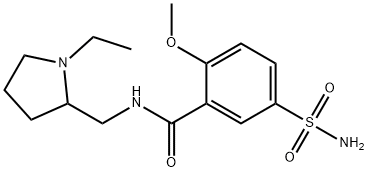
Amisulpride
Synonym(s):4-Amino-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide;Amisulpride;DAN-2163;Deniban
- CAS NO.:71675-85-9
- Empirical Formula: C17H27N3O4S
- Molecular Weight: 369.48
- MDL number: MFCD00866691
- EINECS: 275-831-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-27 17:19:27
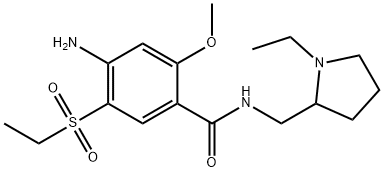
What is Amisulpride?
Absorption
Following oral administration, amisulpride is rapidly absorbed with absolute bioavailability of 48%. Amisulpride has two absorption peaks, with one rapidly achieved within one hour post-dose and a second peak occurring between three to four hours post-dose. Following oral administration of a 50 mg dose, two peak plasma concentrations were 39 ± 3 and 54 ± 4 ng/mL.
Following intravenous administration, the peak plasma concentration of amisulpride is achieved at the end of the infusion period and the plasma concentration decreases by 50% within approximately 15 minutes. The AUC(0-∞) increases dose-proportionally in the dose range from 5 mg to 40 mg, which is about four times the maximum recommended dose. In healthy patients receiving intravenous amisulpride, the mean (SD) Cmax was 200 (139) ng/mL at the dose of 5 mg and 451 (230) ng/mL at the dose of 10 mg. The AUC ranged from 136 to 154 ng x h/mL in the dose range of 5 mg to 10 mg. In patients undergoing surgery, the mean (SD) Cmax ranged from 127 (62) to 161 (58) ng/mL at the dose of 5 mg. At the dose of 10 mg, it was 285 (446) ng/mL. The AUC ranged from 204 to 401 ng x h/mL.
Toxicity
In mice, oral LD50 is 1024 mg/kg, intraperitoneal LD50 is 175 mg/kg, and subcutaneous LD50 is 224 mg/kg. The Lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) following subcutaneous administration is 0.24 mg/kg in rats. The oral TDLo in men is 4.3 mg/kg.
Oral doses of amisulpride above 1200 mg/day are associated with adverse effects related to dopamine-2 (D2) antagonism. Cardiovascular adverse reactions include prolongation of the QT interval, torsades de pointes, bradycardia, and hypotension. Neuropsychiatric adverse reactions include sedation, coma, seizures, and dystonic and extrapyramidal reactions. As there is no specific antidote for amisulpride overdosage, management includes cardiac monitoring and treatment of severe extrapyramidal symptoms. Drug elimination with the use of hemodialysis is effective. Severe extrapyramidal effects may be managed with anticholinergic drugs.
Description
Amisulpride i s a n antipsychotic agent structurally related to sulpiride and sultopride. Useful in the treatment of schizophrenia, it is not, however, without EPS liability.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
SESIF (Delagrange) (France)
The Uses of Amisulpride
Amisulpride is a neuroleptic agent, an analogue of Sulpiride (S689145). Amisulpride is used as an antipsychotic. Amisulpride is a dopamine receptor antagonist.
The Uses of Amisulpride
Neuroleptic agent, an analogue of sulpiride. Used as an antipsychotic. Dopamine receptor antagonist
Indications
Intravenous amisulpride is indicated in adults for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting, either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class. It is also indicated for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients who have received anti-emetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis.
Oral amisulpride is indicated for the treatment of acute and chronic schizophrenic disorders, characterized by positive symptoms with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, hostility and suspicious behavior; or primarily negative symptoms (deficit syndrome) with blunted affect, emotional and social withdrawal. Amisulpride also controls secondary negative symptoms in productive conditions as well as affective disorders such as depressive mood or retardation.
Background
Amisulpride is a benzamide derivative and a dopamine receptor antagonist that selectively works on dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. As an antipsychotic agent, amisulpride alleviates both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, and it exhibits antidepressant properties in patients with psychiatric disorders, dysthymia, and major depression. Amisulpride predominantly works in the limbic system, which explains its relatively lower risk of extrapyramidal adverse effects compared to other atypical antipsychotic agents. Oral tablets of amisulpride is used in European countries as a treatment for acute and chronic schizophrenic disorders, as well as secondary negative symptoms in mental health disorders such as affective disorders, depressive mood, and mental retardation.
