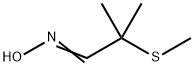
ALDICARB
Synonym(s):O-(Methylcarbamoyl)-2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyd-oxime
- CAS NO.:116-06-3
- Empirical Formula: C7H14N2O2S
- Molecular Weight: 190.26
- MDL number: MFCD00041807
- EINECS: 204-123-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06
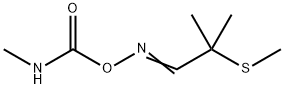
What is ALDICARB?
Description
Aldicarb is a carbamate pesticide that reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase. It is the active ingredient in mixtures used to control insect, mite, and nematode pests in agriculture. Aldicarb has a high acute mammalian toxicity (LD50 = 0.3-0.5 mg/kg) following oral or parenteral administration. Aside from its use as a pesticide, aldicarb has applications as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for research purposes.
Chemical properties
Aldicarb is a noncombustible, white crystalline solid with a slight sulfurous odor.It is not compatible with alkaline materials and is non-corrosive to metals and plastics. It is sparingly soluble in water, but soluble in acetone, xylene, ethyl ether, toluene, and other organic solvents. Aldicarb has been classifi ed as an RUP and hence should only be used by trained and certifi ed workers. Aldicarb is used to control mites, nematodes, and aphids and is applied directly to the soil. It is used widely on cotton, peanut, and soybean crops. In the mid-1980s, there were highly publicized incidents in which misapplication of aldicarb contaminated cucumbers and watermelons and led to adverse effects in people. Aldicarb is metabolized in the liver of mammals fi rst into aldicarb sulfoxide and later into aldicarb sulfone.
The Uses of ALDICARB
Aldicarb is a broad-spectrum, systemic carbamate insecticide used to control nema-todes in soil and a variety of insects and mites on citrus crops, dry beans, grain, sorghum, ornamentals, pecans, peanuts, potatoes, seed alfalfa, soybeans, sugar beets, sugarcane, sweet potatoes, and tobacco.
The Uses of ALDICARB
Aldicarb is a soil applied systemic oxime carbamate insecticide with both contact and oral activities. It controls a broad spectrum of chewing and sucking insects, mites and nematodes on a wide variety of field, fruit and vegetables crops such as cotton, citrus, potatoes, sugar beet and peanuts.
What are the applications of Application
Aldicarb is A cholinesterase inhibitor which prevents the breakdown of ACh in the synapse
Definition
ChEBI: The oxime carbamate resulting from the addition of 2-methyl-2-(methylsulfanyl)propanaldoxime to methyl isocyanate. A member of the class of oxime carbamate insecticides, aldicarb is a mixture of E and Z isomers; it is not nown which isomer is more active.
Preparation
Aldicarb is prepared by treating isobutene with nitrosyl chloride, treating the resulting dimeric adduct with sodium methyl sulfide, and converting the resulting oxime to the carbamate with methyl isocyanate. Warning: the dimeric isobutene nitrosochloride is unstable and decomposes explosively at 94 °C. The oxime and end product also decompose vigorously above 140 and 160 °C, respectively.
General Description
White crystals with a slightly sulfurous odor. Commercial formulations are granular Used as an insecticide, acaricide, and nematocide.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
ALDICARB is a carbamate ester. ALDICARB decomposes at temperatures greater than 212° F. ALDICARB is incompatible with highly alkaline substances. ALDICARB is rapidly converted by oxidizing agents.
