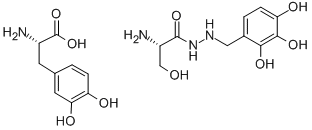
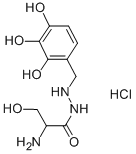
2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide
- CAS NO.:322-35-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H15N3O5
- Molecular Weight: 257.24
- MDL number: MFCD00242633
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
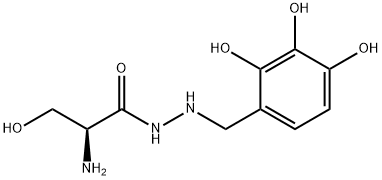
What is 2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide?
Absorption
In a study, three patients were administered 50 mg of radiolabelled 14C-benserazide by both intravenous and oral routes . Three additional patients received oral doses of 50 mg 14C-benserazide alone . Comparison of the time-plasma concentration curves of total radioactivity in the patients receiving oral and intravenous 14C-benserazide indicated that between 66% and 74% of the administered dose was absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract . Peak plasma concentrations of radioactivity were detected one hour after oral administration in five of the six patients .
Toxicity
Overdosage may lead to cardiovascular side effects like cardiac arrhythmias, psychiatric disturbances like confusion and insomnia, gastrointestinal effects like nausea and vomiting, and abnormal involuntary movements .
Various LD50 values have been established for the rat model, including an oral LD50 of 5300 mg/kg in rats .
Originator
Madopar,Roche,Italy,1974
The Uses of 2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide
Inhibitor (decarboxylase).
Background
When levodopa is used by itself as a therapy for treating Parkinson's disease, its ubiquitous metabolism into dopamine is responsible for a resultant increase in the levels of circulating dopamine in the blood and to various extracerebral tissues. This can result in a number of side effects like nausea, vomiting, or even cardiac arrhythmias that may diminish patient adherence . A decarboxylase inhibitor like benserazide is consequently an effective compound to combine with levadopa as it is incapable of crossing the blood-brain barrier itself but acts to prevent the formation of dopamine from levadopa in extracerebral tissues - thereby acting to minimize the occurrence of extracerebral side effects .
Levodopa/benserazide combination products are used commonly worldwide for the management of Parkinson's disease. In particular, although the specific levodopa/benserazide combination is formally approved for use in Canada and much of Europe, the FDA has approved another similar levodopa/dopa decarboxylase inhibitor combination in the form of levodopa and carbidopa.
Moreover, the European Medcines Agency has conferred an orphan designation upon benseraside since 2015 for its potential to be used as a therapy for beta thalassaemia as well .
Indications
The primary therapeutic use for which benserazide is currently indicated for is as a combination therapy with levadopa for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in adults > 25 years of age, with the exception of drug-induced parkinsonism .
At certain doses, the combination product of levodopa and benserazide may also be used to treat restless legs syndrome, which is sometimes associated with Parkinson's disease .
There have also been some studies that have prompted the European Medicines Agency to confer orphan designation upon benserazide hydrochloride as a potential therapy for beta thalassaemia . Although studies are ongoing, no evidence has been formally elucidated as of yet .
Definition
ChEBI: A carbohydrazide that results from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of DL-serine with the primary amino group of 4-(hydrazinylmethyl)benzene-1,2,3-triol. An aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase nhibitor (DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor) that does not enter the central nervous system, it is used as its hydrochloride salt as an adjunct to levodopa in the treatment of parkinsonism. By preventing the conversion of levodopa to dopamine in the periphery, t causes an increase in the amount of levodopa reaching the central nervous system and so reduces the required dose. Benserazide has no antiparkinson actions when given alone.
Manufacturing Process
35.5 grams of DL-seryl-hydrazide hydrochloride was dissolved in 350 ml of
water and 35 grams of pyrogallolaldehyde (2,3,4-trihydroxy-benzaldehyde)
added thereto at one time. In about 5-10 minutes a clear solution resulted,
whereupon slow crystallization occurred and the temperature rose to about
6°-7°C. The crystallization was permitted to continue overnight at 5°C, and
the very fine precipitate was then isolated by centrifugation and in the
centrifuge washed with water, ethanol, and ether, yielding the dihydrate of DLseryl-(
2,3,4-trihydroxy-benzylidene) hydrazide hydrochloride, which melted at
134°-136°C and was poorly soluble in cold water, but very readily dissolved in
hot water. The condensation was also effected in absolute ethanol yielding the
anhydrous form of the hydrazone, which melted at 225°-228°C.
33.5 grams of the hydrazone-dihydrate was suspended in 330 ml of methanol
and hydrogenated with 2.5 grams of palladium-carbon. After the absorption of
2.8 liters of hydrogen, the catalyst was filtered off and the solution evaporated
in vacuo to a weight of about 52-55 grams. It was then immediately mixed
with 160 ml of absolute ethanol and permitted to crystallize for 24 hours at
room temperature and then for a further 24 hours at 0°C. The product was
then filtered off with suction and washed with absolute ethanol and absolute
ether. The so-obtained DL-seryl-(2,3,4-trihydroxy-benzyl)-hydrazide
hydrochloride formed a white crystalline powder which was readily soluble in
water and which melted at 146°-148°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antiparkinsonian
Pharmacokinetics
When used as a therapy for treating Parkinson's disease, levadopa's specific mechanism of action revolves around its metabolism into dopamine in the body . Unfortunately, the resultant increase in the levels of circulating dopamine in the blood and to various extracerebral tissues can result in a number of side effects like nausea, vomiting, or even cardiac arrhythmias that may diminish patient adherence . A decarboxylase inhibitor like benserazide is consequently an effective compound to combine with levadopa as it is incapable of crossing the blood-brain barrier itself and therefore allows levadopa to elicit its primary action in the central nervous system, but will prevent the formation of dopamine from levadopa in extracerebral tissues - thereby acting to minimize the occurrence of extracerebral side effects .
Metabolism
Benserazide is hydroxylated to trihydroxybenzylhydrazine in the intestinal mucosa and the liver . Trihydroxybenzylhydrazine is a potent inhibitor of the aromatic acid decarboxylase , and it is believed that the levodopa in a levodopa/benserazide combination product is largely protected against decarboxylation mainly by way of this benserazide metabolite .
Properties of 2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide
| Boiling point: | 574.2±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.541±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 9.40±0.40(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 322-35-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for 2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide
Computed Descriptors for 2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide
2-Amino-3-hydroxy-2'-(2,3,4-trihydroxybenzyl)propionohydrazide manufacturer
VIVAN Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Benserazide 98%View Details
Benserazide 98%View Details -
 Benserazide 98%View Details
Benserazide 98%View Details -
 Benserazide 99%View Details
Benserazide 99%View Details
322-35-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1