tranylcypromine
- CAS NO.:155-09-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H11N
- Molecular Weight: 133.19
- MDL number: MFCD00001302
- EINECS: 205-841-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
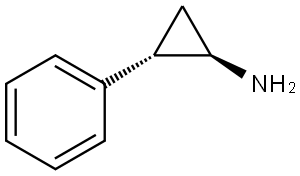
What is tranylcypromine ?
Absorption
Interindividual variability in absorption. May be biphasic in some individuals. Peak plasma concentrations occur in one hour following oral administration with a secondary peak occurring within 2-3 hours. Biphasic absorption may represent different rates of absorption of the stereoisomers of the drug, though additional studies are required to confirm this.
Toxicity
In overdosage, some patients exhibit insomnia, restlessness and anxiety, progressing in severe cases to agitation, mental confusion and incoherence. Hypotension, dizziness, weakness and drowsiness may occur, progressing in severe cases to extreme dizziness and shock. A few patients have displayed hypertension with severe headache and other symptoms. Rare instances have been reported in which hypertension was accompanied by twitching or myoclonic fibrillation of skeletal muscles with hyperpyrexia, sometimes progressing to generalized rigidity and coma.
Originator
Parnate,SKF,UK,1960
Indications
For the treatment of major depressive episode without melancholia.
Background
A propylamine formed from the cyclization of the side chain of amphetamine. This monoamine oxidase inhibitor is effective in the treatment of major depression, dysthymic disorder, and atypical depression. It also is useful in panic and phobic disorders (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p311).
Tranylcypromine is a racemate comprising equal amounts of (1R,2S)- and (1S,2R)-2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine with the chiral centers both located on the cylopropane ring. An irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor that is used as an antidepressant (INN tranylcypromine).
Definition
ChEBI: (1R,2S)-tranylcypromine is a 2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine that is the (1R,2S)-enantiomer of tranylcypromine. It is a conjugate base of a (1R,2S)-tranylcypromine(1+). It is an enantiomer of a (1S,2R)-tranylcypromine.
Manufacturing Process
A solution containing 167 grams of stabilized styrene and 183 grams of ethyl
diazoacetate is cooled to 0°C and dropped into 83.5 grams of styrene with
stirring, in a dry nitrogen atmosphere, at 125° to 135°C. This produced the
ester ethyl 2-phenylcyclopropanecarboxylate.
A solution of the above ester (207.8 grams) and 64.5 grams of sodium
hydroxide in 80 cc of water and 600 cc of ethanol is refluxed for 9 hours. The
carboxylic acid of 2-phenylcyclopropane is liberated with 200 cc of
concentrated hydrochloric acid. The 2-phenylcyclopropanecarboxylic acid
contains 3 to 4 parts of the trans isomer to 1 part of the cis isomer. The acid
is recrystallized from hot water. The pure trans isomer comes out as
crystalline material (solid) while the cis isomer stays in solution.
A solution of 4.62 grams of 2-phenylcyclopropanecarboxylic acid in 15 cc of
dry benzene is refluxed with 4 cc of thionyl chloride for 5 hours, the volatile
liquids are removed and the residue once more distilled with benzene.
Fractionation of the residue yields the carbonyl chloride of 2-
phenylcyclopropane.
A mixture of 15 grams of technical sodium azide and 50 cc of dry toluene is
stirred and warmed and a solution of 10 grams of 2-
phenylcyclopropanecarbonyl chloride in 50 cc of dry toluene is added slowly.
Inorganic salts are filtered and washed well with dry benzene and the solvents
are removed under reduced pressure. The RCON3 compound produced
undergoes the Curtius rearrangement to RNCO + N2. The residual isocyanate
is a clear red oil of characteristic odor. It is cooled to 10°C and treated
cautiously with 100 cc of 35% hydrochloric acid whereupon RNCO + H2O gives
RNH2 + CO2.After most of the evolution of carbon dioxide has subsided the
mixture is refluxed for 13 hours, the cooled solution is diluted with 75 cc of
water and extracted with three 50 cc portions of ether. The acid solution is
evaporated under reduced pressure with occasional additions of toluene to
reduce foaming.
The almost dry residue is cooled to 0°C and made strongly alkaline with a
50% potassium hydroxide solution. The amine is extracted into several
portions of ether, dried over potassium hydroxide, the solvent removed, and
the base fractioned. Reaction of the base with a half-molar quantity of sulfuric
acid gives the sulfate.
brand name
Cuait;Estelapar;Jatrosom;Oculocidon;Parnate tylciprine;Parnetene;Parstelazin;Parstelin;Transaminase sgo;Transaminase sgp.
Therapeutic Function
Psychostimulant
World Health Organization (WHO)
Tranylcypromine, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), was introduced in 1961 for the treatment of depressive illness. By 1964 its use had been associated with transient hypertensive crises and other adverse effects when taken together with certain cheeses and other foods containing tyramine. This led to the withdrawal of the drug in several countries and the suspension of marketing on a worldwide basis by the major manufacturer pending review of these adverse reactions. Subsequently, in response to requests from the medical profession, tranylcypromine was resubmitted for registration with appropriate warnings in the product information and it is now marketed in more than 30 countries.
Pharmacokinetics
Tranylcypromine belongs to a class of antidepressants called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Tranylcypromine is a non-hydrazine monoamine oxidase inhibitor with a rapid onset of activity. MAO is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of a number of amines, including serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine. Two isoforms of MAO, A and B, are found in the body. MAO-A is mainly found within cells located in the periphery and catalyzes the breakdown of serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and tyramine. MAO-B acts on phenylethylamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and tyramine, is localized extracellularly and is found predominantly in the brain. While the mechanism of MAOIs is still unclear, it is thought that they act by increasing free serotonin and norepinephrine concentrations and/or by altering the concentrations of other amines in the CNS. It has been postulated that depression is caused by low levels of serotonin and/or norepinephrine and that increasing serotonergic and norepinephrinergic neurotransmission results in relief of depressive symptoms. MAO A inhibition is thought to be more relevant to antidepressant activity than MAO B inhibition. Selective MAO B inhibitors, such as selegiline, have no antidepressant effects.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Properties of tranylcypromine
| Melting point: | 28 °C |
| Boiling point: | bp1.5-1.6 79-80° |
| Density | 1.065±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 8.24±0.10(Predicted) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyclopropanamine, 2-phenyl-, (1R,2S)-rel- (155-09-9) |
Safety information for tranylcypromine
Computed Descriptors for tranylcypromine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
