Benzydamine
- CAS NO.:642-72-8
- Empirical Formula: C19H23N3O
- Molecular Weight: 309.41
- MDL number: MFCD00864286
- EINECS: 211-388-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
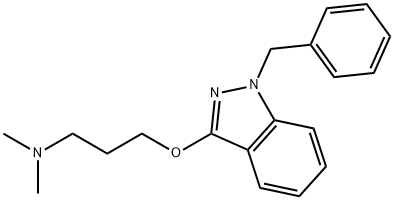
What is Benzydamine?
Absorption
Oral doses of benzydamine are well absorbed and plasma drug concentrations reach a peak fairly rapidly and then decline with a half-life of approximately 13 hours. When applied topically, although the local drug concentrations are relatively large, the systemic absorption of topically applied benzydamine is relatively low compared to oral doses. This low topical absorption contributes to a decreased potential for any systemic drug side-effects when benzydamine is administered in this way.
Toxicity
A possible adverse reaction associated with the use of the mouthwash or oromucosal spray formulations of benzymadine is potential numbness and/or stinging in the mouth and/or throat .
Some possible adverse reactions that tend to be associated more with topical cream formulations of benzymadine include increased sensitivity to sunlight, and localized itching, skin rash, redness, or swelling .
The prescribing information for all formulations of benzymadine however, warn against the possibility of severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) associated with swelling of the throat and mouth, difficulty in swallowing, speaking, and breathing, or wheezing .
As benzydamine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), it is necessary to determine if a patient is allergic to NSAIDs before considering its use .
Intoxication is expected as a consequence of accidental ingestion of large quantities of benzydamine (over 300 mg ingestion). Other symptoms associated with overdose of ingested benzydamine include gastrointestinal and central nervous system symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, oesophageal irritation, dizziness, hallucinations, agitation, anxiety, and irritability .
The official prescribing information for benzydamine generally suggest that benzydamine mouthwashes and sprays should not be used in pregnancy . Similarly, the official prescribing information for benzydamine also generally suggest that benzydamine mouthwashes and sprays should not be used during lactation unless considered essential by a physician .
The prescribing information for topical cream formulations of benzydamine note that benzydamine cream should not be used in pregnancy or lactation unless considered necessary by the physician .
Overall, non-clinical data reveal no special hazards for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated toxicity, genotoxicity, cardiogenic potential, and toxicity to reproduction . Additionally, there is no evidence of teratogenic effects in animal studies .
Description
Benzydamine is an analytical reference standard categorized as an analgesic. Benzydamine has been abused and is associated with hallucinations, muscle weakness, and excitability. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
The Uses of Benzydamine
Benzydamine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with local anaesthetic, analgesic and antipyretic properties.
The Uses of Benzydamine
Analgesic; antipyretic; anti-inflammatory.
Background
Benzydamine (also known as Tantum Verde or Difflam), available as the hydrochloride salt, is a locally-acting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with local anaesthetic and analgesic properties. It is used topically for pain relief and anti-inflammatory treatment of the mouth, throat, or muscoskeletal system.
Although the indazole analogue benzydamine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), it has various physicochemical properties and pharmacologic activities that are different from those of traditional aspirin-like NSAIDs but facilitate benzydamine's mechanism of action as an effective locally-acting NSAID with local anaesthetic and analgesic properties. Moreover, unlike aspirin-like NSAIDs which are acids or metabolised to acids, benzydamine is in fact a weak base.
Indications
Available predominantly as a liquid mouthwash, oromucosal spray, or topical cream, benzydamine is most frequently employed as a locally acting analgesic and anti-inflammatory treatment for the relief of painful inflammatory conditions.
When formulated as a mouthwash or spray, benzydamine may be used to treat traumatic conditions like pharyngitis following tonsillectomy or the use of a naso-gastric tube, inflammatory conditions like pharyngitis, aphthous ulcers and oral ulceration due to radiation therapy, dentistry operations and procedures, or more general conditions like sore throat, sore tongue, sore gums, mouth ulcers, or discomfort caused by dentures.
When used as a topical cream, benzydamine may be employed to relieve symptoms associated with painful inflammatory conditions of the muscolo-skeletal system including acute inflammatory disorders such as myalgia and bursitis or traumatic conditions like sprains, strains, bruises, sore muscles, stiff joints, or even the after-effects of fractures.
Definition
ChEBI: Benzydamine is a member of the class of indazoles carrying benzyl and 3-(dimethylamino)propyl groups at positions 1 and 3 respectively. A locally-acting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that also exhibits local anaesthetic and analgesic properties. It has a role as a central nervous system stimulant, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a hallucinogen, a local anaesthetic and an analgesic. It is a member of indazoles, an aromatic ether and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a benzydamine(1+).
brand name
Tantum (Angelini Francesco, Italy).
Pharmacokinetics
Benzydamine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) designed to elicit local anesthetic and analgesic effects mainly for the mouth and throat. It specifically acts on the local mechanisms of inflammation such as pain, oedema, or granuloma. Typically applied topically, the drug demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity reducing oedema as well as exudate and granuloma formation. Moreover, benzydamine exhibits analgesic properties and local anaesthetic activity if pain is caused by an inflammatory condition. Benzydamine can be absorbed into the oral mucosa and intact skin. Once absorbed in the local area of pain or inflammation, benzydamine binds selectively to local inflamed tissues, usually allowing it to act with few adverse systemic effects. On average a period of 2 to 4 hours is necessary for the substance to reach peak plasma concentration.
Benzydamine can be synthesized with the reaction of the N-benzyl derivative from methyl anthranilate with nitrous acid to give N-nitoso derivative. This is next reduced by sodium thiosulfate to give transient hydrazine. This hydrazine can then undergo spontaneous internal hydrazide formation. Treating this resultant enolate with 3-chloro-1-dimethylamkino propane ultimately yields benzydamine.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal andintravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion andsubcutaneous routes. When heated to decomposition itemits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Benzydamine is primarily metabolized by oxidation, dealkylation, and conjugation into hydroxy, dealkylated, and N-oxide metabolites .
In general, however, when used at the recommended doses the levels at which benzydamine is absorbed or exposed into the body are usually not sufficient to produce systemic pharmacological effects [L
Properties of Benzydamine
| Melting point: | 167-170 °C |
| Boiling point: | bp0.05 160° |
| Density | 1.1106 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5900 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Oil |
| pka | 9.25±0.28(Predicted) |
| color | Orange |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 642-72-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Propanamine, n,n-dimethyl-3-[[1-(phenylmethyl)-1h-indazol-3-yl]oxy]-(642-72-8) |
Safety information for Benzydamine
Computed Descriptors for Benzydamine
Benzydamine manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Benzydamine 98%View Details
Benzydamine 98%View Details -
 642-72-8 98%View Details
642-72-8 98%View Details
642-72-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8