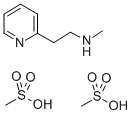
Betahistine
- CAS NO.:5638-76-6
- Empirical Formula: C8H12N2
- Molecular Weight: 136.19
- MDL number: MFCD00006362
- EINECS: 227-086-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-18 17:17:19

What is Betahistine?
Absorption
When given orally, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. In the fasted state, Cmax is achieved within 1 hour of administration; in the fed state, Cmax is delayed, but the total drug absorption is similar. Food, therefore, has little effect on the absorption of betahistine.
Toxicity
Symptoms of an overdose with betahistine (< 640 mg) include dry mouth, nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, and somnolence. Serious complications such as convulsions, pulmonary or cardiac effects may occur with higher doses (> 640 mg), especially during intentional overdoses and combination with other drugs. In the case of an overdose with betahistine, provide supportive therapy, and contact the local poison control center for further management.
Description
Betahistine is an analogue of histamine with weak agonist properties at histamine H1 receptors and more potent antagonistic effects at histamine H3 receptors.
This drug is broadly used worldwide, except for the USA, since it has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Betahistine is a structural analog of histamine that acts as a weak partial postsynaptic histamine H1 receptor agonist and presynaptic H3 receptor antagonist, with no effect on postsynaptic H2 receptors (Gbahou et al, 2010). The mechanism of action of the drug appears to depend mainly on its action on H3 receptors mediated by two metabolites, aminoethylpyridine and hydroxyethylpyridine (Bertich et al, 2014).
The Uses of Betahistine
Betahistine is a vasodilator, a mild H1 histamine agonist, and a potent H3 histamine antagonist. The mechanism of action in Meniere's disease is unknown, but theories include reducing the endolymphatic pressure through improved circulation in the stria vascularis or inhibiting activity in the vestibular nuclei. It has been found to be a safe drug with a very low side effect profile. Betahistine was FDA approved for Meniere's disease in the US market for a short period of time in the 1970s, but approval was then rescinded due to lack of evidence supporting its efficacy. However, based on clinical experience and several observational studies, it is still widely used elsewhere in the world.
The Uses of Betahistine
Anti - Vertigo/Anti-Nauseants/Antiemetics
Indications
Betahistine is indicated for the reduction of recurrent vertigo episodes associated with Ménière's disease in patients 18 years old and above.
Background
Ménière's disease is a progressive disease of the inner ear characterized by vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. It has a significant impact on both the physical and social functioning of affected individuals.
Betahistine is a histamine-like antivertigo drug used for treating symptoms associated with Ménière's disease. It is thought to reduce symptoms through its actions on histamine receptors. Betahistine was first approved by the FDA in the 1970s but withdrawn within approximately 5 years due to a lack of evidence supporting its efficacy. It is currently marketed in Canada by various companies, including Teva Pharmaceuticals.
What are the applications of Application
2-(2-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine is a histidine analog and H1 receptor agonist
Indications
Betahistine is indicated in treatment of Meniere's disease (vertigo, hearing loss and tinnitus); it is not effective in preventing vertigo attacks.
Definition
ChEBI: Betahistine is an aminoalkylpyridine that is pyridine substituted by a 2-(methylamino)ethyl group at position 2. It acts as a histamine agonist and a vasodilator, and is thought to improve the microcirculation of the labyrinth, resulting in reduced endolymphatic pressure. It is used (generally as the hydrochloride or mesylate salt) to reduce the symptoms of vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss associated with Meniere's disease. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and a H1-receptor agonist. It is an aminoalkylpyridine and a secondary amino compound.
brand name
Serc (Unimed).
Mechanism of action
The precise mechanism of betahistine's actions is unclear; it has antagonistic actions on histamine H3 receptors, and is a weak agonist at H receptors. In animal studies, it inhibits generation of spikes in vestibular nuclei. Its vasodilator activity (similar to histamine's) presumably improves blood flow in the inner ear and brainstem.
Pharmacokinetics
Through its actions on the histamine receptors, betahistine provides relief from vertigo associated with Ménière's disease.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, betahistine is rapidly and completely absorbed, rapidly metabolised (to one major metabolite, 2-pyridylacetic acid) and 90% excreted within 24 hours. Plasma and urinary half-lives are about 3.5 hours.
Side Effects
Common adverse reactions include headache, nausea and dyspepsia. More rarely, hypersensitivity reactions (rash, pruritis, bronchospasm) and hypotension may occur.
Drug interactions
Co-administration of betahistine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors type B reduces metabolism of betahistine. Theoretically, interactions might occur with concurrent antihistamines; however, no significant problems have been reported.
Metabolism
Betahistine is metabolized primarily into the inactive metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid. There is both clinical and in vitro evidence that monoamine oxidase enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of betahistine.
Dosage forms
Betahistine is provided as scored tablets, 16 mg. Dose is 8-16 mg taken three times daily. It should be taken with food to minimise risk of GIT upsets. Patients are warned that it may take several weeks for beneficial effects to be noticed.
Precautions
Betahistine should be used with caution in individuals with asthma, urticaria, phaeochromocytoma or hypersensitivity to any components of tablets. Betahistine is contraindicated in people with active or history of peptic ulcer. Betahistine is classified in Pregnancy Safety Category B2: insufficient data available; it is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation, and in children under 18.
Properties of Betahistine
| Boiling point: | 113-114 °C30 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.984 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 17.7Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 206 °F |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Sli |
| form | Oil |
| pka | pKa 3.46 (Uncertain) |
| color | Light Yellow to Yellow |
| Water Solubility | 1000g/L at 25℃ |
| Merck | 13,1181 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5638-76-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Pyridineethanamine, N-methyl- (5638-76-6) |
Safety information for Betahistine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Betahistine
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 5638-76-6 BETAHISTINE 12% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
5638-76-6 BETAHISTINE 12% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
5638-76-6 -
 Betahistine 98%View Details
Betahistine 98%View Details -
 Betahistine 99%View Details
Betahistine 99%View Details
5638-76-6 -
 Betahistine 5638-76-6 98%View Details
Betahistine 5638-76-6 98%View Details
5638-76-6 -
 5638-76-6 Betahistine 98%View Details
5638-76-6 Betahistine 98%View Details
5638-76-6 -
 N-Methyl-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amine 95% CAS 5638-76-6View Details
N-Methyl-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amine 95% CAS 5638-76-6View Details
5638-76-6 -
 2-(2-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine CAS 5638-76-6View Details
2-(2-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine CAS 5638-76-6View Details
5638-76-6 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
