Anagliptin
- CAS NO.:739366-20-2
- Empirical Formula: C19H25N7O2
- Molecular Weight: 383.45
- MDL number: MFCD19443729
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
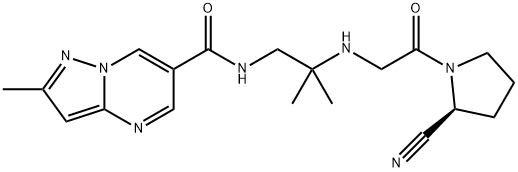
What is Anagliptin?
Description
Anagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that was approved in Japan in November 2012 for the treatment of patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Anagliptin (also known asSK-0403) is a treatment for diabetes based on inhibition of DPP-4, an enzyme that is responsible for degradation of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), a 30-amino acid peptide that is secreted in response to food intake. GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion, which leads to lower levels of plasma glucose. Following the introduction of the first DPP-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, in 2006, several members of the gliptin class have been approved worldwide. Anagliptin was discovered from an effort to replace a metabolically labile isoindoline group from an earlier DPP-4 inhibitor series with a stable bioisostere. Anagliptin is a potent DPP-4 inhibitor, with an IC50=3.8 nM and >10,000-fold selectivity over inhibition of DPP-8 and DPP-9.
Originator
Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho (Japan)
The Uses of Anagliptin
Anagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that suppresses proliferation of vascular smooth muscles and monocyte inflammatory reaction. It also attenuates atherosclerosis in male apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Definition
ChEBI: Anagliptin is an amino acid amide.
brand name
Suiny
Clinical Use
Anagliptin, which is marketed as Beskoa or Suiny, is a dipeptidyl peptidase–IV (DPP-4) inhibitor which was approved in September 2012 and launched in November 2012 in Japan for the treatment of Type II diabetes. The drug was co-developed by three Japanese companies; Kowa, Sanwa Kagaku and JW pharmaceutical. Anagliptin, which is more selective against several recombinant human proteases by comparison to sitagliptin and vildagliptin, has more than 10,000-fold selectivity over the structurally homologous DPP-8 and DPP-9 enzymes.
Synthesis
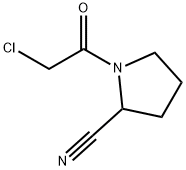
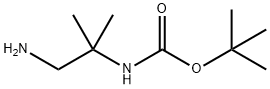
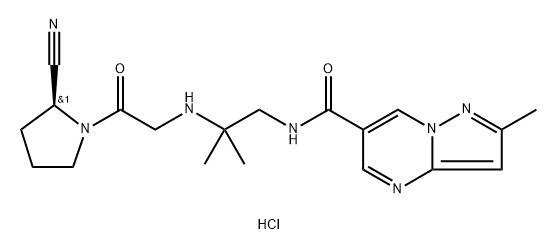
The most likely process-scale synthesis has been published and is depicted in Scheme 3.24 Commercially available (S)-1-(2-chloroacetyl)-pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile (12) was alkylated with t-butyl (2-amino-2-methyl-1-propyl)carbamate (13), giving rise to (S)-t-butyl (2-((2-(2-cyanopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2- oxoethyl)amino)-2-methylpropyl)carbamate (14). This Boc-protected system was subsequently treated with strong acid to give the ethylene diamine derivative 15 in 96% yield. Activation of 15 with CDI followed by coupling with commercially available 2-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid (16) gave anagliptin (III) in 90% yield.

Properties of Anagliptin
| Melting point: | 115 - 119°C |
| Density | 1.33±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Dichloromethane (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.40±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Anagliptin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Anagliptin
Anagliptin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 739366-20-2 Anagliptin 98%View Details
739366-20-2 Anagliptin 98%View Details
739366-20-2 -
 739366-20-2 98%View Details
739366-20-2 98%View Details
739366-20-2 -
 Anagliptin 98%View Details
Anagliptin 98%View Details
739366-20-2 -
 Anagliptin 739366-20-2 98%View Details
Anagliptin 739366-20-2 98%View Details
739366-20-2 -
 Anagliptin CAS 739366-20-2View Details
Anagliptin CAS 739366-20-2View Details
739366-20-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1