(±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid
Synonym(s):(±)-γ-Vinyl-GABA;(±)-4-Aminohexenoic acid;(R,S)-4-Amino-5-hexenoic acid
- CAS NO.:68506-86-5
- Empirical Formula: C6H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 129.16
- MDL number: MFCD00274577
- EINECS: 270-929-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:55:07
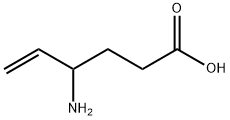
What is (±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid?
Absorption
Absorption following oral administration is essentially complete. The Tmax is approximately 2.5 hours in infants (5m - 2y) and 1 hour in all other age groups.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of vigabatrin in mice and rats is 2830 mg/kg and 3100 mg/kg, respectively. Symptoms of overdose tend to involve significant CNS depression - e.g. coma, unconsciousness, and/or drowsiness - with less common symptoms including neurologic disorders (e.g. seizure activity, speech disorder, headache) and psychiatric sequelae (e.g. psychosis, agitation, abnormal behaviour, confusion).
In cases of overdose, symptoms generally resolve with symptomatic and supportive care. Standard measures to remove unabsorbed drug may be employed (e.g. gastric lavage), although an in vitro study found that activated charcoal did not significantly absorb vigabatrin. Although vigabatrin is not protein-bound, the effectiveness of hemodialysis in drug removal during overdose is unknown - isolated reports of patients in renal failure undergoing hemodialysis who were receiving therapeutic doses of vigabatrin note a reduction in vigabatrin plasma concentrations of 40-60% following dialysis.
The Uses of (±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid
rac-Vigabatrin a novel antiepileptic drug. Antidepressant; antipsychotic; anxiolytic.
Indications
Vigabatrin is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of refractory complex partial seizures in patients 2 years of age and older who have had inadequate responses to multiple previous treatments (i.e. not to be used for first-line therapy). It is also indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of infantile spasms in patients between 1 month and 2 years of age for whom the potential benefits outweigh the risk of vision loss.
Background
Vigabatrin is an analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, used in the treatment of refractory seizures and infantile spasms. It irreversibly inhibits the enzyme responsible for GABA metabolism, thereby increasing levels of circulating GABA. Although administered as a racemic mixture, only the S(+) enantiomer is pharmacologically active.
It was first introduced as an antiepileptic agent in the United Kingdom in 1989 and was used extensively until 1997, when an association with vision loss became apparent. Its use is now generally reserved for patients who have failed alternative therapies, and its US approval by the FDA in 2009 mandated the creation of a drug registry to monitor patients for visual deficits.
Definition
ChEBI: Vigabatrin is a gamma-amino acid having a gamma-vinyl GABA structure. It is an irreversible inhibitor of gamma-aminobutyric 664 acid transaminase It has a role as an anticonvulsant and an EC 2.6.1.19 (4-aminobutyrate--2-oxoglutarate transaminase) inhibitor.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Irreversible GABA transaminase inhibitor. Increases intracellular concentration of GABA in nerve endings; possesses antiepileptic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Vigabatrin is an antiepileptic agent chemically unrelated to other anticonvulsants. Vigabatrin prevents the metabolism of GABA by irreversibly inhibiting GABA transaminase (GABA-T). As vigabatrin is an irreversible inhibitor of gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase (GABA-T), its duration of effect is thought to be dependent on the rate of GABA-T re-synthesis rather than on the rate of drug elimination.
Metabolism
Vigabatrin is not metabolized to any significant extent.
storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of (±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid
| Melting point: | 209℃ |
| Boiling point: | 277.7±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.064±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.36±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water |
Safety information for (±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for (±)-4-aminohex-5-enoic acid
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Vigabatrin 95.00% CAS 68506-86-5View Details
Vigabatrin 95.00% CAS 68506-86-5View Details
68506-86-5 -
 Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
68506-86-5 -
 Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
68506-86-5 -
 Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
Vigabatrin CAS 68506-86-5View Details
68506-86-5 -
 7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 -
 1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 -
 N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
5434-30-0