Anagrelide
- CAS NO.:68475-42-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H7Cl2N3O
- Molecular Weight: 256.09
- MDL number: MFCD00866794
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 15:44:27
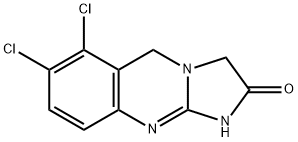
What is Anagrelide?
Absorption
Following oral administration, the bioavailability of anagrelide is approximately 70%. Given on an empty stomach, the Cmax is reached within 1 hour (Tmax) of administration. Co-administration with food slightly lowers the Cmax and increases the AUC, but not to a clinically significant extent.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of anagrelide as reported in rats and mice is >1500mg/kg and >2500mg/kg, respectively. Symptoms of overdose may include hypotension, sinus tachycardia, and vomiting. As the therapeutic effect of anagrelide (i.e. platelet reduction) is dose-related, significant thrombocytopenia is expected in instances of overdose. Treatment of overdose should involve careful monitoring of platelet counts and complications such as bleeding. Employ symptomatic and supportive measures if clinically indicated.
Originator
Agrylin,Shire Pharmaceuticals
The Uses of Anagrelide
Anagrelide; Potent PDE 3 inhibitorIt can be used to inhibit cancer cell invasion.
The Uses of Anagrelide
the treatment of primary thrombocytosis
Indications
Anagrelide is indicated for the treatment of thrombocythemia, secondary to malignant neoplasms, to reduce platelet count and the associated risk of thrombosis. It is also beneficial in the amelioration of thrombocythemia symptoms including thrombo-hemorrhagic events.
What are the applications of Application
Anagrelide is a PDE 3 (Phosphodiesterase 3) Inhibitor
Background
Anagrelide is a platelet-reducing agent used to lower dangerously elevated platelet levels (i.e. to treat thrombocythemia) in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. It is an oral imidazoquinazoline that was first approved for use in the US in 1997. It appears to carry a better response rate than other thrombocythemia treatments (e.g. busulfan, hydroxyurea) and may be better tolerated.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,5-dihydroimidazo[2,1-]quinazoline having an oxo substituent at the 2-position and chloro substituents at the 6- and 7-positions.
Manufacturing Process
6,7-Dicloro-1,2,3,5-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one was produced
from 6-chloro-7-bromo-1,2,3,5-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinozolin-2-one by
substitution the bromine an equimolar quantity chlorine.
6-Chloro-7-bromo-1,2,3,5-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one was
produced next way: to a solution of 1.30 g (8 mmole) of anhydrous ferric
chloride in 30 ml of nitromethane was added 1.30 g (5 mmole) of solid 6-
chloro-1,2,3,5-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one and 0.80 g (5
mmole) of bromine. The system was stoppered, warmed to 50°C in an oil
bath overnight, cooled to room temperature and the solvent removed in
vacuo. The resulting solid was suspended in water (50 ml), the mixture was
made basic (pH=10) with sodium bicarbonate and stirred at home
temperature for 20 min. The solid was filtered under suction, washed with
water, then isopropyl alcohol and dried yielding 1.19 g of 6-chloro-7-bromo-
1,2,3,5-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one (78% yield). Purification
was effected by formation of the hydrochloride salt (mp 275°C) from
acetonitrile.
6-Chloro-1,2,3,5,-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one was produced
from 6-chloro-2-nitrobenzylchloride, ethylglycine hydrochloride and cyanogen
bromide in 3 steps.
brand name
Agrylin (Shire).
Therapeutic Function
Platelet aggregation inhibitor
Pharmacokinetics
Anagrelide decreases platelet counts by suppressing transcription factors necessary for the synthesis and maturation of platelet-producing cells. The drug itself appears to have a relatively short residence time in the body necessitating twice or four times daily dosing. However, given that the pharmacological effect of anagrelide therapy is reliant on a gradual suppression of platelet-producing cells, it may take 7 to 14 days for its administration to be reflected in reduced platelet counts - for this reason any changes to anagrelide doses should not exceed 0.5 mg/day in any one week.
Evidence from animal studies suggests anagrelide may impair female fertility. Female patients of reproductive age should be advised of the potential for adverse effects on fertility prior to initiating therapy.
