2-Butanol
Synonym(s):sec-Butyl alcohol;2-Butanol;sec-Butyl alcohol
- CAS NO.:78-92-2
- Empirical Formula: C4H10O
- Molecular Weight: 74.12
- MDL number: MFCD00004569
- EINECS: 201-158-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:18
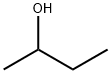
What is 2-Butanol?
Chemical properties
Colourless liquid
Physical properties
Clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a pleasant odor. Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 400 μg/m3 (120 ppbv) and 1.2 mg/m3 (410 ppbv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974).
The Uses of 2-Butanol
Preparation of methyl ethyl ketone, sol- vent, organic synthesis, paint removers, industrial cleaners.
The Uses of 2-Butanol
2-Butanol is used in the production of methylethyl ketone and sec-butyl acetate, as asolvent in lacquers and alkyd enamels, inhydraulic brake fluids, in cleaning compounds,and its xanthate derivatives in oreflotation.
The Uses of 2-Butanol
Polishes, cleaning materials, paint removers, fruit essences, perfumes, and dyestuffs; synthesis of methyl ethyl ketone; lacquer solvent
Production Methods
There are two ways to produce 2-Butanol in industry. The first is the butene hydration method. After pretreatment, n-butene is hydrated with sulfuric acid to obtain 2-Butanol, which is purified to obtain 2-Butanol. The second is the ion exchange resin hydration method, which uses n-butene as raw material, acidic cation exchange resin as catalyst, carries out liquid-phase esterification reaction with organic acid, and then undergoes hydrolysis and rectification to obtain the product.
Production Methods
2-Butanol is produced commercially by the indirect hydration of n-butenes.
What are the applications of Application
2-Butanol is a useful alcohol for proteomics research
Definition
ChEBI: A secondary alcohol that is butane substituted by a hydroxy group at position 2.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an alcohol odor. Flash point below 0 °F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Soluble in water. Moderately irritates the eyes and skin. Prolonged and repeated contact may cause defatting and drying of the skin. Vapors may irritate the nose, throat and respiratory tract. May be harmful by ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Attacks plastics. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 236]. Acetyl bromide reacts violently with alcohols or water (Merck 11th ed. 1989). Mixtures of alcohols with concentrated sulfuric acid and strong hydrogen peroxide can cause explosions. Example: An explosion will occur if dimethylbenzylcarbinol is added to 90% hydrogen peroxide then acidified with concentrated sulfuric acid. Mixtures of ethyl alcohol with concentrated hydrogen peroxide form powerful explosives. Mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and 1-phenyl-2-methyl propyl alcohol tend to explode if acidified with 70% sulfuric acid [Chem. Eng. News 45(43):73 1967; J, Org. Chem. 28:1893 1963]. Alkyl hypochlorites are violently explosive. They are readily obtained by reacting hypochlorous acid and alcohols either in aqueous solution or mixed aqueous-carbon tetrachloride solutions. Chlorine plus alcohols would similarly yield alkyl hypochlorites. They decompose in the cold and explode on exposure to sunlight or heat. Tertiary hypochlorites are less unstable than secondary or primary hypochlorites [NFPA 491 M 1991]. Base-catalysed reactions of isocyanates with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents. Such reactions in the absence of solvents often occur with explosive violence [Wischmeyer 1969].
Hazard
Toxic, mutagenic, upper respiratory tract irritant, central nervous system impairment.
Health Hazard
Exposure to 2-butanol may cause irritationof the eyes and skin. The latter effect isproduced by its defatting action on skin. Thistoxic property is mild and similar to thatof other butanol isomers. High concentrationmay produce narcosis. The narcotic effect isstronger than that of n-butanol, probably dueto the higher vapor pressure of the secondaryalcohol.
