Vorinostat
- CAS NO.:149647-78-9
- Empirical Formula: C14H20N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 264.32
- MDL number: MFCD00945317
- EINECS: 682-505-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
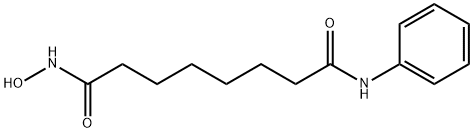
What is Vorinostat?
Description
Vorinostat is the first drug in a new class of anti-cancer agents that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). It was launched as an oral treatment for cutaneous manifestations in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) who have progressive, persistent, or recurrent disease on or following two systemic therapies. HDACs are enzymes that catalyze the removal of the acetyl modification on lysine residues of proteins, including the core nucleosomal histones. Together with their counterpart histone acetyltransferases (HATs), HDACs regulate the acetylation level of the histones, which plays an important role in the regulation of chromatin plasticity and gene transcription. Hypoacetylation of histones is associated with a condensed chromatin structure resulting in the repression of gene transcription, whereas acetylated histones are associated with a more open chromatin structure and activation of transcription. In some cancer cells, there is an overexpression of HDACs, resulting in hypoacetylation of histones. Inhibitors of HDAC are thought to transcriptionally reactivate dormant tumor-suppressor genes by allowing for the accumulation of acetyl groups on histones and an open chromatin structure. Vorinostat inhibits the enzymatic activity of HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, and HDAC6 at nanomolar concentrations (IC50 <86 nM). In vitro, it induces growth arrest, differentiation or apoptosis in a variety of tumor cells. In addition, vorinostat inhibits tumor growth in animal models bearing solid tumors, including breast, prostate, lung and gastric cancers, as well as hematologic malignancies such as multiple myeloma and leukemias.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Columbia University (US)
The Uses of Vorinostat
A potent, selective, cell permeable histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDAC). Displays anti-angiogenic activity by interfering with VEGF signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Induces differentiation in uman breast cancer cells.
The Uses of Vorinostat
antineoplastic, histone deacetylase inhibitor
The Uses of Vorinostat
Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid is a potent, selective, cell permeable histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDAC). Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid displays anti-angiogenic activity by interfering with VEGF signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid induces differentiation in uman breast cancer cells.
The Uses of Vorinostat
A potent HDAC inhibitor; also causes cell cycle arrest at G1
The Uses of Vorinostat
Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor from Merck, was approved for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Vorinostat was shown to inhibit HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC6 at nanomolar concentrations. HDAC inhibitors are potent differentiating agents toward a variety of neoplasms, including leukemia and breast and prostate cancers.
What are the applications of Application
Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid is a potent HDAC inhibitor; also causes cell cycle arrest at G1
Background
Vorinostat (rINN) or suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), is a drug currently under investigation for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), a type of skin cancer, to be used when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after treatment with other medicines. It is the first in a new class of agents known as histone deacetylase inhibitors. A recent study suggested that vorinostat also possesses some activity against recurrent glioblastoma multiforme, resulting in a median overall survival of 5.7 months (compared to 4 - 4.4 months in earlier studies). Further brain tumor trials are planned using combinations of vorinostat with other drugs.
Indications
For the treatment of cutaneous manifestations in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma who have progressive, persistent or recurrent disease on or following two systemic therapies.
Definition
ChEBI: A dicarboxylic acid diamide comprising suberic (octanedioic) acid coupled to aniline and hydroxylamine. A histone deacetylase inhibitor, it is marketed under the name Zolinza for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL).
brand name
Zolinza
General Description
Histones are proteins around which DNA is wound in the process of packing DNA into the nucleus. They also havea role in regulating the transcription of genes, and this iscontrolled by the covalent modifications acetylation, phosphorylation,and methylation to which they are subject.
Vorinostat fits the basic pharmacophore for the HDACis, which consists of a hydrophobic cap regionconnected to a zinc coordinating functionality by a hydrophobiclinker.The hydroxamic acid functionality iscapable of bidendate binding to zinc present in the enzymeand is a major factor in the overall binding of the compound.The compound inhibits HDAC1, 2, 3, and 6 classes of thisenzyme with nanomolar (<86 nM) IC50 values.
The agent is given orally and is available in 100-mg capsulesfor the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Thebioavailability is 43%, and the agent is 71% bound toplasma proteins. Extensive metabolism of the agent occursto give the O-glucuronide of the hydroxamic acid functionand 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid with minimal involvementof isozymes of CYP. The metabolites, both of whichare inactive, are eliminated in the urine and the drug has aterminal elimination half-life of 2 hours. The most commonlyreported adverse effects are fatigue, diarrhea, andnausea.
Biochem/physiol Actions
SAHA or Vorinostat facilitates the transcription of genes that result in apoptosis, differentiation and growth arrest. It has been observed to give beneficial results in lymphoma but not in solid tumors.
Synthesis
Commercially available monomethyl ester 125 was reacted with aniline in the presence of DCC and HOBt in DMF to give amide 127 in 89% yield.

Metabolism
The major pathways of vorinostat metabolism involve glucuronidation and hydrolysis followed by β-oxidation. Human serum levels of two metabolites, O-glucuronide of vorinostat and 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid were measured. Both metabolites are pharmacologically inactive. Compared to vorinostat, the mean steady state serum exposures in humans of the O-glucuronide of vorinostat and 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid were 4-fold and 13-fold higher, respectively. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicate negligible biotransformation by cytochromes P450 (CYP).
Storage
-20°C
References
1) Vrana et al. (1999), Induction of apoptosis in U937 human leukemia cells by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) proceeds through pathways that are regulated by Bcl-2/Bcl-XL, c-Jun and p21CIP1, but independent of p53; Oncogene, 18 7016 2) Butler et al. (2002), The histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA arrests cancer cell growth, up-regulates thioredoxin-binding protein-2, and down-regulates thioredoxin; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99 11700 3) Tang et al. (2012), Sorafenib and HDAC inhibitors synergize to kill CNS tumor cells, 13 567
Properties of Vorinostat
| Melting point: | 161-162°C |
| Density | 1.2 |
| RTECS | RG8835000 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥15mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 9.48±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | white to tan |
| Merck | 14,10034 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 6 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 149647-78-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Vorinostat
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Vorinostat
| InChIKey | WAEXFXRVDQXREF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
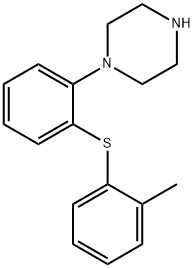
![1-[2-[(3,4-diMethylphenyl)thio]phenyl]- Piperazine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/1293489-74-3.gif)
![1-[(2-Bromophenyl)thio]-2,4-dimethylbenzene](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/960203-41-2.gif)

You may like
-
 149647-78-9 Vorinostat 98%View Details
149647-78-9 Vorinostat 98%View Details
149647-78-9 -
 Vorinostat 98%View Details
Vorinostat 98%View Details
149647-78-9 -
 N-Hydroxy-N'-phenyloctanediamide CAS 149647-78-9View Details
N-Hydroxy-N'-phenyloctanediamide CAS 149647-78-9View Details
149647-78-9 -
 Vorinostat 98% CAS 149647-78-9View Details
Vorinostat 98% CAS 149647-78-9View Details
149647-78-9 -
 SAHA CAS 149647-78-9View Details
SAHA CAS 149647-78-9View Details
149647-78-9 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
