ANTIMYCIN A
- CAS NO.:1397-94-0
- Empirical Formula: C28H40N2O9
- Molecular Weight: 548.6252
- MDL number: MFCD01779723
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-14 15:18:27
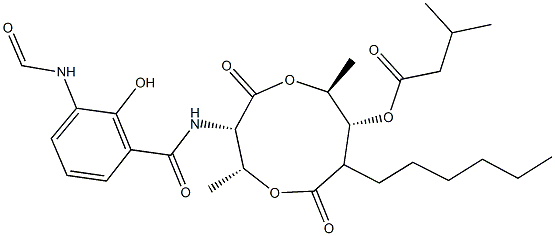
What is ANTIMYCIN A?
Description
Antimycin (A3 C26H36N2O9) and (AntimycinA1) C28H40N2O9 are crystalline solids. Molecularweight= 512.8 (A); 520.64 (A3-); 506.6 (A4-); Freezing/Melting point= 170°175℃; 149°150℃ (A1); 174°175℃(A3). They are complex 9-membered (2 oxygens and 7 carbons) ring derivatives with complex side chains. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Practically insolublein water.
Chemical properties
Antimycin (A3C26H36N2O9) and (Antimycin A1) C28H40N2O9 are crystalline solids.
The Uses of ANTIMYCIN A
Antimycin A is a complex of related macrocyclic lactones, predominantly A1 to A4, isolated from several species of Streptomyces, first reported in the early 1950s for potent antifungal activity. There are over 20 known analogues in the antimycin A class, mostly involving variation of the fatty acid ester chain length or adjacent alkyl starting unit. Antimycin A binds to cytochrome C reductase at the Qi site, inhibiting the oxidation of ubiquinol to ubiquinone. Antimycin A is widely used as a bioprobe of respiration and other applications with over 5,000 literature citations.
The Uses of ANTIMYCIN A
antifungal, antiviral, interferes in cytochrome oxidation
The Uses of ANTIMYCIN A
Antimycin A is used to study the specific sites of reactive oxygen species production in mitochondria isolated from skeletal muscle of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients, and its relationship with local oxidative stress induced by exercise.
What are the applications of Application
Antimycin A is a mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor and antibiotic that induces apoptosis.
Definition
ChEBI: Antimycin A is a nine-membered bis-lactone having methyl substituents at the 2- and 6-positions, an n-hexyl substituent at the 8-position, an acyloxy substituent at the 7-position and an aroylamido substituent at the 3-position. It is produced by Streptomyces bacteria and has found commercial use as a fish poison. It has a role as a piscicide, a mitochondrial respiratory-chain inhibitor and an antifungal agent. It is a macrodiolide, a member of formamides, a member of benzamides and a member of phenols.
General Description
Solid. Specific uses for ANTIMYCIN A were not found. ANTIMYCIN A1,and ANTIMYCIN A3 are reported as antibiotics produced by Streptomyces for use as a fungicide and possibly as an insecticide and miticide. Registered only as a pesticide in the U.S.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, ANTIMYCIN A emits toxic fumes of oxides of nitrogen.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Piscicide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). May also be used as an insecticide.
Trade name
FINTROL®; VIROSIN®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion,intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes.When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes ofNOx.
Potential Exposure
Specific uses for antimycin A were not found, however, antimycin A1, and antimycin A3 are reported to be antibiotic substances produced by streptomyces for use as a fungicide, possible insecticide and miticide. Registered as a pesticide in the U.S.
First aid
f this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immedi ately with soap and water. Seek medical attention258 Antimycin Aimmediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, removefrom exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store ina secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemicalyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Properties of ANTIMYCIN A
| Melting point: | 141-142℃ |
| Boiling point: | 598.78°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.6009 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Ethanol: soluble |
| form | White to faint yellow powder. |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in 100% ethanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Antimycin A (1397-94-0) |
Safety information for ANTIMYCIN A
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for ANTIMYCIN A
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Antimycin A from Streptomyces sp. CAS 1397-94-0View Details
Antimycin A from Streptomyces sp. CAS 1397-94-0View Details
1397-94-0 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4