2-Iodoacetamide
Synonym(s):α-Iodoacetamide - CAS 144-48-9 - Calbiochem;2-Iodoacetamide
- CAS NO.:144-48-9
- Empirical Formula: C2H4INO
- Molecular Weight: 184.96
- MDL number: MFCD00008028
- EINECS: 205-630-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-23 21:28:46
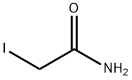
What is 2-Iodoacetamide?
Chemical properties
White solid in amber, foil sealed microtubes. Soluble in hot water, easily soluble in ethanol.
The Uses of 2-Iodoacetamide
2-Iodoacetamide is an alkylating reagent for cysteine residues in peptide sequencing. Its actions are similar to those of iodoacetate. By virtue of reaction with cysteine, it is an irreversible inhibitor of enzymes with cysteine at the active site. It reacts much more slowly with histidine residues, but that activity is responsible for inhibition of ribonuclease.
What are the applications of Application
α-Iodoacetamide is an electrophilic acetamide useful for protein modification
What are the applications of Application
Alkylating agent used in peptide mapping because it covalently binds with the thiols in cysteine to prevent disulfide bond formation 2-Iodoacetamide is used as an electrophile for covalent modification of nucleophilic residues on proteins such as cysteine, methionine and histidine. It is used to bind with thiol group of cysteine, thereby it protects the formation disulfide bonds. It is involved as an inhibitor of deubiquitinase enzymes (DUBs). Further, it acts as an alkylating sulfhydryl reagent.
Biological Activity
Iodoacetamide acts as an alkylating reagent for cysteine residues in peptide sequencing. It is an irreversible inhibitor of enzymes with cysteine at the active site. It reacts much more slowly with histidine residues, but that activity is responsible for inhibiting ribonuclease.
Synthesis
2-Iodoacetamide is synthesized by reacting chloroacetamide with sodium iodide. The chloroacetamide, anhydrous acetone, and anhydrous sodium iodide were refluxed on the bath for 15h. Cool to room temperature, filter out sodium chloride, recover acetone, pour into ice water of sodium bisulfate after a little cooling, and then neutralize to pH 6 with saturated sodium sulfate solution. Cool to crystallize and filter to obtain crude product. The crude product is recrystallized with water to obtain the finished product.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from water or CCl4. It is used for tagging proteins. [Gurd Methods Enzymol 25 424 1972, Beilstein 2 IV 536.]
Preparation and handling
Alkylation Procedure
Iodoacetamide is unstable and light-sensitive. Prepare solutions immediately before use and perform alkylation in the dark. If iodoacetamide is present in limiting quantities and a slightly alkaline pH, cysteine modification will be the exclusive reaction. Excess iodoacetamide or non-buffered iodoacetamide reagent can also alkylate amines (lysine, N-termini), thioethers (methionine), imidazoles (histidine) and carboxylates (aspartate, glutamate).
1. Add 5 μl of 2% SDS and 45 μl of 200 mM ammonium bicarbonate (pH 8.0) to 20-100 μg of protein sample. Adjust volume to 100 μl with ultrapure water.
2. Add 5 μl of 200 mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP.HCl, Product No. 20490) and incubate sample at 55°C for 1 hour.
3. Immediately before use, dissolve one tube of iodoacetamide (9.3 mg) with 132 μl of 200 mM ammonium bicarbonate (pH 8.0) to make 375 mM iodoacetamide. Protect solution from light.
4. Add 5 μl of the 375 mM iodoacetamide to the sample and incubate for 30 minutes protected from light.
5. Proceed to proteolytic digestion before MS analysis or other processing.
Precautions
Store in a cool place. Light and moisture sensitive. Keep the container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents and strong reducing agents.
Properties of 2-Iodoacetamide
| Melting point: | 92-95 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 297.1±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 2.1103 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in water, dimethyl formamide and ethanol. Slightly soluble in methanol. |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 15.16±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to pale yellow or beige |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 0.5M at 20°C, clear, colorless |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| BRN | 1739080 |
| Stability: | Stable, but light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, reducing agents, acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144-48-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Alpha-iodo acetamide(144-48-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Iodoacetamide (144-48-9) |
Safety information for 2-Iodoacetamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Iodoacetamide
| InChIKey | PGLTVOMIXTUURA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Iodo acetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
Iodo acetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 2-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
2-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 Iodoacetamide 98% CAS 144-48-9View Details
Iodoacetamide 98% CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 α-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
α-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 2-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
2-Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9 -
 Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
Iodoacetamide CAS 144-48-9View Details
144-48-9