EPA
Synonym(s):CLGI;EPA;EPO;Timnodonic acid;TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1
- CAS NO.:25378-27-2
- Empirical Formula: C20H30O2
- Molecular Weight: 302.45
- MDL number: MFCD00065716
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06

What is EPA?
Description
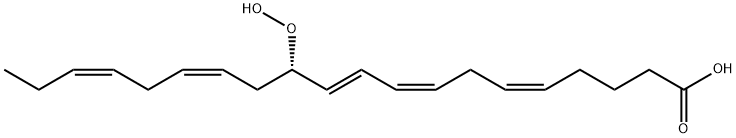
Eicosa pentaenoic acid ( EPA or also icosapentaenoic acid ) is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and five cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end.
EPA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that acts as a precursor for prostaglandin-3 (which inhibits platelet aggregation), thromboxane-3, and leukotriene-5 groups (all eicosanoids).
Description
5,8,11,14,17-Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is a straight-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid whose double bonds all have the cis configuration. E. Klenk and D. Eberhagen isolated EPA from cod-liver oil in 1957. It is a biochemical precursor to the prostaglandin-3, thromboxane-3, and leukotriene-5 lipid families.
The supply of marine fish as the main source of EPA and other so-called omega-3 fatty acids is limited and unsustainable. Recently,?Q. Zhu and co-workers at DuPont engineered?Yarrowia lipolytica, an oleaginous yeast that accumulates lipids, to produce large amounts of EPA. These researchers believe that other?Y. lipolytica?strains may be able to produce other fatty acids and lipids for uses such as biodiesel fuel.
?
Occurrence
It is obtained in the human diet by eating oily fish or fish oil — e.g., cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon, menhaden and sardine, and various types of edible seaweed. It is also found in human breast milk.
However, fish do not naturally produce EPA, but obtain it from the algae they consume. It is available to humans from some non - animal sources (e.g., commercially, from microalgae). Microalgae are being developed as a commercial source. EPA is not usually found in higher plants, but it has been reported in trace amounts in purslane.
The human body converts alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) to EPA. ALA is itself an essential fatty acid, an appropriate supply of which must be ensured. The efficiency of the conversion of ALA to EPA, however, is much lower than the absorption of EPA from food containing it. Because EPA is also a precursor to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), ensuring a sufficient level of EPA on a diet containing neither EPA nor DHA is harder both because of the extra metabolic work required to synthesize EPA and because of the use of EPA to metabolize DHA. Medical conditions like diabetes or certain allergies may significantly limit the human body's capacity for metabolization of EPA from ALA.
The Uses of EPA
eicosapentaenoic acid is also known as ePA. With emollient and skin-conditioning properties, this omega-3 fatty acid helps repair and maintain the skin barrier functions. It is said to improve the structure and function of the skin cell membrane. In addition, it may also have anti-irritant and anti-inflammatory properties.
brand name
Decabid (Lilly).
Properties of EPA
| Melting point: | −54-−53 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.943 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| form | liquid |
Safety information for EPA
Computed Descriptors for EPA
EPA manufacturer
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
Glyra Health Care Pvt Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 Icosapent ethyl 99%View Details
86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 Icosapent ethyl 99%View Details
86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 -
 86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 98%View Details
86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 98%View Details
86227-47-6 / 73310-10-8 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1