aqueous bromacil solution lead to photodegradation products. The ozonization yields three main products which are identified as 3-sec-butyl-5-acetyl-5-hydroxyhydantoin, 3-sec-butylparabanic acid, and 3-sec-butyl-5,5- dibromo-6-hydroxyuracil. The main products of photoirradiation are 3-sec-butyl-6-methyluracil, its dimeric compound, and 3-sec-butyl-5-acetyl-5- hydroxyhydantoin.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Color Code—Green: Generalstorage may be used. Prior to working with bromacil youshould be trained on its proper handling and storage. Storein tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from strong acids, oxidizers, heat, and open flame.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1—Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
Bromacil is a nonvolatile, slightly water-soluble compound with a low octanol–water partition coefficient (Kow) and a pKa of 9. Although the lithium salt is more soluble in water than bromacil, its environmental fate is identical, since the extent of ionization of bromacil, that is, the ratio of unionized bromacil to its anionic form, will be controlled by the pH and buffering capacity of the terrestrial or aquatic system to which it is applied. The physicochemical properties are reflected in the environmental fate properties. Bromacil is weakly absorbed to soil and is considered highly mobile. The low Kow indicates that bromacil will not bioaccumulate. Bromacil is stable in water over the pH range of 5–9, and photolyzes through both direct and indirect mechanisms in surface water with a half-life of 4–7 days at pH 9. In soil under aerobic conditions in the laboratory, bromacil degrades slowly forming several metabolites as a result of microbial activity. In anaerobic environments, bromacil may degrade very rapidly through a debromination reaction. In field dissipation studies, bromacil half-lives of 124–1155 days were observed.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong acids; oxidizers, heat. Decomposes slowly in strong acids.
Waste Disposal
Bromacil should be incinerated in a unit operating @ 850° C equipped with gas scrubbing equipment
Properties of Bromacil
| Melting point: | 157-160°C |
| Density | 1.55 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5410 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO: Soluble,Methanol: Slightly Soluble |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 8.79±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White, tan |
| Water Solubility | 0.71g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,1365 |
| BRN | 6804755 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: 1 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 1 ppm. |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 314-40-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Bromacil(314-40-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bromacil (314-40-9) |
Safety information for Bromacil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Bromacil
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Bromacil CAS 314-40-9View Details
Bromacil CAS 314-40-9View Details
314-40-9 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
