Trichlorfon
Synonym(s):(2,2,2-Trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)phosphonic acid dimethyl ester;Metrifonate;Trichlorfon
- CAS NO.:52-68-6
- Empirical Formula: C4H8Cl3O4P
- Molecular Weight: 257.44
- MDL number: MFCD00055272
- EINECS: 200-149-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
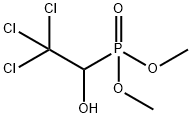
What is Trichlorfon?
Description
Trichlorfon is a colorless crystalline powder. It is soluble in water (120 g/L) and most organic solvents, except aliphatic hydrocarbons. Log Kow = 0.43. Trichlorfon is rapidly converted to dichlorvos by alkalis (2) and then hydrolyzed; DT50 (22 ?C) values at pH 4, 7, and 9 are 510 d, 46 h, and <30 min, respectively.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Chemical properties
Trichlorfon is a white to pale yellow crystalline solid.
The Uses of Trichlorfon
Trichlorfon is an irreversible organophosophate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and the prodrug of Dichlorvos (D435950). Trichlorfon have also shown potential actions to be utilized as an effective org anophosphorus pesticide.
The Uses of Trichlorfon
One of the biologically active forms of nicotinic acid. Differs from NAD by an additional phosphate group at the 2?position of the adenosine moiety. Serves as a coenzyme of hydrogenases and dehydrogenases. Present in living cells primarily in the r
The Uses of Trichlorfon
anticholinergic, urinary incontenance therapy
The Uses of Trichlorfon
Insecticide used to control ?ies and roaches.
The Uses of Trichlorfon
Trichlorfon is used to control a wide range of insects in many crops and to control household pests, flies in animal houses and ectoparasites in domestic animals.
Definition
ChEBI: A phosphonic ester that is dimethyl phosphonate in which the hydrogen atom attched to the phosphorous is substituted by a 2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl group.
Indications
Metrifonate is an organophosphorous compound that is effective only in the treatment of S. haematobium. The active metabolite, dichlorvos, inactivates acetylcholinesterase and potentiates inhibitory cholinergic effects. The schistosomes are swept away from the bladder to the lungs and are trapped. Therapeutic doses produce no untoward side effects except for mild cholinergic symptoms. It is contraindicated in pregnancy, previous insecticide exposure, or with depolarizing neuromuscular blockers. Metrifonate is not available in the United States.
Antimicrobial activity
Useful activity is restricted to Schistosoma haematobium. It has little activity against other schistosomes. Although it exhibits activity against several other helminths, it is not used for their treatment.
General Description
Chlorophos is a white crystalline solid. Soluble in water, benzene, chloroform, ether; insoluble in oils. Chlorophos is a wettable powder. Chlorophos can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. Chlorophos is used as a pesticide.
General Description
Metrifonate is an organophosphate thatwas originally developed to treat schistosomiasis under thetrade name Bilarcil. It is an irreversible cholinesteraseinhibitor with some selectivity for BuChE over AChE. Itachieves sustained cholinesterase inhibition by its nonenzymaticmetabolite dichlorvos (DDVP), a long-actingorganophosphate. Its use in mild-to-moderate Alzheimerdisease was suspended recently because of adverse effectsexperienced by several patients during the clinical evaluationof this product. Toxicity at the neuromuscular junctionis probably attributable to the inhibition by the drug of neurotoxicesterase, a common feature of organophosphates.
Air & Water Reactions
Chlorophos decomposes at higher temperatures in water and at pH <5.5. Chlorophos is sensitive to prolonged exposure to moisture. Chlorophos is unstable in alkaline solutions.
Reactivity Profile
Chlorophos is incompatible with alkalis. Chlorophos is corrosive to black iron and mild steel. Chlorophos is corrosive to metals. Chlorophos is subject to hydrolysis.
Health Hazard
INHALATION, INGESTION, AND SKIN ABSORPTION. Inhibits cholinesterase. Headache, depressed appetite, nausea, miosis are symptoms of light exposures. Moderate effects are peritoneal paralysis, diarrhea, salivation, lacrimation, sweating, dyspnea, substernal tightness, slow pulse, tremors, muscular cramps and ataxia. Severe symptoms are: pyrexia, cyanosis, pulmonary edema, areflexia, loss of sphincter control, paralysis, coma, heart block, shock and respiratory failure. EYES: Increases permeability of blood vessels in anterior eye. Reduces corneal sensitivity with glaucoma, abnormalities in intraocular tension or decreased visual acuity.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Anthelmintic: Not approved for use in EU countries . Registered for use in the U.S. except California. Trichlorfon has non-agriculture uses on golf course turf, home lawns and similar venues, and in non-food contact areas of food and meat processing plants. Also on ornamental shrubs and plants, and ornamental and bait fish ponds. Overseas, trichlorfon is used as cattle pour-on, which is classified as a food-use. It is used against insects such as lepidopteran larvae (caterpillars), white grubs, mole crickets, cattle lice, sod webworms, leaf miners, stink bugs, flies, ants, cockroaches, earwigs, crickets, diving beetles, water scavenger beetles, water boatman, backswimmers, water scorpions, giant water bugs and pillbugs. All food and feed uses in the U.S. were voluntarily canceled November 21, 1995. It was used on Brussels sprouts, barley, beets, blueberries, beans (dryand snap), corn, field corn, popcorn, sweet corn, cotton, cow peas, lima beans, tomatoes, cabbage, carrots (including tops), cauliflower, collards, cowpeas, southern peas, blackeyed peas, crowder peas, pumpkins, collards, lettuce and alfalfa, cotton, peanuts, peppers, pumpkins, tobacco, soybeans and treatment to manure. U.S. Maximum Allowable Residue Levels for the residues of Trichlorfon [40 CFR 180.198]: in or on the following raw agricultural commodities: cattle, fat 0.1ppm (negligible residue); cattle, meat byproducts 0.1ppm (negligible residue); and cattle, meat 0.1ppm (negligible residue)
Pharmaceutical Applications
An organophosphorus compound. It is soluble in water and stable at room temperature. At higher temperatures it decomposes to the insecticide dichlorvos.
