ALDICARB-SULFONE
- CAS NO.:1646-88-4
- Empirical Formula: C7H14N2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 222.26
- MDL number: MFCD00041804
- EINECS: 216-710-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
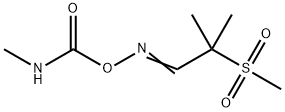
What is ALDICARB-SULFONE?
Description
Aldoxycarb, is also called 2-mesyl-2-methylpropionaldehyde O-methylcarbamoyloxime (IUPAC), the sulfone analog of aldicarb, is also a systemic insecticide effective for control of insects (mainly sucking insect pests such as aphids, leafhoppers, etc.).
Chemical properties
Aldoxycarb is a carbamate pesticide used mainly as an insecticide and acaricide. It is a white crystalline powder with a slightly sulfurous odor. Aldoxycarb is extremely toxic to wildlife. Aldoxycarb (Aldicarb sulfone) is a breakdown product of aldicarb. Aldoxycarb is a degradate/metabolite of aldicarb produced by the oxidation of the thio-moiety.
The Uses of ALDICARB-SULFONE
Aldicarb Sulfone is an analog of Aldicarb (A514650) detected in agricultural products as pesticide residue.
The Uses of ALDICARB-SULFONE
Aldoxycarb is a soil applied systemic oxime carbamate insecticide effective for the control of insects (mainly sucking pests such as aphids, leafhoppers, etc.), mites and nematodes on many field (cotton, maize, etc.) and vegetable crops.
Definition
ChEBI: Aldoxycarb is a sulfone.
General Description
White crystalline solid. Insecticide.
Reactivity Profile
ALDICARB-SULFONE is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Health Hazard
Exposures to high levels of aldoxycarb cause adverse health effects and damages the nervous system of humans and laboratory animals. Chemicals that cause adverse health effects in humans and laboratory animals after high levels of exposure may pose a risk of adverse health effects in humans exposed to lower levels over long periods of time. Ingestion and other exposures to the chemical cause various health disorders. The type and severity of symptoms varies depending on the amount of chemical involved and the nature of the exposure. The symptoms include, but are not limited to, eye irritation, skin irritation, dizziness, sweating, malaise, CNS depression, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, salivation, headache, ataxia, muscle twitching, muscle weakness, runny nose, tearing eyes, pinpoint pupils or dark vision, wheezing, increased or decreased heart rate, seizures, convulsions, and death. It has not caused any delayed neurotoxicity in animals. The onset of these symptoms is rapid and the severity of symptoms depends on the dose. The immediate cause of death is usually respiratory failure.
Health Hazard
Highly toxic by all routes of exposure;cholinesterase inhibitor; ingestion of 1–3 gmay cause death to adult humans.
LD50 oral (mouse): 20 mg/kg
LD50 inhalation (rat): 140 mg/m3/4 hr
LD50 skin (rabbit): 200 mg/kg.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide, Nematicide: Used to control honey locust, gall midge and other insects and mites on cotton, potatoes, sugar beets and ornamentals. Applied to the soil by soluble mixture or spikes. Not listed for use in EU countries.
Trade name
ALDICARB SULFONE®; TEMIK SULFONE®; SULFOCARB®; STANDAK®; UC-21865®
Metabolic pathway
Aldoxycarb is the sulfone analogue of aldicarb. It has now been superseded but, because of its close relationship with aldicarb, it is included here. The degradation and metabolic pathway of these two structurally related compounds are consistent with each other. Information on the metabolism of aldoxycarb discussed in this summary is based on results obtained from studies where aldoxycarb was the test substance. Additional information can be obtained from the aldicarb summary. The metabolism of aldoxycarb in soils, plants and animals follow common metabolic pathways which include the hydrolysis and elimination of the oxime carbamate to yield the corresponding oximes and nitriles. These primary metabolites are further degraded via hydrolysis to the corresponding amides and acids. Other reactions also include the hydrolysis/ oxidation of the oxime to the corresponding alcohol, aldehyde and acid. Further degradation to methane sulfonic acid was observed in plants and animals. The metabolic pathways of aldoxycarb are presented in Scheme 1.
Degradation
Aldoxycarb (1) is susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis. It was stable under acidic (pH 5) conditions, slowly degraded (DT50 82 days) in neutral conditions (pH 7) and rapidly degraded (DT50 0.8 days) under basic (pH 9) conditions (Andrawes, 1976a). Aldoxycarb oxime (2), aldoxycarb nitrile (3) and methanesulfonic acid (4) were the major hydrolysis products. Aldoxycarb degraded slowly in water under photolytic conditions (xenon lamp) with a half-life of approximately 38 days (Andrawes, 1976b) to yield aldoxycarb nitrile (3) as the major degradation product.
Properties of ALDICARB-SULFONE
| Melting point: | 132-135 °C |
| Density | 1.3816 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.2×10-2 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5690 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 10 g l-1 (25 °C) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.44±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| BRN | 2215242 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aldicarb sulfone (1646-88-4) |
Safety information for ALDICARB-SULFONE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for ALDICARB-SULFONE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4