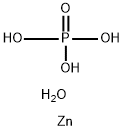
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Dry Powder; Dry Powder, Liquid, Other Solid; Liquid; Liquid, Other Solid; Water or Solvent Wet Solid |
|---|---|
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Phosphates, Metallic Salts |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 386.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 383.69116 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 381.69427 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 173 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 36.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Zinc phosphate is a phosphate of zinc. It is found naturally as the minerals hopeite, parahopeite, and tarbuttite. Zinc phosphate is used as a dental cement and corrosion resistant coating. Zinc is a metallic element with the atomic number 30. It is found in nature most often as the mineral sphalerite. Though excess zinc in harmful, in smaller amounts it is an essential element for life, as it is a cofactor for over 300 enzymes and is found in just as many transcription factors. (L48, L49, L74) Zinc phosphate (Zn3(PO4)2) is an inorganic chemical compound used as a corrosion resistant coating on metal surfaces either as part of an electroplating process or applied as a primer pigment (see also red lead). Zinc phosphate coats better on a crystalline structure than bare metal, so a seeding agent is often used as a pre-treatment. One common agent is sodium pyrophosphate.