Amisulpride is also used as an antiemetic agent. In the US, the intravenous formulation of amisulpride is used to treat and prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults, either as monotherapy or in combination with another antiemetic agent of a different drug class. It is marketed under the brand name Barhemsys.
What are the applications of Application
Amisulpride is a selective D2DR and D3DR inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Amisulpride is a member of the class of benzamides resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-amino-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzoic acid with the primary amino group of 2-(aminomethyl)-1-ethylpyrrolidine. It is a potent, selective dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. It is an atypical antipsychotic/antischizophrenic agent with limited extrapyrimidal side effects. It has a role as a second generation antipsychotic, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a member of pyrrolidines, an aromatic amine, a sulfone, a member of benzamides and an aromatic amide.
Manufacturing Process
2-Methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylthiobenzoic acid:
159 g of 2-methoxy-4-amino-5-mercaptobenzoic acid, 355 ml of water and
160 ml of caustic soda solution are placed in a flask fitted with a condenser.
The mixture is heated until the solid dissolves, then 123 g of ethyl sulfate is
added. The mixture is heated to reflux, treated with 10 ml of 30% caustic
soda solution, then heated to reflux for 1 hour. After cooling, 800 ml of water
is added and the solution is filtered. The precipitate obtained by adding 100
ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid in the presence of ether is drained,
washed with water and dried. 162 g of 2-methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylthiobenzoic
acid is obtained (yield=88%).
2-Methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylsulfonylbenzoic acid:
123 g of 2-methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylthiobenzoic acid is dissolved hot in 542
ml of acetic acid. The solution obtained is cooled to 35°C, then 185 ml of
hydrogen peroxide is added in small quantities while the temperature is raised
to 80°C. The temperature is lowered to 40°C and the mixture is kept at that
temperature for some hours and then cooled to 10°C. The precipitate formed
is drained, washed with acetic acid and dried, then dissolved in 600 ml of
water and 100 ml of 20% ammonia. The precipitate formed by adding 70 ml
of concentrated hydrochloric acid is cooled, drained, washed with water and
dried. 61.5 g of 2-methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylsulfonylbenzoic acid is obtained
(yield 42%, M.P. 95-100°C).
4-Amino-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-
methoxybenzamide:
81 g of 2-methoxy-4-amino-5-ethylsulphonylbenzoic acid and 297 ml of
acetone are placed in a flask fitted with an agitator, a thermometer and a
dropping funnel, followed by 33 g of triethylamine. The solution is cooled to
0°C, then 30 g of ethyl chloroformate is added drop by drop between 0° and
5°C. When the mixture has been agitated 51 g of 1-ethyl-2-
aminomethylpyrrolidine is added drop by drop between 5° and 10°C. The
mixture is agitated at 10°C then at ambient temperature. The triethylamine
hydrochloride which precipitates is drained, then the acetone is distilled. The
residue is dissolved in 600 ml of water in the presence of caustic soda solution. The base crystallizes after seeding and is drained, washed with water
and dried. When the crystals have been purified by passing them through
hydrochloride and recrystallising them in acetone, 66 g of 4-amino-N-[(1-
ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamideis obtained
(yield 61%, M.P. 126-127°C).
brand name
SOCIAN
Therapeutic Function
Antipsychotic
Biological Activity
Potent, selective dopamine D 2 and D 3 receptor antagonist. K i values are 2.8 and 3.2 nM respectively for human D 2 and D 3 and > 1000 nM for human D 1 , D 4 and D 5 receptors. Shows selectivity for presynaptic dopamine autoreceptors at low doses and blocks postsynaptic D 2 /D 3 receptors at higher doses. Preferentially interacts with limbic D 2 -like receptors in vivo . Atypical antipsychotic/antischizophrenic agent with limited extrapyrimidal side effects and a profile distinct from that of haloperidol and remoxipride.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Amisulpride is a highly selective D2/D3 dopamine receptor antagonist and atypical antipsychotic.
