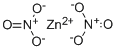CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Zinc nitrate is a colorless crystalline solid. Noncombustible, but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving this material. It is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of other chemicals, in medicine, and in dyes. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White powder |
| Melting Point | 97 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Solubility | SOLUBILITY: 184.3 G/100 CC WATER @ 20 °C /HEXAHYDRATE/ |
| Density | 2.07 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomp it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and zinc oxide/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | COLORLESS LUMPS; LOSES WATER OF CRYSTALLIZATION BETWEEN 105 & 131 °C /HEXAHYDRATE/ |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 189.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 187.904778 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 187.904778 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 126 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 18.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Zinc nitrate is a colorless crystalline solid. Noncombustible, but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving this material. It is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of other chemicals, in medicine, and in dyes.