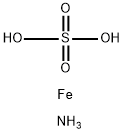
Ammonium bisulfate
Synonym(s):Ammonium bisulfate;Ammonium sulfate monobasic
- CAS NO.:7803-63-6
- Empirical Formula: H5NO4S
- Molecular Weight: 115.11
- MDL number: MFCD00051073
- EINECS: 232-265-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
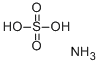
What is Ammonium bisulfate?
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder or chunks. This compound is one of several salts that can form from the reaction of ammonia and sulfur bearing gases, most particularly sulfur trioxide. This product is frequently found in the overhead of crude distillation units and can be quite corrosive to steel equipment. Chemical corrosion inhibitors are often used to control corrosion from ammonium bisulfate.
The Uses of Ammonium bisulfate
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate is used as pharmaceutical intermediates and chemical reagents.
The Uses of Ammonium bisulfate
In hair-waving preparations; as catalyst for organic reactions.
General Description
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate is a colorless to white, powdered solid. Ammonium hydrogen sulfate is toxic by ingestion. When heated to high temperatures, Ammonium hydrogen sulfate may release toxic sulfur oxide and nitrogen oxide fumes. Ammonium hydrogen sulfate is soluble in water. Ammonium hydrogen sulfate is a chemical catalyst, used in hair preparations.
Air & Water Reactions
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate dissolves in water with the evolution of some heat and hydrolyzes to form some amounts of sulfuric acid. Deliquescent.
Reactivity Profile
Acidic salts, such as Ammonium hydrogen sulfate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. A corrosive. See also SULFATES. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of sulfuric acid and SO,, NH3, and NOx,.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from water at room temperature (1mL/g) on adding EtOH and cooling. (NH4) HSO4 is formed as deliquescent rhombic crystals on cooling a solution of (NH4)2SO4 in hot conc H2SO4 but EtOH decomposes it to (NH4)3H(SO4)2 [Dunnicliff J Chem Soc 123 476 1923]. When powdered (NH4)2SO4 is heated below 100o, it loses NH3, and at 300o it is completely converted to fused (NH4) HSO4, m 140o, but >300o it decomposes to SO2 and N2 [Smith J Chem Soc 30 253 1911].
Properties of Ammonium bisulfate
| Melting point: | 147 °C |
| Boiling point: | 350 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 1.79 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.79 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (~115.1 mg/ml at 20°C). Insoluble in acetone, alcohol, and pyridine. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 13,500 |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Incompatible with acids, bases, oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/H3N.H2O4S/c;1-5(2,3)4/h1H3;(H2,1,2,3,4) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7803-63-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonium bisulfate (7803-63-6) |
Safety information for Ammonium bisulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium bisulfate
| InChIKey | BIGPRXCJEDHCLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | S(=O)(=O)(O)O.N |
Ammonium bisulfate manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
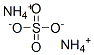
You may like
-
 Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
7803-63-6 -
 Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
7803-63-6 -
 Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
7803-63-6 -
 Ammonium bisulphate, 98% CAS 7803-63-6View Details
Ammonium bisulphate, 98% CAS 7803-63-6View Details
7803-63-6 -
 Ammonium hydrogensulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
Ammonium hydrogensulfate CAS 7803-63-6View Details
7803-63-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1