BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
Synonym(s):Bismuth oxysalicylate;Bismuth subsalicylate;Bismuth(III) salicylate basic
- CAS NO.:14882-18-9
- Empirical Formula: C7H5BiO4
- Molecular Weight: 362.09
- MDL number: MFCD00085368
- EINECS: 238-953-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-16 15:32:52
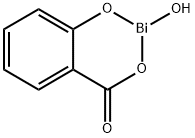
What is BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE?
Absorption
Following oral administration, bismuth subsalicylate hydrolyzes into bismuth and salicylic acid in the stomach. Salicylic acid is almost completely absorbed in the small intestine and reaches plasma peak levels one to two hours after dosing. In one study involving healthy male subjects, oral administration of 60 mL Pepto-Bismol, a common over-the-counter product of bismuth subsalicylate, equivalent to 1050 mg of bismuth subsalicylate, resulted in the peak plasma concentration of salicylate of 40.1 μg/mL, with a time to peak concentration (Tmax) of 1.8 hours.
Less than 1% of bismuth from bismuth subsalicylate is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the systemic circulation. In one study, oral administration of 787 mg bismuth subsalicylate in the chewable tablet form for two weeks resulted in the mean trough blood bismuth concentration was 5.1 ± 3.1 ng/mL. In another study, the mean trough blood bismuth concentration ranged from five to 32 ng/mL following oral administration of 525 mg bismuth subsalicylate in the liquid suspension form.
Toxicity
Lowest Lethal Dose (LDLo) in humans is 700 mg/kg. LD50 in rats is 1200 mg/kg via oral route, 542 mg/kg via intraperitoneal route, and 980 mg/kg via subcutaneous route.
Overdose of bismuth subsalicylate over an extended period of time and consequently, bismuth toxicity, can lead to blackening of the tongue and teeth, fatigue, mood changes, deterioration of mental status, and neurotoxicity. Other signs and symptoms include impaired cognition, tremors, lethargy, somnolence, insomnia, delirium, myoclonus, seizures, depressed mood, anxiety, and a depressed mood. Salicylate toxicity can occur from chronic bismuth subsalicylate use : it mostly occurs from ingestion of more than 150 mg/kg of salicylates (or >6.5 g of aspirin equivalent). As there are no specific antidotes for bismuth salicylate toxicity, overdose should be managed with supportive care, with or without decontamination with activated charcoal. Hemodialysis may be considered in more severe cases and with the presence of altered mental status and metabolic acidosis.
Description
Bismuth subsalicylate was originally used in a formula developed 100 years ago by a doctor in his home to combat cholera infantum. A staple of many medicine cabinets, bismuth subsalicylate, in the form of Pepto-Bismol, is be taken by countless people during the holiday season to help reverse the effects of overindulging.
Chemical properties
White or almost white powder.
The Uses of BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
To impart pearly surface to cellulose-base, polystyrene, and phenolformaldehyde resins. Typical tap bulk density 0.43g/cm^3Bismuth subsalicylate is used to treat temporary discomforts of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, such as diarrhea, indigestion, heartburn and nausea. It also acts as an antacid. It is practiced to decrease the number of bowel movements and to make the stool firmer. It is also used to reduce inflammation within the intestine. It is further used in growth media for selective isolation of microorganisms.
The Uses of BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
anticoagulant
The Uses of BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
Used to treat nausea, heartburn, indigestion, upset stomach, diarrhea, and other temporary discomforts of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract.
Indications
Bismuth subsalicylate is indicated to temporarily relieve diarrhea, travelers' diarrhea, and upset stomach due to overindulgence in food and drink, including heartburn, indigestion, nausea, gas, belching, and fullness.
Bismuth subsalicylate is a component of HELIDAC Therapy (bismuth subsalicylate, metronidazole, and tetracycline), which is a treatment regimen indicated for the eradication of H. pylori for treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease.
Background
Bismuth subsalicylate is an antacid and anti-diarrheal agent. Exhibiting antibacterial and gastroprotective properties, bismuth subsalicylate is an insoluble salt of salicylic acid linked to trivalent bismuth cation. Each molecule of bismuth subsalicylate contains 58% bismuth and 42% salicylate by weight. Bismuth subsalicylate has been around for over 100 years: it was originally developed in 1901 for hygienic use and sanitation for cholera infection.
Bismuth subsalicylate was first approved by the FDA in 1939 and is now mainly used to relieve nausea, diarrhea, and gastrointestinal discomfort. It is an active ingredient found in Pepto-Bismol, a common over-the-counter medication that is used to temporarily treat discomforts of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract. Bismuth subsalicylate is a component of HELIDAC Therapy (bismuth subsalicylate, metronidazole, and tetracycline), which is a treatment regimen indicated for the eradication of H. pylori for treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease.
