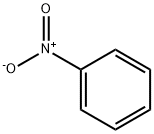
2-Nitroaniline
Synonym(s):2-Nitroaniline;o-Nitraniline
- CAS NO.:88-74-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H6N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 138.12
- MDL number: MFCD00007687
- EINECS: 201-855-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
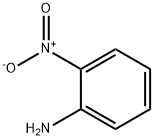
What is 2-Nitroaniline?
Chemical properties
orange solid
The Uses of 2-Nitroaniline
2-Nitroaniline is the main precursor to?phenylenediamines, which are converted to?benzimidazoles, a family of?heterocycles?that are key components in pharmaceuticals.
The Uses of 2-Nitroaniline
Dyestuff intermediate.
Production Methods
2-Chloronitrobenzene is heated with excess (10 mol/mol) strong aqueous ammonia in an autoclave. The temperature is gradually increased to 180 ℃ over 4 h and held there for 5 h more. The pressure builds up to around 4 MPa and is released to an ammonia recycle loop before the product is isolated by filtration and washing. The reaction is extremely exothermic, and too rapid heating or inadequate temperature control can result in a runaway reaction. Because of this hazard, I.G. Farbenindustrie developed a continuous amination unit for amination of chloronitrobenzenes; the process is summarized under 4-nitroaniline.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 77, p. 5688, 1955 DOI: 10.1021/ja01626a066
Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 1, p. 388, 1941
General Description
Orange solid with a musty odor. Sinks and mixes slowly with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2-Nitroaniline may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. Mixtures of 2-Nitroaniline with magnesium are hypergolic on contact with nitric acid. 2-Nitroaniline forms extremely explosive addition compounds with hexanitroethane. 2-Nitroaniline has a vigorous reaction with sulfuric acid above 392° F. 2-Nitroaniline is incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizers.
Hazard
Explosion risk. Toxic when absorbed by skin.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or ingestion causes headache, nausea, methemo- globinemia, vomiting, weakness, and stupor; cyanosis caused by contact usually develops in 4-6 hrs.; prolonged and excessive exposure may also cause liver damage. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation; continued exposure may cause same symptoms as inhalation or ingestion.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may form in fire.
Safety Profile
A poison. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by skin contact. Mutation data reported. Mixtures with magnesium are hypergolic on contact with nitric acid. Forms extremely explosive addltion compounds with hexanitroethane. Vigorous reaction with sulfuric acid above 200°C. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also m- NITROANILINE, p-NITROANILINE, and ANILINE DYES.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Under aerobic and anaerobic conditions using a sewage inoculum, 2-nitroaniline
degraded to 2-methylbenzimidazole and 2-nitroacetanilide (Hallas and Alexander, 1983). A
Pseudomonas sp. strain P6, isolated from a Matapeake silt loam, did not grow on 2-nitroaniline as
the sole source of carbon. However, in the presence of 4-nitroaniline, approximately 50% of the
applied 2-nitroaniline metabolized to nonvolatile products which could not be identified by HPLC
(Zeyer and Kearney, 1983). In activated sludge inoculum, following a 20-d adaptation period, no
degradation was observed (Pitter, 1976).
Plant. 2-Nitroaniline was degraded by tomato cell suspension cultures (Lycopericon
lycopersicum). Transformation products identified were 2-nitroanilino-β-D-glucopyranoside, β-(2-
amino-3-nitrophenyl)glucopyranoside, and β-(4-amino-3-nitrophenyl)-glucopyranoside (Pogány et
al., 1990).
Purification Methods
Crystallise the aniline from hot water (charcoal), then from aqueous 50% EtOH, or EtOH, and dry it in a vacuum desiccator. It has also been chromatographed on alumina, then recrystallised from *benzene. [Beilstein 12 IV 1563.]
Properties of 2-Nitroaniline
| Melting point: | 70-73 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 284 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1,255 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 8.1 at 25 °C (Mabey et al., 1982) |
| refractive index | 1.6349 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 168 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| form | Crystals or Flakes |
| pka | -0.26(at 25℃) |
| Colour Index | 37025 |
| color | Orange to brown |
| PH | 6.1 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | 1.1 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6582 |
| BRN | 509275 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 5.88 x 10-8 atm?m3/mol at 25 °C (thermodynamic method-GC/UV spectrophotometry, Altschuh et al., 1999) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidizing agents, chloroformates, hexanitroethane. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 88-74-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | o-Nitroaniline(88-74-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | o-Nitroaniline (88-74-4) |
Safety information for 2-Nitroaniline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Nitroaniline
2-Nitroaniline manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2-Nitro aniline CAS 88-74-4View Details
2-Nitro aniline CAS 88-74-4View Details
88-74-4 -
 2-NITROANILINE Pure CAS 88-74-4View Details
2-NITROANILINE Pure CAS 88-74-4View Details
88-74-4 -
 2-Nitroaniline CAS 88-74-4View Details
2-Nitroaniline CAS 88-74-4View Details
88-74-4 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
