Brefeldin A
Synonym(s):BFA;1,6,7,8,9,11a,12,13,14,14a-Decahydro-1,13-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-cyclopent[f]oxacyclotridecin-4-one;Ascotoxin;γ,4-Dihydroxy-2-(6-hydroxy-1-heptenyl)-4-cyclopentanecrotonic acid λ-lactone;Cyanein
- CAS NO.:20350-15-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H24O4
- Molecular Weight: 280.36
- MDL number: MFCD12913297
- EINECS: 606-528-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
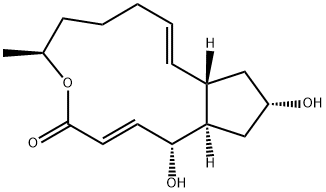
What is Brefeldin A?
Description
Brefeldin A (20350-15-6) is a specific inhibitor of protein translocation from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi. Induces apoptosis. Brefeldin A activates sphingomyelin metabolism. Cell permeable.
Description
Brefeldin A1 (BFA) is a bicyclic lactone produced by fungi of the genus Penicillium. In 1958, V. I. Singleton*, N. Bohonos, and A. J. Ullstrup at Purdue University (Lafayette2, IN) isolated it from the species P. decumbens and named it decumbin. Five years later, H. P. Sigg* and co-workers at Sandoz (Basel, Switzerland) isolated it from another species, P. brefeldianum and changed its name to brefeldin A.
Sigg and his group went on to determine BFA’s biosynthesis (1968) and elucidate its structure (1971). Several total syntheses followed, including that of E. J. Corey* and Robert H. Wollenberg at Harvard University (Cambridge, MA) in 1976, who made the racemic compound. In 1990, Corey and Philip Carpino reported a simplified synthesis of the (+)-enantiomer.
Why all the interest in BFA? It was recognized early on to have antiviral properties, as in a 1968 report by Seikichi Suzuki and coauthors at the University of Tokyo and Chugai Pharmaceutical (Tokyo), who observed moderate activity in two in vitro studies. But subsequent research did not result in its development as an antiviral drug.
BFA, however, found new life as a model compound for the study of protein transport. Beginning in 1986, Yukio Ikehara and collaborators at the Fukuoka University School of Medicine, Saga Medical School, and the University of Tokyo (all in Japan) demonstrated that BFA strongly blocks protein secretion in cultures of rat hepatocytes.
Then, in a 2002 article titled “Brefeldin A: Deciphering an Enigmatic Inhibitor of Secretion”, Andreas Nebenführ, Christophe Ritzenthaler, and David G. Robinson*3 reported on their study of dozens of plants and other eukaryotes and concluded: “The molecular target for BFA appears to be the same in all eukaryotic cells, namely, a Sec7-type GEF that is necessary for activation of Arf1p.” For the biochemically uninitiated, GEF is guanine nucleotide exchange factor; Sec7 is a domain responsible for some GEF catalytic activity; and Arf1p is a hydrolase enzyme that binds to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate.
1. SciFinder: 4H-Cyclopent[f]oxacyclotridecin-4-one, 1,6,7,8,9,11a,12,13,14,14a-decahydro-1,13-dihydroxy-6-methyl-, (1R,2E,6S,10E,11aS,13S,14aR)-.
2. Now West Lafayette.
3. Authors at the University of Tennessee (Knoxville), the Institute of Molecular Biology of Plants of the CNRS (Strasbourg, France), and the University of Heidelberg (Germany), respectively,
Chemical properties
White Powder
The Uses of Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A is a potent inhibitor of cell growth first described in 1958, then independently rediscovered by several groups as a potent active in a broad range of bioassays. Brefeldin has antiviral, antibiotic, antifungal, antitumour and herbicidal activity. Early studies on the mode of action of brefeldin identified inhibition of protein and nucleic acid synthesis by disruption of the Golgi apparatus. The precise molecular target is a subset of Sec7-type GTP exchange factors (GEFs) that activate a small GTPase, Arf1p, an integral component of protein trafficking and signalling.
