Activated carbon
Synonym(s):Activated charcoal;Charcoal activated;Charcoal bone
- CAS NO.:64365-11-3
- Empirical Formula: CH4
- Molecular Weight: 16.0400009155273
- MDL number: MFCD00217223
- EINECS: 264-846-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-19 05:41:50
What is Activated carbon?
Absorption
No evidence of systemic absorption of activated charcoal
Toxicity
Adverse effects from the treatment include aspiration into the lungs and possibly pneumonitis, black stools, vomiting, and constipation or diarrhea. The oral LD50 value in rats is 15400mg/kg.
Chemical properties
Black, light powder free from grittiness
The Uses of Activated carbon
Activated carbons are internally porous microcrystalline, non-graphitic forms of carbon. The activated carbons possess large surface area (~1000 m2/g) and pore volumes which make them useful for applications in energy storage devices, catalysis, and for removal of impurities from gases and liquids.Our activated carbon has been modified with Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate and is well suited for metal ion removal from water.
The Uses of Activated carbon
Adsorbent.
The Uses of Activated carbon
Activated charcoal is used as an oral absorbent in treating oral intoxication from many substances.
Indications
Used as a antidote to treat poisonings following excessive oral ingestion of certain medications or poisons.
Background
Activated charcoal, or activated carbon, is an amorphous form of carbon prepared from incomplete combustion of carbonaceous organic matter. It is activated by an oxidizing gas flow at high temperature passed over its surface to make a fine network of pores, producing a material with large surface area and high affinity for various substances. It is used as a gastric decontaminant and emergency medication to treat poisonings following excessive oral ingestion of certain medications or poisons by absorbing most drugs and toxins. However its effects is rendered poor on some compounds including strong acids or bases, methanol and substances with limited absorptive capacity (including iron, lithium, arsenic). It works by binding to the poison in the gastric contents in a reversible fashion thus may be adminstered together with a cathartic to reduce the small intestine transit time. The clinical applications of activated charcoal occured in the early 1800's. While this management for acute poisoning is considered fairly invasive, it is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines that includes the most important medications needed in a basic health system.
Definition
An amorphous form of carbon made by heating wood or other organic material in the absence of air. Activated charcoal is charcoal that has been heated to drive off absorbed gas. It is used for absorbing gases and for removing impurities from liquids.
Pharmacokinetics
Activated charcoal is used as a gastric decontamination agent in emergency clinical settings in case of poison or medication overdose. Studies show that early administration of one dose of activated charcoal can adsorb poison in the stomach and reduce absorption while it also works long after ingestion, by interruption of enterohepatic and enterovascular cycling of poison.
Safety Profile
It can cause a dust irritation, particularly to the eyes and mucous membranes. Combustible when exposed to heat. Dust is flammable and explosive when exposed to heat or flame or oxides.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Activated carbon
| solubility | Practically insoluble in all usual solvents |
| form | powder |
| Dielectric constant | 12.0(Ambient) |
Safety information for Activated carbon
Computed Descriptors for Activated carbon
Activated carbon manufacturer
Neelam Aqua and Speciality Chem. P Ltd.
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

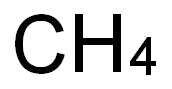
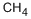

You may like
-
 ACTIVATED CARBON 99%View Details
ACTIVATED CARBON 99%View Details -
 Activated Carbon 99%View Details
Activated Carbon 99%View Details -
 64365-11-3 99%View Details
64365-11-3 99%View Details
64365-11-3 -
 Activated Charcoal CASView Details
Activated Charcoal CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8