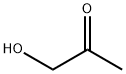
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
Synonym(s):1,3-Dihydroxidimethyl ketone, DHA, 1,3-Dihydroxidimethyl ketone;Dihydroxyacetone
- CAS NO.:96-26-4
- Empirical Formula: C3H6O3
- Molecular Weight: 90.08
- MDL number: MFCD00004670
- EINECS: 202-494-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 12:07:08
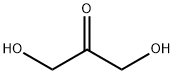
What is 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone?
Chemical properties
white powder
Chemical properties
Dihydroxyacetone has a characteristic sweet, cooling aroma.
Occurrence
A derivative of naturally occurring starch
The Uses of 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone can be used as artificial tanning agent.
The Uses of 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is a self-tanning agent used in cosmetics designed to provide a tanned appearance without the need for sun exposure. It is also a uV protector and a color additive. As a self-tanning agent, it reacts with amino acids found on the skin’s epidermal layer. Its effects last only a few days as the color it provides fades with the natural shedding of the stained cells. Reportedly, it works best on slightly acidic skin. DHA, when combined with lawsone, becomes an FDA Category I (approved) uV protectant. In 1973, the FDA declared that DHA is safe and suitable for use in cosmetics or drugs that are applied to color the skin, and has exempted it from color additive certification.
The Uses of 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
These Secondary Standards are qualified as Certified Reference Materials. These are suitable for use in several analytical applications including but not limited to pharma release testing, pharma method development for qualitative and quantitative analyses, food and beverage quality control testing, and other calibration requirements.
Definition
ChEBI: Dihydroxyacetone is a ketotriose consisting of acetone bearing hydroxy substituents at positions 1 and 3. The simplest member of the class of ketoses and the parent of the class of glycerones. It has a role as a metabolite, an antifungal agent, a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a ketotriose and a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone.
Preparation
1,3-dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is prepared by acetalization, oxidation, and hydrolysis of glycerol. Usually produced commercially from Bacillus macerans or Bacillus circulans fermentation of starch or starch hydrolysate
Taste threshold values
Reported to have a taste threshold value lower than that of sucrose with a detection level of 3.9 to 27 ppm and a recognition level of 11 to 52 ppm.
General Description
Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is a browning ingredient widely used in cosmetics such as sunless tanning formulations. It participates in a chemical staining reaction called Milliard reaction in which it reacts with the amino groups of proteins to result in a mixture of high molecular weight pigments.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. When heated to decompositionit emits acrid smoke and irritating vapors.
Safety
Cells that were treated with 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) showed dose- and time-dependent changes that included cytoplasmic budding, chromatin condensation, and cell detachment. There was a significant decrease in cell proliferation after 24 hours of DHA exposure. After exposure to a 5% DHA solution for 21 days, epidermal thickening and dermatitis of the skin were noted in laboratory animals. After 42 days of treatment with the same solution, hyperplastic and dyskeratotic changes and moderate inflammatory reactions were seen. Long-lasting topical tanning products contain the sugars DHA or erythrulose, which cause a "Maillard reaction" when contacting proteins in the outer layers of the stratum corneum and epidermis. This reaction happens when free amino acids from skin proteins combine with DHA in the stratum corneum. This combination creates the tanned appearance of skin. Results are generally seen within a few hours of application. UV light exposure is not needed to initiate this chemical reaction[1].
References
[1] Gallagher, Mary. “Exposureto Dihydroxyacetone in Sunless Tanning Products.”Journal of the Dermatology Nurses'Association 10(1): 11-17.
Properties of 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
| Melting point: | 75-80 °C |
| Boiling point: | 107.25°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1385 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0.002-0.33Pa at 20-50℃ |
| refractive index | 1.4540 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 4033 | DIHYDROXYACETONE |
| storage temp. | Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
| solubility | >112.4 mg/mL in DMSO; >5.09 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
| form | powder |
| pka | 12.45±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. minty |
| Water Solubility | >250 g/L (20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 1716 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 96-26-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Propanone, 1,3-dihydroxy-(96-26-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Propanone, 1,3-dihydroxy- (96-26-4) |
Safety information for 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Dihydroxy Acetone 98%View Details
Dihydroxy Acetone 98%View Details -
 96-26-4 Dihydroxy Acetone 98%View Details
96-26-4 Dihydroxy Acetone 98%View Details
96-26-4 -
 1,3-Dihydroxyacetone, 98% 99%View Details
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone, 98% 99%View Details
96-26-4 -
 Dihydroxyacetone, 98% CAS 96-26-4View Details
Dihydroxyacetone, 98% CAS 96-26-4View Details
96-26-4 -
 Dihydroxyacetone CAS 96-26-4View Details
Dihydroxyacetone CAS 96-26-4View Details
96-26-4 -
 1 3 DihydroxyacetoneView Details
1 3 DihydroxyacetoneView Details
96-26-4 -
 1 3 DihydroxyacetoneView Details
1 3 DihydroxyacetoneView Details
96-26-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
