Valine
- CAS NO.:7004-03-7
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00064220
- EINECS: 200-773-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-28 13:53:23
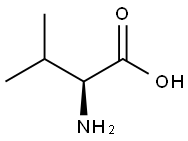
What is Valine?
Chemical properties
Valine(2-amino-3-methylbutyric acid) is one of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins. It is an essential 8 amino acids and glucogenic amino acids for the human body. And Valine works with isoleucine and leucine to promote normal body growth, repair tissues, regulate blood sugar, and provide the required energy.
Physical properties
Valine, White crystal or crystalline powder; odorless, slightly sweet and then bitter. Soluble in water, almost insoluble in ethanol.
Definition
ChEBI: L-valine is the L-enantiomer of valine. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a human metabolite, an algal metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a pyruvate family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, a valine and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a L-valinium. It is a conjugate acid of a L-valinate. It is an enantiomer of a D-valine. It is a tautomer of a L-valine zwitterion.
Synthesis
Valine can be synthesized by hydrolysis of aminoisobutyronitrile which is obtained by amination and cyanation of aminoisoaldehyde. Valine can also be isolated from fish proteins.
Properties of Valine
| Melting point: | 315° C (under decomposition). |
| solubility | 9% soluble in water, practically insoluble in alcohol and oils. |
| form | Leafy crystals |
| Odor | virtually odorless |
Safety information for Valine
Computed Descriptors for Valine
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1