Benfotiamine
Synonym(s):Benfotiamine
- CAS NO.:22457-89-2
- Empirical Formula: C19H23N4O6PS
- Molecular Weight: 466.45
- MDL number: MFCD00057343
- EINECS: 245-013-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-27 18:34:20
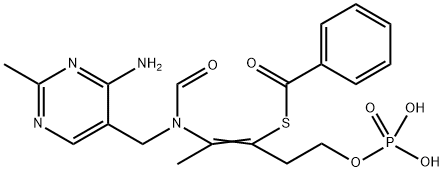
What is Benfotiamine?
Chemical properties
crystals
Originator
Biotamin,Sankyo
The Uses of Benfotiamine
Vitamin B1 analog. Synthetic S-acyl derivative of Thiamine (T344185).
The Uses of Benfotiamine
S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate has been used to determine its effect on ischemia and reperfusion in skeletal muscles of rat.
Background
Benfotiamine has been investigated for the treatment and prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2.
What are the applications of Application
Benfotiamine is a lipid-soluble thiamine derivative
Definition
ChEBI: A thioester that is a synthetic analogue of thiamine obtained by acylative cleavage of the thiazole ring and O-phospohorylation.
Manufacturing Process
28.6 g 84% phosphoric acid was heated to temperature about 270°C. After
cooling to 100°C 4 g thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1 hydrochloride) was
added and left at temperature 100°C before an isolation of HCl was ended.
After adding of an ice water and acetone, phosphate ester of vitamin B1 was
fallen. The precipitate was dissolved in 17 ml 1 N HCl and stood at ambient
temperature 7 days for a hydrolysis. Then a solution was with acetone diluted
and the mixture was cooled, whereupon vitamin B1 monophosphate
hydrochloride was isolated.
The solution of 4.3 parts vitamin B1 monophosphate hydrochloride in 16 parts
of water was diluted with 11 parts 15% NaOH, 2.1 parts benzoyl chloride was
dropwise added with stirring and cooling. The obtained mixture was
neutralized, evaporated in vacuum, acidified with concentrated HCl to pH 3.5-
4, whereupon a crude S-derivative of vitamin B1 monophosphate ester was
precipitated. The product was suspended in water, was bringing with NaOH to
pH 7 and was acidified to pH 4. 3.4 g refined S-benzoylthiamine Omonophosphate
was prepared; MP: 165°C (with decomposition).
Therapeutic Function
Analgesic
General Description
S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate (Benfotiamine) is an amphiphilic S-acyl thiamine derivative. It is a lipid-soluble vitamin. Benfotiamine?contains a thiazole ring. Benfotiamine has a greater bioavailability than thiamine.
Biochem/physiol Actions
S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate (Benfotiamine) is a therapeutic agent. It helps in the prevention of diabetic complications such as, retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy. Benfotiamine inhibits the synthesis of glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetes. Benfotiamine is considered as a nutraceutical product for the prevention of diabetic neuropathy.
Mechanism of action
Benfotiamine acts by modulating the advanced glycation end products (AGEs). It can also act through non-AGE-dependent pathways. Advanced glycation end products are modified proteins or lipids that become non-enzymatically glycated on exposure to sugars such as aldose. AGEs may generate reactive oxygen species, attach to specific receptors, and form cross-linking structures. AGEs are present in the diabetic vasculature and are involved in the progression of atherosclerosis. Benfotiamine inhibits the synthesis of AGEs and thus decreases metabolic stress. Benfotiamine thus helps in vascular complications associated with diabetes. Benfotiamine can also regulate non-AGE dependent pathways such as nuclear transcription Factor κB, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β). It can also modulate mechanisms related to cell survival, repair, and apoptosis.
Metabolism
When administered orally, benfotiamine is dephosphorylated by alkaline phosphatases in the intestine to S-benzoylthiamine, which is lipophilic and can cross cell membranes. S-Benzoylthiamine diffuses through the intestinal epithelium into the bloodstream, which is converted to free thiamine by erythrocytes. Because thiamine absorption is limited by thiamine transporters, oral administration of benfotiamine results in higher plasma concentrations of thiamine than oral administration of equal concentrations of thiamine itself; for this reason, benfotiamine is frequently used in conditions characterized by thiamine deficiency (TD).
Side Effects
Side effects noted with Benfotiamine are skin irritation, allergic reactions, shortness of breath, difficulty in swallowing, feeling of discomfort, rash, itching, cough, decreased blood pressure, facial swelling, increased sweating, restlessness, weakness, and wheezing.
Properties of Benfotiamine
| Melting point: | 165 C |
| Boiling point: | 745.1±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.444±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Acid (Slightly), DMSO (Heated, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 1.84±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,1041 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 22457-89-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Benfotiamine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Benfotiamine
| InChIKey | BTNNPSLJPBRMLZ-GHRIWEEISA-N |
| SMILES | C(C1=CN=C(C)N=C1N)N(C=O)C(C)=C(CCOP(O)(O)=O)SC(C1C=CC=CC=1)=O |
Benfotiamine manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Benfotiamine 99%View Details
Benfotiamine 99%View Details -
 Benfothiamine 99%View Details
Benfothiamine 99%View Details -
 Benfothiamine 98%View Details
Benfothiamine 98%View Details -
 22457-89-2 Benfothiamine 99%View Details
22457-89-2 Benfothiamine 99%View Details
22457-89-2 -
 Benfotiamine 95% CAS 22457-89-2View Details
Benfotiamine 95% CAS 22457-89-2View Details
22457-89-2 -
 Benfotiamine Clay PowderView Details
Benfotiamine Clay PowderView Details
22457-89-2 -
 Benfotiamine Powder APIView Details
Benfotiamine Powder APIView Details
22457-89-2 -
 Benfotiamine Api PowderView Details
Benfotiamine Api PowderView Details
22457-89-2
