Uric acid
Synonym(s):2,6,8-Trihydroxypurine
- CAS NO.:69-93-2
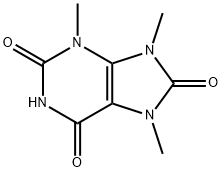
- Empirical Formula: C5H4N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 168.11
- MDL number: MFCD00005712
- EINECS: 200-720-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
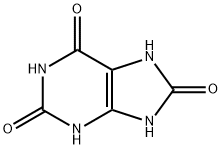
What is Uric acid?
Description
Uric acid is a purine derivative and an oxidative metabolic product of purine nucleotides in humans and other carnivorous animals. It is a weak acid with a pKa of 5.6 and is sparingly soluble in water.
In 1776, Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele discovered uric acid in human urine and kidney stones. The same year, his discovery was confirmed by his colleague Torbern B. Bergman. Uric acid is also found in the feces of birds, reptiles, and some mammals.
Ukrainian–Austrian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski reported an early synthesis of uric acid from glycine in 1882. More recently (1962), C. Wayne Bills and co-workers at the University of Colorado (Boulder) serendipitously synthesized uric acid from urea while they were seeking a new route to pyrimidines.
Uric acid is notorious for the excruciating pain it produces in gout? patients. When the acid is present in high concentrations in the blood, its low solubility causes it to precipitate as sharp crystals in and around joints, notably in the feet. Uric acid concentration increases in the body when people consume large amounts of purine-rich foods such as red meat and seafood.
There has been some speculation that the presence of uric acid and its concomitant gout play a role in COVID-19, but this connection would be indirect at most. People with gout tend to have other serious health problems such as obesity, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease, which uric acid can exacerbate. According to Theodore R. Fields at the Hospital for Special Surgery (New York City), “Gout does not typically affect immune system function.” Adds Shailendra Singh at White River Medical Center (Batesville, AR), “People with gout don’t have a greater risk of getting coronavirus than the general population, but they do have an increased risk of complications if they do get it.”
Chemical properties
Uric acid (C5H4O3N4) is a white solid that is insoluble in cold water, alcohol, or ether and sparingly soluble in hot water. It acts as a weak dibasic acid, creating two series of salts, with most being very slightly soluble in water (except for lithium urate, which is soluble).
Occurrence
Uric acid is found in the urine, blood, and muscle juices of carnivorous animals (herbivorous animals secrete hippuric acid), in the excrement of birds, serpents and insects, and is an oxidation product of the complex nitrogenous compounds of the animal organism.
The Uses of Uric acid
Uric Acid is a heterocyclcic compound that is created when purine nucleotides are broken down of by the human body. High blood concetration of Uric Acid is known as hyperuricemia and is often associated with a wide range of disorders and medical conditions such as gout, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Uric acid may be a marker of oxidative stress and may have a potential therapeutic role as an antioxidant.
What are the applications of Application
Uric acid is a xanthine oxidase product
Definition
A nitrogen compound produced from purines. In certain animals (e.g. birds and reptiles), it is the main excretory product resulting from breakdown of amino acids. In humans, uric acid crystals in the joints are the cause of gout.
Definition
uric acid: The end product of purinebreakdown in most primates, birds,terrestrial reptiles, and insects andalso (except in primates) the majorform in which metabolic nitrogen isexcreted. Being fairly insoluble, uricacid can be expelled in solid form,which conserves valuable water inarid environments. The accumulationof uric acid in the synovial ?uidof joints causes gout.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Uric acid is an insoluble catabolite produced by adenine and guanine metabolism. Accumulation of uric acid leads to gout, hyperuricemia, arthritis and renal failure. Elevated uric acid levels contributes to hypertension and pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Low uric acid levels associated with Parkinson′s disease and multiple sclerosis, may elicit protective functionality. High levels of uric acid in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may serve as potential marker for diagnosis.
Safety Profile
Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Purification Methods
Crystallise uric acid from hot distilled H2O (the solubility in H2O is 1part/39,000parts at 18o and 1part/2,000parts at 100o). It is best purified by dissolving in an alkaline solution and acidifying with dilute HCl and drying it at 100o in a vacuum. [Bergmann & Dikstein J Am Chem Soc 77 691 1955, Lister Purines Part II, Fused Pyrimidines Brown Ed, Wiley-Interscience pp256-257 1971, ISBN 0-471-38205-1, Beilstein 26 H 513, 26 I 151, 26 II 293, 26 III/IV 2619.]
References
Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion DOI:10.1002/RECL.19881071209
Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, Fourth Edition. By W. L. F. DOI:10.1002/RECL.19881071209
Van Nostrand’s Scientific Encyclopedia DOI:10.1007/978-1-4757-6918-0
The Facts on File Dictionary of Chemistry DOI:10.5860/choice.37-4227
A Dictionary of Chemistry (6th edition) DOI:10.1108/09504120910935291
Uric Acid in Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis DOI:10.3390/ijms222212394
Properties of Uric acid
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 297.02°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,9 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.9900 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Sparingly, Heated) |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 3.89(at 12℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in 1M sodium hydroxide solution. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ether and alcohol. |
| Merck | 14,9875 |
| BRN | 156158 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, bases, oxidising agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69-93-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Uric acid (69-93-2) |
Safety information for Uric acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Uric acid
Uric acid manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

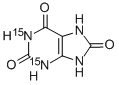
![URIC ACID, [8-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB4279020.gif)

You may like
-
 Uric Acid CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric Acid CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 Uric acid 95% CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric acid 95% CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 Uric acid, GR 99%+ CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric acid, GR 99%+ CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 Uric acid reagent CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric acid reagent CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 Uric acid CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric acid CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 Uric Acid CASView Details
Uric Acid CASView Details -
 Uric Acid Chemical CAS 69-93-2View Details
Uric Acid Chemical CAS 69-93-2View Details
69-93-2 -
 URIC ACID REAGENT CASView Details
URIC ACID REAGENT CASView Details