Health Hazard
Aldicarb is the most potent of the commercially available carbamate pesticides and is an unusual source of acute human poisoning. Aldicarb has severe systemic toxicity to animals and humans. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor that prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. In the case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure. The primary route of human exposure to aldicarb is consumption of contaminated food and water from contaminated wells. Occupational exposure to high levels of aldicarb is due to product handling, and most cases of aldicarb poisoning occur from loading and application of the pesticide. Aldicarb is extremely toxic both through the oral and dermal route. Absorption from the gut is rapid and almost complete. When administered in oil or other organic solvents, aldicarb is absorbed rapidly through the skin. Its skin toxicity is roughly 1000 times that of other carbamates. In humans, the onset of symptoms is rapid (15 min to 3 h). Symptoms disappear in 4–12 h.The acute oral LD50 of aldicarb in rats, mice, guinea pigs, and rabbits ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 mg/kg when administered in a liquid or oil form. The toxicities of the dry granules are distinctly lower (LD50 7.0 mg/kg), though still highly toxic. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor and therefore can result in a variety of symptoms including weakness, blurred vision, headache, nausea, tearing, sweating, and tremors. At very high concentrations, aldicarb causes paralysis, respiratory system damage, eventually leading to the death of the exposed worker. There is very little evidence of chronic effects from aldicarb exposure. Rats and dogs fed low doses of aldicarb for 2 years showed no signifi cant adverse effects. One epidemiological study suggested a possible link between low-level exposure and immunological abnormalities. The result of this study, however, has been widely disputed. Aldicarb administered to pregnant rats at very low levels (0.001–0.1 mg/kg/day) depressed AChE activity more in the fetuses than in the mother. The aldicarb was also retained in the mother’s body for longer periods than in non-pregnant rats. A three-generation study at doses of 0.05 and 0.10 mg/kg/day produced no signifi cant toxic effects, and in another study, a dose of 0.70 mg/kg/day produced no adverse effects. Thus, reproductive effects in humans are unlikely at expected exposure levels.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, ALDICARB emits very toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. Incompatible with highly alkaline substances. Unstable in alkali; poor stability at 122F.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Nematicide, Acaricide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not approved for use in EU countries.
Trade name
TEMIC®; TEMIK®; OMS 771®; TERNIC®; TEMIK 10 G®
Safety Profile
Deadly poison by ingestion, skin contact, subcutaneous, and possibly other routes. Human mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. A powerful systemic poison. In 1985 over 150 people in California exhibited toxic effects from eating watermelons contaminated with aldicarb. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx
Potential Exposure
Exposure to aldicarb and aldicarb sulfoxide and sulfone will occur mainly through the ingestion and contaminated drinking water derived from contaminated ground water as well as contaminated food.
Environmental Fate
Aldicarb and its degradation products are generally very soluble in water and mobile in soil. Adsorption in soil is primarily to organic matter, so leaching is most exten- sive in sandy or sandy loam soils. Aldicarb is very persistent in groundwater, typi- cally degrading to nontoxic products with a half-life between a few weeks to as long as several years. The primary mode of degradation is chemical hydrolysis, with some microbial decay in shallow groundwater. In soils, the primary mode of degradation is oxidation by soil microorganisms and hydrolysis, depending on soil conditions.
Metabolic pathway
In an aqueous buffer solution in the pH range 2.91 ? 5.51, the Cu(II) ion promotes the decomposition of aldicarb, forming the degradation products 2-methyl- 2-(methylthio)propionitrile and 2-methyl-2- (methylthio)propanal.
storage
Aldicarb should be kept stored in a dry, cool area, out of reach of children and animals, and away from food, feedstuffs, fertilizers, and seed.
Shipping
UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Degradation
Aldicarb (1) is susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis. Under basic conditions (pH 9), aldicarb hydrolysed slowly with a DT50 of approximately 75 days. Cleavage of the oxime carbamate linkage to yield aldicarb oxime (2) and the aldicarb nitrile (3) was the primary degradation pathway. Aldicarb was stable to hydrolysis under acidic (pH 5) and neutral (pH 7) conditions (Andrawes, 1976a). Aldicarb also degraded in water under photolytic conditions (xenon lamp) with a DT50 of approximately 4 days (Das, 1990a). The major photolytic degradation products were aldicarb oxime (2) and aldicarb nitrile (3) (Andrawes, 1976b).
Incompatibilities
Strong alkalis
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposedproperly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of ALDICARB
| Melting point: | 99-100° with dec >100° |
| Density | d425 1.195 |
| vapor pressure | 1.3×10-2 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4920 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMSO: slightly soluble; Methanol: slightly soluble |
| pka | 11.7 |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 4.9 g l-1(pH 7,20 °C) |
| BRN | 2209304 |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 53) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aldicarb (116-06-3) |
Safety information for ALDICARB
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for ALDICARB
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



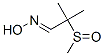
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4