Pharmacokinetics
Amisulpride is a selective dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist with no affinity towards other dopamine receptor subtypes. Amisulpride is an atypical antipsychotic agent that works as an antagonist at dopamine receptors in the limbic system. Since it works preferentially in the limbic system, amisulpride is less likely to be associated with extrapyramidal adverse effects than other atypical antipsychotic agents. Amisulpride has no affinity for serotonin, alpha-adrenergic, H1-histamine, cholinergic, and sigma receptors. In clinical trials, amisulpride improved reduced secondary negative symptoms, affective symptoms, and psychomotor retardation in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Notably, amisulpride has a differential target binding profile at different doses: at low doses, amisulpride selectively binds to presynaptic dopamine autoreceptors. At high doses, it preferentially binds to post-synaptic dopamine receptors. This explains how amisulpride reduces negative symptoms at low doses and mediates antipsychotic effects at high doses. One study alluded that the antinociceptive effects of amisulpride are mediated through opioid receptor acvitation and D2 receptor antagonism. The actions of amisulpride at opioid receptors may explain its pro-convulsant properties.
Amisulpride is also an antiemetic agent that prevents and alleviates postoperative nausea and vomiting. It primarily works by blocking dopamine signalling in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which is a brain area that relays stimuli to the vomiting center.
In clinical trials comprising Caucasian and Japanese subjects, amisulpride caused dose- and concentration-dependent prolongation of the QT interval; thus, intravenous infusion under a strict dosing regimen and close monitoring of patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions are recommended. Amisulpride increases plasma prolactin levels, leading to an association with benign pituitary tumours such as prolactinoma.
Clinical Use
Treatment of acute and chronic schizophrenia
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alcohol: may enhance CNS effects of alcohol.
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative
effects with opioids; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with methadone - avoid.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with anti-arrhythmics that prolong the
QT interval; avoid with amiodarone, disopyramide
and procainamide (risk of ventricular arrhythmias).
Antibacterials: avoid with erythromycin (increased
risk of ventricular arrhythmias).
Antidepressants: increased level of tricyclics.
Antiepileptics: antagonises anticonvulsant effect.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hypotension.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether/lumefantrine.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with droperidol, sertindole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by ritonavir.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: increased sedative effects.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with vandetanib - avoid; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with arsenic trioxide.
Diuretics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
due to hypokalaemia.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias - avoid.
Metabolism
Amisulpride undergoes minimal metabolism and its metabolites in plasma are largely undetectable. Two identified metabolites, formed by de-ethylation and oxidation, are pharmacologically inactive and account for approximately 4% of the dose. Metabolites remain largely uncharacterized. Metabolism of amisulpride does not involve cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Metabolism
Amisulpride is weakly metabolised: two inactive metabolites, accounting for approximately 4% of the dose, have been identified. Amisulpride is eliminated unchanged in the urine. Fifty percent of an intravenous dose is excreted via the urine, of which 90% is eliminated in the first 24 hours.
storage
-20°C
References
[1] schoemaker h1, claustre y, fage d, rouquier l, chergui k, curet o, oblin a, gonon f, carter c, benavides j, scatton b. neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine d2/d3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. j pharmacol exp ther. 1997 jan;280(1):83-97.
Properties of Amisulpride
| Melting point: | 124-128 |
| Boiling point: | 558.9±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.200±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥5 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.73±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,485 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C17H27N3O4S/c1-4-20-8-6-7-12(20)11-19-17(21)13-9-16(25(22,23)5-2)14(18)10-15(13)24-3/h9-10,12H,4-8,11,18H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 71675-85-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Amisulpride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Amisulpride
| InChIKey | NTJOBXMMWNYJFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(NCC1CCCN1CC)(=O)C1=CC(S(CC)(=O)=O)=C(N)C=C1OC |
Amisulpride manufacturer
Biochemical and Synthetic Products PvtLtd
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Amisulpride 99%View Details
Amisulpride 99%View Details -
 Amisulpride 98%View Details
Amisulpride 98%View Details -
 Amisulpride 99% (HPLC) CAS 71675-85-9View Details
Amisulpride 99% (HPLC) CAS 71675-85-9View Details
71675-85-9 -
 Amisulpride 98% (HPLC) CAS 71675-85-9View Details
Amisulpride 98% (HPLC) CAS 71675-85-9View Details
71675-85-9 -
 Amisulpride 99%View Details
Amisulpride 99%View Details -
 Amisulpride CAS 71675-85-9View Details
Amisulpride CAS 71675-85-9View Details
71675-85-9 -
 Amisulpride 95.00% CAS 71675-85-9View Details
Amisulpride 95.00% CAS 71675-85-9View Details
71675-85-9 -
 Amisulpride CAS 71675-85-9View Details
Amisulpride CAS 71675-85-9View Details
71675-85-9
