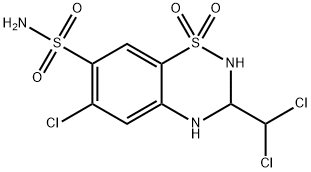
Trichlormethiazide
Synonym(s):6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
(+/-)-;NSC 61560
- CAS NO.:133-67-5
- Empirical Formula: C8H8Cl3N3O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 380.66
- MDL number: MFCD00057315
- EINECS: 205-118-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is Trichlormethiazide?
Toxicity
Oral Rat LD50 = 5600 mg/kg, oral Mouse LD50 = 2600 mg/kg
Chemical properties
Trichlormethiazide occurs as a white or practically white, crystalline powder and may have a slight characteristic odor.
Originator
Naqua,Schering,US,1960
The Uses of Trichlormethiazide
Trichlormethiazide is a diuretic and anti-hypertensive agent from the benzothiadiazide class which is used in veterinary medicine in cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and horses, at the following therapeutic regimen: a single intramuscular dose of 0.4 mg/kg bw followed by two oral doses of 0.8 mg/kg bw given 12 and 36 hours after the first administration.
Trichlormethiazide is also used in humans in the United States as a diuretic and anti-hypertensive substance but not in the European Union. The usual dose is 2 to 4 mg twice a day (i.e. approximately 0.033 to 0.066 mg/kg bw/day).
The Uses of Trichlormethiazide
diuretic, antihypertensive
The Uses of Trichlormethiazide
Trichlormethiazide, is a diuretic, having similar properties as Hydrochlorothiazide (H714560). It is used for the treatment of oedema (including that which is associated with heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis and corticosteroid therapy) and hypertension.
Indications
Used in the treatment of oedema (including that associated with heart failure) and hypertension.
Background
A thiazide diuretic with properties similar to those of hydrochlorothiazide. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p830)
Definition
ChEBI: Trichlormethiazide is a benzothiadiazine, hydrogenated at positions 2, 3 and 4 and substituted with an aminosulfonyl group at C-7, a chloro substituent at C-6 and a dichloromethyl group at C-3 and with S-1 as an S,S-dioxide. A sulfonamide antibiotic, it is used as a diuretic to treat oedema (including that associated with heart failure) and hypertension. It has a role as a diuretic and an antihypertensive agent. It is a benzothiadiazine and a sulfonamide antibiotic.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 5.7 grams (0.02 mol) of 5-chloro-2,4-disulfamylaniline and 4.9 grams (0.04 mol) of dichloroacetaldehyde in 25 ml of dimethyl formamide was heated at the boiling temperature and under reflux for 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was thereafter poured into a mixture of ice and water to precipitate the desired 6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3-dichloromethyl-3,4-dihydro- 1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide as a crystalline solid melting at 250° to 270°C with decomposition.
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic
Pharmacokinetics
Trichloromethiazide is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Trichloromethiazide has also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomer-ulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. Trichloromethiazide is also indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension. Like other thiazides, Trichloromethiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). They inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Trichlormethiazide
| Melting point: | 248-250℃ |
| Boiling point: | 631.3±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.748 |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 6.9(acetone/H2O) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,9624 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 133-67-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Trichlormethiazide (133-67-5) |
Safety information for Trichlormethiazide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Trichlormethiazide
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Trichloromethiazide CAS 133-67-5View Details
Trichloromethiazide CAS 133-67-5View Details
133-67-5 -
 Trichlormethiazide 95% CAS 133-67-5View Details
Trichlormethiazide 95% CAS 133-67-5View Details
133-67-5 -
 Trichlormethiazide CAS 133-67-5View Details
Trichlormethiazide CAS 133-67-5View Details
133-67-5 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4