The Uses of Brefeldin A
A macrolide isolated from Penicillium brefeldianum. It affects the vesticular transport of the Golgi apparatus and induces DNA fragmentation which leads to apoptosis
The Uses of Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A (BFA) is a natural fungal metabolite which has been used extensively to study intracellular transport by vesicles or endosomes. Early studies demonstrated that BFA reversibly interferes with protein trafficking and secretion mediated by the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. BFA directly and reversibly inhibits Sec7 domain-containing guanine-exchange factors which are necessary for ADP-ribosylation factor activation associated with vesicular transport (IC50 = ~10 μM). BFA is used to study endosomal trafficking and function in cells of plants as well as those of fungi, invertebrates, and vertebrates.
What are the applications of Application
Brefeldin A is a fungal metabolite exhibiting a wide range of antibiotic activities and activator of caspase-3
Definition
ChEBI: A metabolite from Penicillium brefeldianum that exhibits a wide range of antibiotic activity.
General Description
Specifically and reversibly blocks translocation of proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus without affecting endocytosis or lysosome function. Inhibitor of HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux. Causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and ER swelling in a variety of mammalian cell lines at <40 ng/ml. Blocks binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to the Golgi and inhibits the GDP-GTP exchange. Inhibits the activity of BIG1 and BIG2, the guanine-nucleotide exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors. Also available as a 25 mM solution in DMSO (Cat. No. 500583).
Biological Activity
Reversible inhibitor of protein translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus. Blocks binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to the Golgi apparatus and inhibits GDP-GTP exchange.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Primary TargetBlocks translocation of proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus
storage
-20°C (desiccate)
Purification Methods
Brefeldin A was isolated from Penicillium brefeldianum and recrystallised from aqueous MeOH/EtOAc or MeOH. Its solubility in H2O is 0.6mg/mL, 10mg/mL in MeOH and 24.9mg/mL in EtOH. The O-acetate recrystallises from Et2O/pentane and has m 130-131o, [] D +17o (c 0.95, MeOH). [Sigg Helv Chim Acta 47 1401 1964, UV and IR: H.rri et al. Helv Chim Acta 46 1235 1963, total synthesis: Kitahara et al. Tetrahedron 3021 1979, X-ray : Weber et al. Helv Chim Acta 54 2763 1971, Beilstein 18 III/IV 1220.]
References
1) Fujiwara et al. (1988) Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum; J. Biol. Chem., 263 18545 2) Shao et al. (1996), Brefeldin A is a potent inducer of apoptosis in human cancer cells independently of p53; Exp. Cell Res., 227 190 3) Linardic et al. (1996), Brefeldin A promotes hydrolysis of sphingomyelin; Cell Growth Differ., 7 765
Properties of Brefeldin A
| Melting point: | 200-205 °C |
| Boiling point: | 492.7±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 93 º (C=2 IN MEOH) |
| Density | 1.108±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0.56 hPa ( 20 °C) |
| Flash point: | 87 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | methanol: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| pka | 12.92±0.60(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to almost white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in dimethylsulfoxide, dichloromethane and ethanol. Slightly soluble in water. |
| Merck | 13,1355 |
| BRN | 25191 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 20350-15-6 |
Safety information for Brefeldin A
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Brefeldin A
| InChIKey | QSECOIOBNZLGOD-OBCVZTHZSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Brefeldin a 95% CAS 20350-15-6View Details
Brefeldin a 95% CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 (+)-Brefeldin A, Eupenicillium brefeldianum CAS 20350-15-6View Details
(+)-Brefeldin A, Eupenicillium brefeldianum CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 (+)-Brefeldin A, Eupenicillium brefeldianum CAS 20350-15-6View Details
(+)-Brefeldin A, Eupenicillium brefeldianum CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
Brefeldin A CAS 20350-15-6View Details
20350-15-6 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1