Trade name
AEROL 1 (PESTICIDE)®; AGROFOROTOX®; ANTHON®; BAY 15922®; BAYER 15922®; BAYER L 13/59®; BILARCIL®; BOVINOX®[C]; BRITON®; BRITTEN®; CEKUFON®; CHLORAK®; CHLOROFTALM®; CICLO-SOM®; COMBOT®; COMBOT EQUINE®; DANEX®[C]; DEP®; DEPTHON®; DIMETOX®; DIPTEREX®; DIPTEREX® 50; DIPTEVU®; DITRIFON®; DYLOX®; DYLOX-METASYSTOX-R®; DYREX®; DYVON®; EQUINO-ACID®; EQUINO-AID®; FLIBOL E®; FLIEGENTELLE®; FOROTOX®; FOSCHLOR®; FOSCHLOR R®; FOSCHLOR R-50®; LEIVASOM®; LOISOL®; MASOTEN®[C]; MAZOTEN®; NEGUVON®; NEGUVON A®; PHOSCHLOR R50®; PROXOL®; RICIFON®; RITSIFON®; SATOX 20WSC®; SOLDEP®; SOTIPOX®; TRICHLORPHON FN®; TRINEX®; TUGON®; TUGON FLY BAIT®; TUGON STABLE SPRAY®; VERMICIDE BAYER 2349®; VOLFARTOL®; VOTEXIT®; WEC 50®; WOTEXIT®
Mechanism of action
In vivo, metrifonate rapidly rearranges to O,O-dimethyl O-(2,2-dichlorovinyl) phosphate, which is a potent inhibitor of schistosome acetylcholinesterase. This paralyzes the parasites because of the accumulation of acetylcholine, which functions as inhibitory transmitter . Trade name: Bilarcil (Bayer).
Pharmacokinetics
Metrifonate is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, achieving a peak concentration in plasma within 1–2 h. It undergoes chemical transformation to dichlorvos, which is the active molecule. Dichlorvos is rapidly and extensively metabolized and excreted mainly in the urine.
Clinical Use
Urinary schistosomiasis (especially mass chemotherapy control programs)
Side Effects
Various side effects such as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal upsets and vertigo occur in many patients. As the worms release their hold of the veins in the bladder they pass through the blood system to the lungs, where they disintegrate; this may cause some of the side effects. Cholinesterase levels in the blood and on erythrocytes are depressed, but the significance of this is unknown.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, inti-aperitoneal, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. Human systemic effects: true cholinesterase. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland POx.
Potential Exposure
Trichlorfon is used as an agricultural and forest insecticide.
Carcinogenicity
When rats were fed diets that contained 0, 50, 100, 200, 250, 400, 500, or 1000 ppm (equivalent to about 0.5, 12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg/day) for 17 or 24 months, no treatment-related effects occurred in those fed 50–250 ppm . Histopathological results suggested the occurrence of mammary tumors in rats fed 400, 500, and 1000 ppm. In another study, when rats were fed diets containing 0, 50, 250, 500, or 1000 ppm (equivalent to about 2.5, 12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg/day) trichlorfon for 24 months, no treatment-related effects other than whole-blood cholinesterase depression at 1000 ppm occurred . There was no increase in the incidence of either benign or malignant tumors, including mammary tumors.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Trichlorfon degraded in soil to dichlorvos (alkaline conditions) and desmethyl
dichlorvos (Mattson et al., 1955).
