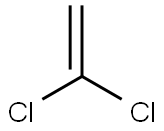
1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
Synonym(s):1,2-Dichloroethene in DMSO;1,2-Dichloroethene solution
- CAS NO.:540-59-0
- Empirical Formula: C2H2Cl2
- Molecular Weight: 96.94
- MDL number: MFCD00062942
- EINECS: 208-750-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18

What is 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE?
Description
Acetylene dichloride is a colourless liquid (usually a mixture of the cis and trans isomers) with a slightly acrid, chloroform-like odour. Acetylene dichloride is a chemical used mainly in the production of perfumes, dyes, and thermoplastics. The type and severity of symptoms varies depending on the amount of chemical involved and the nature of the exposure. It is incompatible with strong oxidisers, strong alkalis, potassium hydroxide, and copper. Acetylene dichloride is highly flammable and in a fire gives off irritating or toxic fumes/gases. (Acetylene dichloride usually contains inhibitors to prevent polymerisation.)
Chemical properties
clear colorless to pale yellow liquid
Chemical properties
Acetylene dichloride is a colorless liquid (usually a mixture of the cis and trans isomers) with a slightly acrid, chloroform-like odor. It is incompatible with strong oxidizers, strong alkalis, potassium hydroxide, and copper. Acetylene dichloride is highly flammable and in a fi re gives off irritating or toxic fumes/gases. (Acetylene dichloride usually contains inhibitors to prevent polymerization.)
Chemical properties
1,2-Dichloroethylene exists in three isomers, sym-, cis-60% and trans-40%. There are variations in toxicity between these two forms. At room temperature, these chemicals are colorless liquids with a slightly acrid, ethereal odor. The Odor Threshold in air is 17 ppm. sym-isomer:
The Uses of 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
1,2-Dichloroethylene is used as a solvent for organic materials and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chlorinated compounds; it may be produced by the chlorination of acetylene but is often produced as a by-product in the manufacture of other chlorinated compounds.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with ether-like odor. Mixture of cis and trans isomers. Flashpoint 36 - 43° F. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE is sensitive to air, light and moisture. Heat contributes to instability. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE reacts violently with sodium, sodium hydroxide, copper and copper alloys. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE can react with caustic alkynes or their concentrated solutions. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE forms explosive mixtures with N2O4. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE is incompatible with strong oxidizers. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE is corrosive to metals. 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE attacks some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes nausea, vomiting, weakness, tremor, epigastric cramps, central nervous depression. Contact with liquid causes irritation of eyes and (on prolonged contact) skin. Ingestion causes slight depression to deep narcosis.
Health Hazard
Exposures to acetylene dichloride cause irritation to the eyes, respiratory system, and CNS depression with symptoms of cough, sore throat, dizziness, nausea, drowsiness, weakness, unconsciousness, and vomiting. It involves the eyes, respiratory system, and the CNS as the target organs. Prolonged periods of exposure to acetylene dichloride defats the skin and may have effects on the liver.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Will not occur under ordinary conditions of shipment. The reaction is not vigorous; Inhibitor of Polymerization: None used.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of Cl-. See also ACETYLENE COMPOUNDS, and CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS, ALIPHATIC .
Potential Exposure
Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction). 1,2-Dichloroethylene is used as a solvent for waxes, resins, and acetylcellulose. It is also used in the extraction of rubber, as a refrigerant; in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and artificial pearls; and in the extraction of oils and fats from fish and meat.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
In genotoxic assays the cis isomer induced
chromosomal aberrations in mouse bone
marrow cells after intraperitoneal injections.7
Neither isomer was mutagenic in bacterial
assays, nor did they produce chromosomal
aberrations or sister chromatid exchanges in
mammalian cells in vitro.
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime-
weighted average (TLV-TWA) for 1,2-
dichloroethylene is 200ppm (793mg/m3).
Storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with 1,2-DCE you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Before entering confined spacewhere this chemical may be present, check to make surethat an explosive concentration does not exist. 1,2-Dichloroethylene must be stored to avoid contact withstrong oxidizers (such as chlorine, bromine, and fluorine)since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat.Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, areprohibited where 1,2-dichloroethylene is used, handled, orstored. Metal containers involving the transfer of=gallonsor more of 1,2-dichloroethylene should be grounded andbonded. Drums must be equipped with self-closing valves,pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially when opening andclosing containers of 1,2-dichloroethylene. Wherever 1,2-dichloroethylene is used, handled, manufactured, or stored,use explosion-proof electrical equipment and fittings.
Shipping
UN1150 Dichloroethylene, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Shake it successively with conc H2SO4, water, aqueous NaHCO3 and water. Dry it with MgSO4 and fractionally distil it to separate the cis-and trans-isomers. [Beilstein 1 IV 707-709.]
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Attacks some plastics, rubber, and coatings. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides. Gradual decomposition results in hydrochloric acid formation in the presence of ultraviolet light or upon contact with hot metal or other hot surfaces. Reacts with strong bases; potassium hydroxide; difluoromethylene, dihypofluoride, nitrogen tetroxide (explosive); or copper (and its alloys) producing toxic chloroacetylene which is spontaneously flammable on contact with air. Attacks some plastics and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≧100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
| Melting point: | −57 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 48-60 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.265 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 5.32 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 43 °F |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), Chloroform (Soluble) |
| form | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Ethereal, slightly acrid; pleasant, chloroform-like. |
| Merck | 13,94 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.6(17℃) |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Volatile |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,2-Dichloroethylene (540-59-0) |
Safety information for 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1,2-Dichloroethylene, mixture of cis and trans CAS 540-59-0View Details
1,2-Dichloroethylene, mixture of cis and trans CAS 540-59-0View Details
540-59-0 -
 Residual Solvent Class 2 - 1,2-Dichloroethene CAS 540-59-0View Details
Residual Solvent Class 2 - 1,2-Dichloroethene CAS 540-59-0View Details
540-59-0 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6