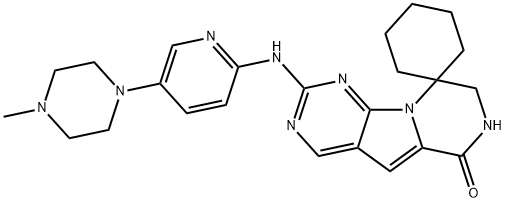
trilaciclib
- CAS NO.:1374743-00-6
- Empirical Formula: C24H30N8O
- Molecular Weight: 446.55
- MDL number: MFCD30747890
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35
What is trilaciclib?
Absorption
Cmax and AUC of trilaciclib increase proportionally with dose.
Toxicity
Data regarding overdoses of trilaciclib are not readily available. For grade 3 or worse injection site reactions, acute drug hypersensitivity reactions, and interstitial lung disease; or any other grade 4 toxicities; permanently discontinue trilacilib.
Description
Trilaciclib is a small molecule, competitive inhibitor of cyclin dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6), with potential antineoplastic and chemoprotective activities.
Characteristics
Class: serine/threonine kinase
Treatment: myelopreservation (IV)
Elimination half-life = 36 h
The Uses of trilaciclib
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the frequency of chemotherapy-induced bone marrow suppression in adults receiving certain types of chemotherapy for extensive-stage (when the cancer has spread beyond the lungs) small cell lung cancer.
Indications
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Background
Trilaciclib, or G1T28, is a CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor, indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients before topotecan-containing or platinum and etoposide-containing chemotherapy for extensive stage small cell lung cancer. CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors have been investigated since the mid 1990s for their use in tumorigenesis and chemotherapy. Trilaciclib was first described in the literature in 2016.
Trilaciclib was granted FDA approval on 12 February 2021.
brand name
CoselaTM
Mechanism of action
Trilaciclib is inhibits cyclin-dependant kinase 4 (CDK4) at a concentration of 1 nmol/L and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) at 4 nmol/L. Inhibition of CDK2, CDK5, and CDK7 is over 1000-fold less at these concentrations and inhibition of CDK9 is 50-fold less. CDK4 and CDK5 are expressed in hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells. They are capable of phosphorylating and inactivating the retinoblastoma protien; a tumor suppressor. When trilaciclib is given to patients with retinoblastoma protein-null small cell lung cancer, it does not interfere with the intended chemotherapy induced cytotoxicity of cancer cells. Inhibition of CDK4 and CDK5 leads to a reversible pause in the cell cycle in the G1 phase for approximately 16 hours. The temporary cell cycle arrest prevents chemotherapy induced DNA damage in healthy cells, reducing the activity of caspases 3 and 7, which reduces apoptosis of healthy cells. Other studies have shown inhibitors of CDK4 and CDK6 enhance T-cell activation, upregulating major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II, and stabilize programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). Together these activities increase T-cell activity, increase antigen presentation, and sensitize cells to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Pharmacokinetics
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. It has a short duration of action of approximately 16 hours, and a narrow therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of injection site reactions, hypersensitivity, and interstitial lung disease.
Pharmacology
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. It has a short duration of action of approximately 16 hours, and a narrow therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of injection site reactions, hypersensitivity, and interstitial lung disease.
Synthesis
The synthesis of trilaciclib is as follows:
Intermediate 2 (21.1 g, 70 mmol) and 1-methyl-4-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)piperazine (13.4 g, 70 mmol) were added to a 100 mL vacuum tube and reacted at 230° C. for 3 h.After the reaction, 300 mL of ethyl acetate was added, washed with water (120 mL) and saturated brine (120 mL) successively, dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered, the obtained solution was evaporated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, and the obtained residue was recrystallized with ethanol, 27.5 g of Trilaciclib was obtained with a purity of 99% and a yield of 88%.
Drug interactions
Trilaciclib is indicated to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy induced myelosuppression in patients prior to receiving platinum and etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Metabolism
Data regarding the metabolism of trilaciclib are not readily available, however it is expected to be extensively metabolised.
storage
Dry, dark and at 0 - 4℃ for short term (days to weeks) or -20℃ for long term (months to years).
Mode of action
The G1 phase (where the cell is preparing to divide) to the S phase where DNA synthesis starts, and inhibition of CDK4/6 causes stem cells to temporarily stay at the G1 phase. In other words, the stem cells stop moving on to the S phase (DNA synthesis) or the G2 phase (growth), and certainly not to the M phase (mitosis). As a result, stem cells are protected from being damaged or even destroyed as chemotherapy only affects cells that are in other phases: the S, the G2, and the M phase. In the meantime, the tumor cells continue to transition to the S and M phases to divide, and they are killed by chemotherapy, causing the tumor to shrink. By preventing the stem cells from injury during chemotherapy, trilaciclib allows the patients to complete their course of treatment on time, and it avoids the expensive treatment of potential myelosuppressive adverse effects. So far, trilaciclib does not appear to reduce the efficacy of chemotherapy. In biochemical assays, trilaciclib reversibly inhibited CDK4/cyclin D1 and CDK6/cyclin D3 with an IC50 of 1 and 4 nM, respectively. It also displayed high selectivity against other CDK/cyclin complex family members and other protein kinases.
Properties of trilaciclib
| Density | 1.46±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | H2O:15.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);33.59(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.33±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to yellow |
Safety information for trilaciclib
Computed Descriptors for trilaciclib
trilaciclib manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1374743-00-6 Trilaciclib 98%View Details
1374743-00-6 Trilaciclib 98%View Details
1374743-00-6 -
 1374743-00-6 98%View Details
1374743-00-6 98%View Details
1374743-00-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1