Plant. In cotton leaves, the metabolites identified included dichlorvos, phosphoric acid,
O-demethyl dichlorvos, O-demethyl trichlorfon, methyl phosphate and dimethyl phosphate
(Bull and Ridgway, 1969). Chloral hydrate and trichloroethanol were r
Pieper and Richmond (1976) studied the persistence of trichlorfon in various foliage
following an application rate of 1.13 kg/ha. Concentrations of the insecticide found at day
0 and 14 were 81.7 ppm and 7 ppb for willow foliage, 12.6 ppm and 670 ppb for
Chemical/Physical. At 100°C, trichlorfon decomposes to chloral. Decomposed by hot
water at pH <5 forming dichlorvos (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Metabolic pathway
The metabolism of trichlorfon has been reviewed by Zayed et al. (1967), Sawicki (1973) and Zayed (1974). Trichlorfon is a non-systemic insecticide with favourable mammalian toxicity. There is considerable evidence that trichlorfon requires in vivu activation via dehydrochlorinatation to yield dichlorvos which is the active acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. This reaction is quite facile in slightly basic solution and the subsequent routes for the metabolism of trichlorfon are apparently the same as those of dichlorvos. However, there has been considerable controversy on the role played by this reaction in vivu since many workers have failed to identify dichlorvos as a metabolite in plants, mammals or insects treated with trichlorfon. It was realised that trichlorfon was a very much poorer inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase than dichlorvos and most considered that its insecticidal activity must be due to metabolism to dichlorvos as an activating step in an analogous way that phosphorothioates are metabolised to phosphates. Metcalf et al. (1959) and Miyamoto (1959) proposed that trichlorfon was totally inactive as an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and that any inhibition seen in vitru was due to some conversion to dichlorvos during the course of the assay for anticholinesterase activity. Metcalf et al. (1959) also reported the identification of dichlorvos in trichlorfon-treated houseflies. This conclusion was by no means universal and Arthur and Casida (1957) argued that trichlorfon was the active acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and the identification of a glucuronide conjugate of trichloroethanol was evidence that the primary route of stage I metabolism was hydrolysis of the P< bond. Other work, however, has provided evidence for the in vivu production of dichlorvos and it seems probable that the failure of some experiments to detect it is due to its rapid metabolism, resulting in a very low steadystate concentration. The metabolism of trichlorfon can be envisaged as being either through a deactivation route via demethylation and/or conjugation followed by breakdown of the demethylated products or an activation reaction to yield dichlorvos which is then degraded via a hydrolytic mechanism to yield dimethyl phosphate and dichloroacetaldehyde or demethylated by glutathione-S-methyl transferase. These competing reactions have been investigated in mammals and insects and it is the balance of activation and degradative metabolism which confers the favourable mammalian toxicity of trichlorfon in comparison with that of dichlorvos.
Metabolism
Trichlorfon administered to mammals is rapidly metabolized and excreted almost completely in the urine within 6 h. Majormetabolites are dimethyl hydrogen phosphate, methyl dihydrogen phosphate, and conjugates of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroethanol. Trichlorfon is rapidly broken down in soil.
Shipping
UN2783 Organophosphorus pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
Trichlorfon is subject to hydrolysis and dehydrochlorination. Decomposition
proceeds more rapidly with heating and above pH 6. It is rapidly
converted by alkalis to dichlorvos (2) which is then hydrolysed. DT50 s at pH 4,7 and 9 were 510 days, 46 hours and <30 min respectively at 20 °C.
Photolysis is slow (PM).
Trichlorfon undergoes a facile rearrangement in the presence of mild
base or heat to yield dichlorvos (2) and one mole of HCI (Barthel et al.,
1955; Lorenz et al., 1955; Mattson et al., 1955). This reaction was shown to
be first order in both trichlorfon concentration and [OH-] with a calculated
t1/2 of 5 hours at pH 7.0 (37 °C) (Miyamoto, 1959). A mechanism for
this reaction is shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is about 450 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats is >0.5 mg/L air. NOEL (2 yr) for rats is 100 mg/kg diet (5 mg/kg/d). ADI is 0.01 mg/kg b.w.
Incompatibilities
This chemical may be characterized as an organo-phosphate or-chlorine compound. Organophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducin g agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.Alkaline materials: lime, lime sulfur, etc. Corrosive to iron, steel and possibly to other metals.
Waste Disposal
Add a combustible solvent and burn in a furnace equipped with an afterburner and an alkali scrubber.In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Trichlorfon
| Melting point: | 77-81 °C |
| Boiling point: | 100°C |
| Density | 1.73 |
| vapor pressure | 2.1×10-4Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.3439 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water, very soluble in methylene chloride, freely soluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | solid |
| pka | 6 (est.) |
| color | Crystals |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. 1-5 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Merck | 13,9696 |
| BRN | 1709434 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Metrifonate(52-68-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Trichlorfon (52-68-6) |
Safety information for Trichlorfon
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Trichlorfon
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![DIMETHYL [2,2,2-TRICHLORO-1-(([3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)ANILINO]CARBONYL)OXY)ETHYL]PHOSPHONATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1243442.gif)

![DIMETHYL (2,2,2-TRICHLORO-1-([(3-CHLORO-4-METHYLANILINO)CARBONYL]OXY)ETHYL)PHOSPHONATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB8758868.gif)

![DIMETHYL (2,2,2-TRICHLORO-1-([(3-CHLOROANILINO)CARBONYL]OXY)ETHYL)PHOSPHONATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB8299761.gif)
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1