What are the applications of Application
Bismuth(III) subsalicylate is an antiinflammatory
Indications
Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) also binds intestinal toxins and may coat irritated mucosal surfaces.
Definition
ChEBI: Bismuth subsalicylate is a bismuth salt of salicylic acid. It is a member of salicylates and a bismuth coordination entity.
General Description
White crystalline powder or fluffy white solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE is stable in air but is sensitive to light. BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE is unstable in alkaline solutions. BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE decomposes in boiling water and alkalis into a more basic salt.
Hazard
A poison by ingestion. Human systemic effects.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE may include headache, nausea, foul breath, blue-black line on the gums and stomatitis.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE are not available, but BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
Bismuth subsalicylate is an antacid and antimicrobial, gastroprotective, anti-secretory, and anti-inflammatory actions. It works to reduce the severity and incidence of flatulence and diarrhea, and consequently relieving gastrointestinal discomfort. In one study, bismuth subsalicylate was prevented traveler's diarrhea with a protection rate >60%.
Organobismuth compounds, formed by the breakdown of bismuth subsalicylate in the gastrointestinal tract, inhibit the growth of Helicobacter pylori and other bacteria implicated in gastrointestinal disorders, and some fungi. In one study, bismuth subsalicylate was shown to eradicate up to 90% of H. pylori infection when used as part of a quadruple therapy regimen containing a proton pump inhibitor, tetracycline, and metronidazole. Bismuth subsalicylate exhibited antimicrobial activity against Clostridium difficile, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O157:H7, norovirus, and other common enteric pathogens such as Salmonella and Shigella.
Side Effects
This compound is a salicylate and may therefore produce signs of salicylate toxicity (e.g., ringing of the ears) if taken chronically, especially with aspirin. Bismuth is radiopaque and may interfere with radiological examinations. Its use may cause temporary gray-black discoloration of the stool and brown pigmentation of the tongue. High dose Pepto-Bismol (8 tablets/day) has been efficacious in some patients with diarrhea secondary to collagenous or lymphocytic colitis.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, bismuth subsalicylate products are used to treat diarrhea and as a component of “triple therapy” for treating Helicobacter GI infections. The drug is also used in humans for other GI symptoms (indigestion, cramps, gas pains) and in the treatment and prophylaxis of traveler’s diarrhea.
Metabolism
Bismuth subsalicylate undergo hydrolysis at pH levels lesser than three. It is largely hydrolyzed in the stomach to bismuth oxychloride and salicylic acid. In the small intestine, unchanged bismuth subsalicylate reacts with other anions such as bicarbonate and phosphate to form insoluble bismuth salts. In the colon, unchanged bismuth subsalicylate and other bismuth salts react with hydrogen sulfide produced by anaerobic bacteria to form bismuth sulfide, a highly insoluble black salt responsible for the darkening of the stools.
Properties of BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
| Melting point: | >350 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 3.05[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water and in alcohol. It dissolves in mineral acids with decomposition. |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble in water, alcoholSoluble in acid and alkali. Insoluble in cold water, ethanol, diethyl ether and n-octanol. |
| Merck | 14,1285 |
| BRN | 9170211 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bismuth subsalicylate (14882-18-9) |
Safety information for BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE
| InChIKey | ZREIPSZUJIFJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
Abamectin manufacturer
Dhara Industries
New Alliance Dye Chem Pvt Ltd
Heni Chemical Industries (Heni Drugs Pvt Ltd)
ShanPar Industries Pvt Ltd
Samuh Laxmi Chemicals (Bom) P Ltd
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 BISMUTH SUB SALICYLATE 99%View Details
BISMUTH SUB SALICYLATE 99%View Details -
 Bismuth subsalicylate 99%View Details
Bismuth subsalicylate 99%View Details -
 Bismuth subsalicylate CAS 14882-18-9View Details
Bismuth subsalicylate CAS 14882-18-9View Details
14882-18-9 -
 Bismuth subsalicylate CAS 14882-18-9View Details
Bismuth subsalicylate CAS 14882-18-9View Details
14882-18-9 -
 Bismuth subsalicylate 98%View Details
Bismuth subsalicylate 98%View Details -
 Bismuth Subsalicylate CASView Details
Bismuth Subsalicylate CASView Details -
 Bismuth(III) subsalicylate 99.00% CAS 14882-18-9View Details
Bismuth(III) subsalicylate 99.00% CAS 14882-18-9View Details
14882-18-9 -
 Bismuth salicylate, 97% CAS 14882-18-9View Details
Bismuth salicylate, 97% CAS 14882-18-9View Details
14882-18-9