3-Nitroaniline
Synonym(s):3-Aminonitrobenzene
- CAS NO.:99-09-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H6N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 138.12
- MDL number: MFCD00007782
- EINECS: 202-729-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
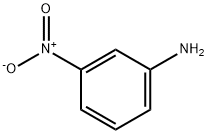
What is 3-Nitroaniline?
Chemical properties
3-Nitroaniline is a ochre-yellow to orange crystalline powder, crystallizes as yellow needles from water. It is moderately soluble in organic solvents and sparingly soluble in water (0.11 %).
Physical properties
Yellow, rhombic crystals or powder. Finely dispersered particles form explosive mixtures. Combustible.
The Uses of 3-Nitroaniline
Dyestuff intermediate. Acetylation of 3-nitroaniline followed by reduction gives 3-aminoacetanilide. Diazotization, followed by reduction of the diazosulfonate with ammonium bisulfite and subsequent hydrolysis, gives (3-nitrophenyl) hydrazine; an intermediate in the production of pyrazolone azo coupling components. 3-Nitroaniline is used as a diazo component (Fast Orange R Base) in azo dyes (e.g., C.I. Disperse Yellow 5 and C.I. Acid Orange 18).
The Uses of 3-Nitroaniline
3-Nitroaniline is commonly used as a raw material for dyes. It is also used as a chemical intermediate for azo coupling component 17 and the dyes disperse yellow 5 and acid blue 29. The chemical is changed to other substances (dyestuffs and m-nitrophenol) during the dyeing process.
Preparation
M-nitroaniline partial reduction.
Production Methods
1,3-Dinitrobenzene is added to warm water containing magnesium sulfate. An aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen sulfide (6 molar equivalents) is added gradually to the vigorously stirred emulsion, and reduction is completed by heating to 90 ℃. The 3-nitroaniline produced solidifies on cooling and is separated by filtration.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 45, p. 4992, 1980 DOI: 10.1021/jo01312a039
Tetrahedron Letters, 30, p. 251, 1989 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)95173-6
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 34, p. 2013, 1986 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.34.2013
General Description
Yellow needles or yellow powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Thermal stability of 3-Nitroaniline is reduced by various impurities. 3-Nitroaniline may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. 3-Nitroaniline may react explosively with ethylene oxide at 266° F. 3-Nitroaniline is incompatible with acids (nitric, sulfuric), acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizing agents. . Unstable when heated.
Hazard
Moderate fire risk. Toxic when absorbed by skin.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 3-Nitroaniline are not available; however, 3-Nitroaniline is probably combustible.
Synthesis
1,3-Dinitrobenzene is added towarmwater containing magnesium sulfate. An aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen sulfide (6molar equivalents) is added gradually to the vigorously stirred emulsion, and reduction is completed by heating to 90℃. The 3-nitroaniline produced solidifies on cooling and is separated by filtration.
Environmental Fate
Biological. A bacterial culture isolated from the Oconee River in North Georgia degraded 3-
nitroaniline to the intermediate 4-nitrocatechol (Paris and Wolfe, 1987). A Pseudomonas sp. strain
P6, isolated from a Matapeake silt loam, did not grow on 3-nitroaniline as the sole source of
carbon. However, in the presence of 4-nitroaniline, all of the applied 3-nitroaniline metabolized
completely to carbon dioxide (Zeyer and Kearney, 1983). In the presence of suspended natural
populations from unpolluted aquatic systems, the second-order microbial transformation rate
constant determined in the laboratory was reported to be 4.6 ± 0.1 x 10-13 L/organism?h (Steen,
1991).
In activated sludge inoculum, following a 20-d adaptation period, no degradation was observed
(Pitter, 1976).
Chemical/Physical. Reacts with acids forming water soluble salts.
Purification Methods
Purify it as for o-nitroaniline. Warning: it is absorbed through the skin. [Beilstein 12 IV 1589.]
Properties of 3-Nitroaniline
| Melting point: | 111-114 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 306 °C |
| Density | 0,901 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 119 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6396 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 196 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 1.25g/l |
| form | Crystals, Crystalline Powder and/or Chunks |
| pka | 2.466(at 25℃) |
| Colour Index | 37030 |
| Specific Gravity | 0.901 |
| color | Yellow to ochre-yellow to orange |
| Water Solubility | 1.25 g/L |
| Merck | 14,6581 |
| BRN | 636962 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.93 x 10-5 atm?m3/mol at 25 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-09-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | m-Nitroaniline(99-09-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | m-Nitroaniline (99-09-2) |
Safety information for 3-Nitroaniline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for 3-Nitroaniline
3-Nitroaniline manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 3-Nitro aniline CAS 99-09-2View Details
3-Nitro aniline CAS 99-09-2View Details
99-09-2 -
 3-NITROANILINE Pure CAS 99-09-2View Details
3-NITROANILINE Pure CAS 99-09-2View Details
99-09-2 -
 3-Nitroaniline CAS 99-09-2View Details
3-Nitroaniline CAS 99-09-2View Details
99-09-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
