2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
Synonym(s):DNC;DNOC;2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol;4,6-Dinitro-2-methylphenol;3,5-Dinitro-2-hydroxytoluene
- CAS NO.:534-52-1
- Empirical Formula: C7H6N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 198.13
- MDL number: MFCD00007105
- EINECS: 208-601-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
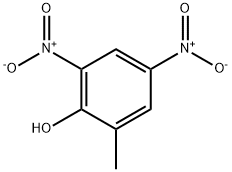
What is 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol?
Description
DNOC exists in 9 isomeric forms of which4,6-dinitro-o-cresol is the most important commercially andthe most heavily regulated. It is a noncombustible, yellowcrystalline solid. Molecular weight= 198.15; Boilingpoint= 312℃; Freezing/Melting point = 88℃; Vaporpressure = 5 3 1025 mmHg. Hazard Identification (based onNFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 0,Reactivity 0. Practically insoluble in water;solubility 5 0.01%.
Chemical properties
yellow to yellow-green crystals or cryst. powder
The Uses of 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol can be used as dormant ovicidal spray for fruit trees (highly phytotoxic and cannot be used successfully on actively growing plants); herbicide; insecticide.
The Uses of 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol is used as a selective herbicide as well as an insecticide.
The Uses of 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
DNOC is a dinitrophenolic compound which exhibits insecticidal, acaricidal and herbicidal activities. It is a non-selective insecticide and controls aphids, Lepidoptera larva and scale insects on pome fruits and stone fruit trees.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxytoluene that is o-cresol carrying nitro substituents at positions 4 and 6.
Production Methods
o-Cresol is sulfonated in excess 75 % sulfuric acid to give the disulfonic acid. The sulfonation mass is diluted with water, and 2 equivalents of nitric acid are added at 70 ℃ to form the dinitro derivative. The product is separated while molten and washed with hot water.
General Description
A yellow solid. Emits toxic oxides of nitrogen fumes when heated to decomposition. Toxic by skin absorption, inhalation or ingestion. Soluble in alcohol, acetone, ether and solutions of sodium or potassium hydroxides.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Health Hazard
Extremely toxic material; probable oral lethal dose is 5-50 mg/kg in humans or between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person.
Health Hazard
4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol exhibits cumulative toxicity in humans; the symptoms of poisoning are manifested when the blood levels of this compound exceeds 15–20 μg/g (ACGIH 1986). Thus chronic exposure to this compound can cause serious health hazard. The signs of toxicity in humans are headache, fever, profuse sweating, rapid pulse and respiration, cough, shortness of breath, and coma. Other symptoms noted are a decrease in hemoglobin, an increase in blood sugar, a loss of muscle tone, dyspnea, kidney and liver injury, and edema of the lung and brain.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 47 mg/kg
LD50 value, skin (rats): 200 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide, Fungicide, Pesticide: DNOC is widely used in agriculture as a herbicide and pesticide; it is also used in the dyestuff industry. Although 4,6-dinitro-o-cresol (DNOC) is no longer registered for use in the United States, it was used as a blossom-thinning agent on fruit trees and as a fungicide, insecticide, and miticides on fruit trees during the dormant season. It is used in mushroom houses to control foreign fungi; to kill locusts and other insects; and as a pre-harvest desiccant of potatoes and leguminous seed crops. DNOC is used as free radical polymerization inhibitor and agricultural chemical intermediate; widely used in agriculture as a herbicide and pesticide; Hence, individuals formulating or spraying the compound incur the highest risk of exposure to the compound. Not approved for use in EU countries. DNOC’s registration in the U.S. as a pesticide was canceled in 1991. Currently, there are 39 global suppliers.
