TUNICAMYCIN
Synonym(s):InSolution Tunicamycin, Streptomyces lysosuperficus - CAS 11089-65-9 - Calbiochem;NSC 177382;Tunicamycin, Streptomyces lysosuperficus - CAS 11089-65-9 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:11089-65-9
- Empirical Formula: C37H60N4O16
- Molecular Weight: 816.89
- MDL number: MFCD00065709
- EINECS: 601-012-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
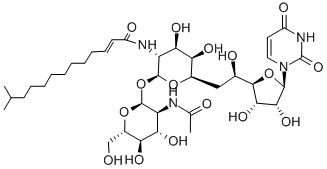
What is TUNICAMYCIN?
Description
Tunicamycin mixture is a mixture of tunicamycins with variable trans-2,3-unsaturated branched chain fatty acid (BFCA) chain lengths. Tunicamycins are anti-microbial agents that are active against Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and viruses. They inhibit the N-acetylhexosamine (HexNAc) phosphotransferase family of enzymes in bacteria and prevent peptidoglycan biosynthesis. In eukaryotes, they inhibit N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) phosphotransferase (GPT), preventing the first step in N-linked glycosylation and inducing the unfolded protein response and cell death. The cellular toxicity of tunicamycins is linked to the trans-2,3-unsaturated BCFA, and saturated BCFA-containing tunicamycin derivatives, such as TunR1 and TunR2 , have reduced toxicity. Tunicamycins impair glycosylation of the receptor tyrosine kinases EGFR, HER2, HER3, and IGF-1R, which prevents their translocation out of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and reduces their protein levels and activity. Tunicamycin sensitizes EGFR inhibitor-resistant U251 glioma and Bx/PC-3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to irradiation.
Chemical properties
White solid
The Uses of TUNICAMYCIN
The tunicamycins are a family of lipophilic nucleosides with fatty acids conjugated to an aminoglycoside group. The complex comprises analogues, tunicamycins I to X. This composition is typical of other products less precisely described as tunicamycins A to D. The tunicamycins act by blocking the formation of N-glycoside linkages to proteins via inhibition of formation of dolichol monophosphate from N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate. Tunicamycin blocks the synthesis of all N-linked glycoproteins (N-glycans) and causes cell cycle arrest in G1 phase. Tunicamycins are broadly active against prokaryotes, eukaryotes and viruses.
The Uses of TUNICAMYCIN
As a tool in studying glycoproteins in a wide variety of biological systems.
The Uses of TUNICAMYCIN
Tunicamycin has been widely used in the study of glycoprotein synthesis in various biological systems. During protein glycosylation, tunicamycin is noted to be an inhibitor of the transfer of saccharide moieties to dolichol during dolichol-linked glycoprotein synthesis. Dose-dependent inhibition of DNA synthesis may be related to the alteration of glycoproteins, which thereby affects the transport of thymidine into cells. Additionally, tunicamycin has been reported to prevent cell cycle progression in primary cultures of rat glial cells, as well as inhibit lipid-mediated protein glycosylation in chick or mouse fibroblasts in a dose-dependent manner.
What are the applications of Application
Tunicamycin is a competitive cell cycle inhibitor exhibiting antiungal properties and is widely used in the study of glycoprotein synthesis
Definition
ChEBI: A mixture of antiviral nucleoside antibiotics produced by Streptomyces lysosuperificus. It contains at least 10 homologues comprising uracil, N-acetylglucosamine, an 11-carbon aminodialdose called tunicamine, and a fatty aci linked to the amino group of the tunicamine. The homologues vary in the composition of the fatty acid moiety.
General Description
Tunicamycin was first isolated from Streptomyces lysosuperificus based on its antiviral activity. It contains N-acetylglucosamine and inhibits glycoprotein biosynthesis, including virus membrane glycoproteins.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable: yes
storage
+4°C
Purification Methods
The components of this nucleotide antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. are purified by recrystallising 3 times from hot glass-distilled MeOH, and the white crystals are dissolved in 25% aqueous MeOH and separated on a Partisil ODS-10_ column (9.4 x 25 cm) [Magnum-9 Whatman] using a 260nm detector. The column is eluted with MeOH/H2O mixture adjusted to 1:4 (v/v) then to 2:4 (v/v). The individual components are recovered and lyophilised. Ten components have been isolated, and all were active (to varying extents) depending on the lengths of the aliphatic side-chains. The mixture has UV max at 205 and 260nm (A 1cm 230 and 110). It is stable in H2O at neutral pH but unstable in acidic solution. It inhibits protein glycosylation. [Mahoney & Duskin J Biol Chem 254 6572 1979, Elnein Trends Biochem Sci 6 219 1981, Takatsuki J Antibiot 24 215 1971.] Uracil, uridine and uridine nucleotides. These are resolved by ion-exchange chromatography with AG1 (Cl form). [Lindsay et al. Anal Biochem 24 506 1968.]
References
1) Langan?et al. (1991),?Isoprenoids and astroglial cell cycling: diminished mevalonate availability and inhibition of dolichol-linked glycoprotein synthesis arrest cycling through distinct mechanisms;? J. Cell Physiol.,?149?284 2) Ding?et al. (2007),?Differential effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy on cell survival;? J. Biol. Chem.,?282?4702 3) Jiang?et al. (2007),?Tunicamycin sensitizes human melanoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of TRAIL-R2 via the unfolded protein response; Cancer Res.,?67?5880 4) Ishii?et al. (1987),?Dolichol-linked glycoprotein synthesis in G1 is necessary for DNA synthesis in synchronized primary cultures of cerebral glia;? J. Neurochem.,?49?1606
Properties of TUNICAMYCIN
| Melting point: | 234-235℃ (decomposition) |
| alpha | D20 +52° (c = 0.5 in pyridine) |
| Flash point: | 87℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in methanol, ethanol, DMSO, or DMF |
| form | White to off-white solid |
| color | White |
| Sensitive | Moisture & Light Sensitive |
| BRN | 6888090 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tunicamycin (11089-65-9) |
Safety information for TUNICAMYCIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for TUNICAMYCIN
| InChIKey | YJQCOFNZVFGCAF-WPTOCQRYSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Tunicamycin, Streptomyces lysosuperficus CAS 11089-65-9View Details
Tunicamycin, Streptomyces lysosuperficus CAS 11089-65-9View Details
11089-65-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8