The toxicity is lower than that of itsprimary alcohol analogue.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 6480 mg/kg.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. See also nBUTYL ALCOHOL and ALCOHOLS. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Auto-oxidizes to an explosive peroxide. Ignites on contact with chromium trioxide. To fight fire, use water spray, alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Potential Exposure
Butyl alcohols are used as solvents for paints, lacquers, varnishes, natural and synthetic resins, gums, vegetable oils, dyes, camphor, and alkaloids. They are also used as an intermediate in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and chemicals; in the manufacture of artificial leather, safety glass; rubber and plastic cements, shellac, raincoats, photographic films, perfumes; and in plastic fabrication.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Bridié et al. (1979) reported BOD and COD values of 2.15 and 2.49 g/g using
filtered effluent from a biological sanitary waste treatment plant. These values were determined
using a standard dilution method at 20 °C for a period of 5 d. The ThOD for sec-butyl alcohol is
2.59 g/g. In activated sludge inoculum, following a 20-d adaptation period, 98.5% COD removal
was achieved. The average rate of biodegradation was 55.0 mg COD/g?h (Pitter, 1976).
Photolytic. The estimated half-life of sec-butyl alcohol for the reaction of OH radicals in air
ranges from 129 d to 23 yr (Anbar and Neta, 1967).
Chemical/Physical. sec-Butyl alcohol will not hydrolyze in water because it does not contain a
hydrolyzable group (Kollig, 1993).
Shipping
UN1120 Butanols, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3— Flammable liquid. UN1212 Isobutanol or Isobutyl alcohol, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3—Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
Purification methods are the same as for n-Butanol. These include drying with K2CO3 or CaSO4, followed by filtration and fractional distillation, refluxing with CaO, distillation, then refluxing with magnesium and redistillation, and refluxing with, then distilling from CaH2. Calcium carbide has also been used as a drying agent. The anhydrous alcohol is obtained by refluxing with sec-butyl phthalate or succinate. (For method see Ethanol.) Small amounts of alcohol can be purified via conversion to the alkyl hydrogen phthalate and recrystallisation [Hargreaves J Chem Soc 3679 1956]. For purification of optical isomers, see Timmermans and Martin [J Chem Phys 25 411 1928]. [Beilstein 2 III 1566.]
Incompatibilities
Butyl alcohols may form explosive mixture with air. In all cases they are Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. n-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids; halogens, caustics, alkali metals; aliphatic amines; isocyanates. sec-Butanol forms an explosive peroxide in air. Ignites with chromium trioxide. Incompatible with strong oxidizers; strong acids; aliphatic amines; isocyanates, organic peroxides. tert-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids (including mineral acid), including mineral acids; strong oxidizers or caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals (i.e., lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, francium). isoButanol is incompatible with strong acids; strong oxidizers; caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals and alkali earth. May react with aluminum at high temperatur
Waste Disposal
Incineration, or bury absorbed waste in an approved land fill.
Properties of 2-Butanol
| Melting point: | −115 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 98 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.808 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 12.5 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 80 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 125g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Colorless |
| Odor | Strong, pleasant. |
| Relative polarity | 0.506 |
| PH Range | 7 |
| explosive limit | 1.4-9.8%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.22ppm |
| Water Solubility | 12.5 g/100 mL (20 ºc) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1541 |
| BRN | 1718765 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.19 (static headspace-GC, Merk and Riederer, 1997) |
| Dielectric constant | 15.8(25℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 450 mg/m3 (150 ppm) (NIOSH),
305 mg/m3 (100 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH
10,000 ppm. |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Substances to be avoided include acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents and halogens. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-92-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Butanol(78-92-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Butanol (78-92-2) |
Safety information for 2-Butanol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P242:Use only non-sparking tools. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Butanol
| InChIKey | BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
2-Butanol manufacturer
Antares Chem Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
2-Butanol, H<sub>2</sub>O <0.01% CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 sec-Butyl Alcohol extrapure CAS 78-92-2View Details
sec-Butyl Alcohol extrapure CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 sec-Butyl Alcohol extrapure AR CAS 78-92-2View Details
sec-Butyl Alcohol extrapure AR CAS 78-92-2View Details
78-92-2 -
 2 Butanol CASView Details
2 Butanol CASView Details -
 2-Butanol CASView Details
2-Butanol CASView Details
