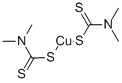
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
Synonym(s):Dimethyldithiocarbamic acid zinc salt;Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate;Ziram
- CAS NO.:137-30-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H12N2S4Zn
- Molecular Weight: 305.83
- MDL number: MFCD00064797
- EINECS: 205-288-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
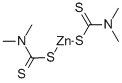
What is Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate?
Chemical properties
White and odorless when pure. Almost insoluble inwater; soluble in acetone, carbon disulfide, chloroform, dilute alkalies, and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
The Uses of Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
Zinc Dimethyldithiocarbamate is a member of a class of dithiocarbamates, and has been used in agriculture as a fungicide and in the rubber industry as a vulcanization accelerator.
The Uses of Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
Rubber vulcanization accelerator; agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
Ziram is a protective fungicide applied to foliage to control diseases on pome fruit, stone fruit, nuts, vines, vegetables and ornamentals. It is used to control scab in apples and pears and Monilia, Alternaria, Septoria, peach leaf curl, shot hole, rusts, black rot and anthracnose. It is also used as a wildlife repellent, smeared as a paste onto tree trunks or sprayed onto ornamentals, dormant fruit trees and other crops.
Definition
ChEBI: A dithiocarbamate salt that is the zinc salt of dimethyldithiocarbamic acid. It is a broad-spectrum fungicide and bird and animal repellent that is also used to accelerate the vulcanisation of rubber.
Air & Water Reactions
Thio and dithiocarbamates slowly decompose in aqueous solution to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate is a dithiocarbamate. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides. Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate is corrosive to iron and copper. Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and acids. Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate is also incompatible with mercury.
Hazard
Strong irritant to eyes and mucous membranes.
Fire Hazard
Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate is combustible. Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate may form explosive dust-air mixtures.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Microbiocide, Animal repellant: Ziram is an agricultural fungicide registered to control fungal diseases on a wide range of crops including stone fruits, pome fruits, nut crops, vegetables and commercially grown ornamentals, and as a soil and seed treatment. In addition, it is formulated as a bird and rabbit repellent for outdoor foliar applications to ornamentals. Registered for use in EU countries . Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
AAPROTECT®; AAVOLEX®; AAZIRA®; ACCELERATOR®-L; ACCELERATOR® MZ® Powder; ACETO ZDED®; ACETO ZDMD®; ALCOBAM ZM®; ANCANZATE ME®; CARBAZINC®; CIRAM®; CORONA COROZATE®; COROZATE®; CUMAN®; CUMAN L®; CYMATE®; DRUPINA® 90; EPTAC-1®; FUCLASIN®; FUCLASIN® ULTRA; FUKLASIN®; FUNGOSTOP®; HERMAT ZDM®; HEXAZIR®; KARBAM WHITE®; KYPZIN®; METHASAN®; METHAZATE®; MEXENE®; MEZENE®; MILBAM®; MILBAN®; MOLURAME®; MYCRONIL®; OCTOCURE ZDM-50®; ORCHARD® BRAND ZIRAM; PERKACIT ZDMC®; POMARSOL® Z FORTE; PRODARAM®; PROKIL® Ziram; RHODIACID®; SOXINAL®-PZ; SOXINOL®-PZ; TRICARBAMIX Z®; TSIMAT®; TSIRAM® (Russian); ULTRA ZINC DMC®; VANCIDE® MZ-96; VANCIDE® 51Z Dispersion (with Zinc 2-mercaptobenzothiazolate); VANCIDE® 51Z Dispersion (with Ziram); ZERLATE®; ZINCMATE®; ZIMATE®; ZIMATE®; METHYL®; ZIRAMVIS®; ZIRASAN®; ZIRBERK®; ZIREX 90®; ZIRIDE®; ZIRTHANE®; ZITOX®
Contact allergens
Ziram is a rubber vulcanization accelerator of the dithiocarbamate group. Sensitization was reported in several patients. Ziram is also used as a fungicide and can cause contact dermatitis in agricultural workers.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion,intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxicby inhalation. Questionable carcinogen with experimentalcarcinogenic and tumorigenic data. An experimentalteratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects.Human mutation d
Metabolic pathway
Ziram is one of the metal containing dithiocarbamates which generates dimethyldithiocarbamic acid by being cleaved in acidic conditions and in biological media. The resulting acid is conjugated with glucose and alanine in plants and with glucuronic acid in mammals. Dimethyldithiocarbamic acid is further degraded to dimethylamine and CS2. An extensive review of the properties of dithiocarbamate pesticides was published by the World Health Organisation (WHO, 1988) from which much of the following information is taken.
Purification Methods
Crystallise this herbicide several times from hot toluene or from hot CHCl3 by addition of EtOH. [Beilstein 4 III 149, 4 IV 234.]
Degradation
Ziram is decomposed in acidic media and by UV irradiation (PM). Ziram is stable in alkaline media but unstable in acidic conditions, decomposing to dimethylamine and carbon disulfide.
Properties of Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
| Melting point: | 248-257 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 335.83℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
| Density | 1.66 |
| vapor pressure | <1 x 10-6 Pa |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | DMSO (Sparingly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.71 |
| Odor | odorless when pure |
| Water Solubility | 0.0065 g/100 mL |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
| Merck | 14,10172 |
| BRN | 3707008 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 137-30-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Zinc, bis(dimethylcarbamodithioato-s,s')-, (t-4)-(137-30-4) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 53) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ziram (137-30-4) |
Safety information for Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate
| InChIKey | DUBNHZYBDBBJHD-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 137-30-4 Ziram 98%View Details
137-30-4 Ziram 98%View Details
137-30-4 -
 137-30-4 99%View Details
137-30-4 99%View Details
137-30-4 -
 Ziram 98%View Details
Ziram 98%View Details
137-30-4 -
 Zinc Dimethyl Dithiocarbamate 99%View Details
Zinc Dimethyl Dithiocarbamate 99%View Details -
 Zinc Dimethyldithiocarbamate CAS 137-30-4View Details
Zinc Dimethyldithiocarbamate CAS 137-30-4View Details
137-30-4 -
 Ziram CAS 137-30-4View Details
Ziram CAS 137-30-4View Details
137-30-4 -
 Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate CAS 137-30-4View Details
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate CAS 137-30-4View Details
137-30-4 -
 Zinc Dimethyl Dithiocarbamate, Bag, 25 kgView Details
Zinc Dimethyl Dithiocarbamate, Bag, 25 kgView Details
137-30-4