Trade name
ANTINONIN®; ANTINONNIN®; ARBOROL®; DEGRASSAN®; DEKRYSIL®; DETAL®; DILLEX®; DINOC®; DINURANIA®; DITROSOL®; DNOC®[C]; EFFUSAN®; EFFUSAN 3436®; ELGETOL®; ELGETOL 30®; ELIPOL®; EXTRAR®; FLAVIN-SANDOZ®; HEDOLIT®; HEDOLITE®; K III®; K IV®; KREOZAN®; KREZOTOL 50®; LIPAN®; NEUDORFF DN 50®; NITROFAN®; PROKARBOL®; RAFEX®; RAFEX 35®; RAPHATOX®; SANDOLIN®; SANDOLIN A®; SELINON®; SINOX®; WINTERWASH®
Safety Profile
Human poison by unspecified route. Experimental poison by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion and inhalation: somnolence, headache, abnormal brain recordings from specific areas of the central nervous system, cardlac and gastrointestinal changes. Mutation data reported. An e~7e and skin irritant. Less toxic than the para form, but is still highly toxic. A pesticide. See also NITRO COMPOUNDS of AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS and other dinitrocresol entries.
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; Human Data;Primary Irritant. DNOC is used as free radical polymerization inhibitor and agricultural chemical intermediate; widelyused in agriculture as an herbicide and pesticide; it is alsoused in the dyestuff industry. Although 4,6-dinitro-o-cresol(DNOC) is no longer manufactured in the United States, alimited quantity is imported and used as a blossom-thinningagent on fruit trees and as a fungicide, insecticide, and miticide, on fruit trees during the dormant season. Hence, individuals formulating or spraying the compound incur thehighest risk of exposure to the compound.
Carcinogenicity
In one chronic feeding study in rats
DNOC did not cause an increased incidence
of any type of tumor. DNOC was clastogenic,
increasing the frequency of chromosomal aberrations
both in vivo and in vitro. Conflicting
results for mutagenicity have been obtained in
bacterial assays.
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime-
weighted average (TLV-TWA) for
dinitro-o-cresol is 0.2mg/m3 with a notation
for skin absorption.
Environmental Fate
Soil/Plant. In plants and soils, the nitro groups reduced to amino groups (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). When 4,6-dinitro-o-cresol was statically incubated in the dark at 25°C with yeast extract and settled domestic wastewater inoculum, no signi?cant biodegradation and necessary acclimation for optimum biooxidation within the 4-week incubation period was observed (Tabak et al., 1981).
Chemical/Physical. 4,6-Dichloro-o-cresol will react with amines and alkali metals forming water-soluble salts which are indicative of phenols (Morrison and Boyd, 1971).
Metabolic pathway
DNOC is metabolised in soils, plants and animals via common metabolic pathways. The primary reaction is the reduction of the nitro groups to the corresponding amino-analogues. Acetylation and deamination via hydroxylation/elimination follow. N- and O-Conjugation as glucosides and glucuronides occurred in plants and animals. The metabolic pathways of DNOC are presented in Scheme 1.
Purification Methods
The cresol crystallises from aqueous EtOH. [Beilstein 6 H 369, 6 III 1276.]
Degradation
DNOC (1) is stable to hydrolytic and photolytic degradation at acidic pH and is readily degraded under alkaline conditions (Molnar, 1935).
Incompatibilities
Dust can form an explosive mixture withair. Keep away from strong oxidizers, strong bases. Protectfrom heat and shock
Properties of 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
| Melting point: | 83-85 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 196°C 1012mm |
| Density | 1.5928 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 5.2(x 10-5 mmHg) at 25 °C (Melnikov, 1971)5(x 10-5 mmHg) at 20 °C (ACGIH, 1986) |
| refractive index | 1.5460 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Solubility Sparingly soluble in water; readily soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether |
| pka | 4.42(at 25℃) |
| form | neat |
| color | Yellow prisms |
| PH Range | Colorless (2.4) to yellow (3.8) |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Merck | 3279 |
| BRN | 2054389 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.4(x 10-6 atm?m3/mol) at 25 °C (gas stripping-UV spectrophotometry, Warner et al., 1987) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 0.2 mg/m3, IDLH 5 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA 0.2 mg/m3. |
| Major Application | Explosives, fungicides, herbicides, insecticides, pesticides, antitumor agent |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 534-52-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol, 2-methyl-4,6-dinitro-(534-52-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol (534-52-1) |
Safety information for 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Methyl-4,6-dinitrophenol
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
![2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%View Details
2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%View Details
740842-50-6 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
5428-54-6 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3