Clinical Use
Platelet-reducing agent
Enzyme inhibitor
This potent platelet aggregation inhibitor (FW = 256.09 g/mol; CAS 68475-42-3), also known as 6,7-dichloro-1,5-dihydroimidazo[2,1- b]quinazolin-2(3H)-one, BL-4162A, and Agrylin?, blocks the action of a variety of aggregating agents added platelet rich plasma, EC50 < 1 μg/mL, or 4 nM. Primary Mode of Action: Although the exact mechanism of its selective inhibition of megakaryocyte (MK) production of platelets remains uncertain, anagrelide is known to be a potent inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-II (IC50 = 36 nM) and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (or Lp-PLA2), the latter also known as platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (or PAF-AH). PDE-II hydrolyzes both cGMP and cAMP. Binding of cGMP to its regulatory GAF-B domain favors cAMP hydrolysis to 5’-AMP, thereby reducing cGMP hydrolysis to 5’-GMP. This property, which facilitates cross-regulation of the cAMP and cGMP pathways, suggests that a potent PDE-II inhibitor should potentiate the effects of cAMP and/or cGMP, the concentrations of which should increase in anagrelide-sensitive cells. Lp-PLA2 plays pivotal role in platelet maturation by specifically hydrolyzing Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF = acetyl-glyceryl-ether-phosphorylcholine) as well as other glycerophos-pholipids containing short, truncated, and/or oxidized fatty acyl groups at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone. At a final concentration of 100 ng/mL, anagrelide selectively blocks in vitro MK maturation, resulting in a 50% decrease in the total number of CD41a+ MKs. In humans, anagreline has the intriguing ability to promote as a species-specific platelet-lowering activity at dose levels lower than those required to inhibit platelet aggregation. Target(s): collagen- and immune complexinduced platelet aggregation and release; suppresses megakaryocytopoiesis by reducing the expression levels of the transcription GATA-1 and FOG-1 via a PDEIII-independent mechanism that is differentiation context-specific but does not involve inhibition of MPL-mediated early signal transduction events.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aspirin: potential risks and benefits must first be
assessed, additive antiplatelet effect.
Cilostazol: avoid concomitant use.
Grapefruit juice: may reduce clearance of anagrelide.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: avoid with milrinone
and enoximone.
Metabolism
Anagrelide is extensively metabolized, primarily in the liver by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), into two major metabolites: 6,7-dichloro-3-hydroxy-1,5 dihydro-imidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one (3-hydroxy anagrelide) and 2-amino-5,6-dichloro-3,4,-dihydroquinazoline (RL603). The 3-hydroxy metabolite is considered pharmacologically active and carries a similar potency and efficacy in regards to its platelet-lowering effects, but inhibits PDE3 with a potency 40x greater than that of the parent drug.
Metabolism
Anagrelide is primarily metabolised by CYP1A2; less than 1% is recovered in the urine as anagrelide. Two major urinary metabolites, 2-amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4-dihydroquinazoline and 3-hydroxy anagrelide (pharmacologically active) have been identified. The mean recovery of 2-amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4-dihydroquinazoline in urine is approximately 18-35% of the administered dose.
Properties of Anagrelide
| Melting point: | 280 °C |
| Density | 1.77±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | pKa 2.87 (H2O t=25 I=0.025) (Uncertain);10(H2O t=25 I=0.025) (Uncertain) |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 68475-42-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Anagrelide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Anagrelide
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![6,7-dichloro-3-hydroxy-5,10-dihydro-3H-imidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180529/GIF/1219393-12-0.gif)


You may like
-
 Anagrelide 98%View Details
Anagrelide 98%View Details -
 68475-42-3 99%View Details
68475-42-3 99%View Details
68475-42-3 -
 Anagrelide 98%View Details
Anagrelide 98%View Details
68475-42-3 -
 Anagrelide 68475-42-3 98%View Details
Anagrelide 68475-42-3 98%View Details
68475-42-3 -
 Anagrelide 98% (HPLC) CAS 68475-42-3View Details
Anagrelide 98% (HPLC) CAS 68475-42-3View Details
68475-42-3 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
