Bergamotine
Synonym(s):Bergamotine;Bergaptin
- CAS NO.:7380-40-7
- Empirical Formula: C21H22O4
- Molecular Weight: 338.4
- MDL number: MFCD00017409
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-25 18:01:03
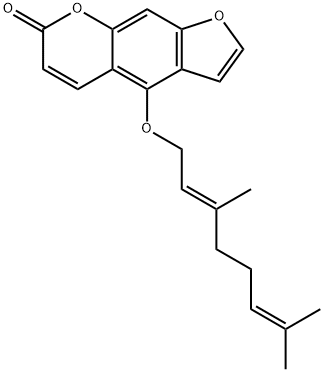
What is Bergamotine?
Description
Furanocoumarins are organic compounds found in the seeds and fruits of many species of plants, notably in the families Rutaceae (citrus fruits) and Apiaceae (celery, carrots, and others). As the name suggests, the central structure of furanocoumarins consists of a furan ring fused to a two-ring coumarin system.
Psoralen1 and angelicin2 are unsubstituted furanocoumarins in which the furan and coumarin rings are fused in linear and angular orientations, respectively. Bergamottin and its oxidation products 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin3 (DHB) and 6′,7′-epoxybergamottin4 are psoralen derivatives that have geraniol-derived side chains attached at the 5-position. Bergamottin is named after the bergamot orange (Citrus bergamia); it was first isolated from bergamot oil in 1937 by Ernst Sp?th and Paul Kainrath at the University of Vienna.
Bergamottin plays a role in the lives of many people. It and DHB inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A, thereby slowing or preventing the metabolism of lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin, and other “statin” drugs that decrease the formation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol in the body. Bergamottins are particularly abundant in grapefruit, which is why statin labels advise against consumption of the fruit or its juice close to the time the drugs are taken.
The oxidized bergamottins and other grapefruit ingredients also inhibit the transport of talinolol5, a substrate for P glycoprotein, an important cell membrane component that removes foreign substances from cells. For more information on bergamottin and its derivatives, see this Science Direct entry.
1. CAS Reg. No. 66-97-7.
2. CAS Reg. No. 523-50-2.
3. CAS Reg. No. 145414-76-2.
4. CAS Reg. No. 206978-14-5.
5. CAS Reg. No.57460-41-0.
The Uses of Bergamotine
Bergamottin (BG), a component of grapefruit juice, is a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP3A4 and contributes, in part, to the grapefruit juice-drug interaction.
What are the applications of Application
Bergamottin is a linear furanocoumarins
Definition
ChEBI: A natural product found in Citrus hystrix.
Properties of Bergamotine
| Melting point: | 75-80 °C |
| Boiling point: | 503.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.153±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| BRN | 1353914 |
Safety information for Bergamotine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Bergamotine
| InChIKey | DBMJZOMNXBSRED-OQLLNIDSSA-N |
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![BERGAMOTTIN [ALL TRANS GERANYL-1-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure5/GIF/CB7749663.gif)
You may like
-
 7380-40-7 Bergamotin 98%View Details
7380-40-7 Bergamotin 98%View Details
7380-40-7 -
 7380-40-7 98%View Details
7380-40-7 98%View Details
7380-40-7 -
 Bergmothin 98%View Details
Bergmothin 98%View Details
7380-40-7 -
 Bergamottin CAS 7380-40-7View Details
Bergamottin CAS 7380-40-7View Details
7380-40-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4