trans-Cinnamaldehyde
Synonym(s):(E)-Cinnamaldehyde;trans-3-Phenyl-2-propenal;Cinnamic aldehyde;trans-Cinnamaldehyde;trans-Cinnamic aldehyde, trans-3-Phenyl-2-propenal
- CAS NO.:14371-10-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H8O
- Molecular Weight: 132.16
- MDL number: MFCD00007000
- EINECS: 604-377-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
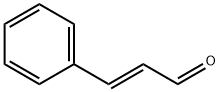
What is trans-Cinnamaldehyde?
Absorption
Cinnamaldehyde is 52% absorbed through the skin and shown to be rapidly absorbed from the gut .
Description
trans-Cinnamaldehyde, as its name suggests, is a natural product that occurs in cinnamon oils. Its cis counterpart is not found in nature; thus, “trans” is often omitted from its name.
As early as the 1830s, chemists reported synthesizing cinnamaldehyde via the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde. But the most economical way of producing it is still by steam distilling the bark of trees in the genus Cinnamomum.
Cinnamaldehyde is an important flavoring in foods (e.g., candy and cookies) and an odorant for perfumes. It has also been used to eradicate mosquito larvae and repel adult mosquitoes. Because it exists naturally, it is suitable for organic agriculture.
Now for a different take on cinnamaldehyde. Halloween is almost here, with its ghosts, witches, hobgoblins—and mummies. It turns out that the ancient Egyptians (ca. 2600 BCE) used the bark of cassia trees (Cinnamomum cassia) as an insecticide to help preserve mummies and give them a pleasing aroma.
Happy Halloween to you and your mummy!
Chemical properties
CLEAR YELLOW LIQUID
Chemical properties
Combustible, yellowish, oily liquid (thickens on exposure to air). Strong pungent, spicy, cinnamon odor.
Chemical properties
trans-Cinnamaldehyde is the
main component of cassia oil (about 90%) and Sri Lanka cinnamon bark oil (about 75%). Smaller quantities are found in many other essential oils. In nature, the
trans-isomer is predominant.
trans-Cinnamaldehyde is a yellowish liquid with a characteristic spicy odor,
strongly reminiscent of cinnamon. Being an ??,??-unsaturated aldehyde, it
undergoes many reactions, of which hydrogenation to cinnamic alcohol, dihydrocinnamaldehyde,
and dihydrocinnamic alcohol is important. Cinnamic acid is
formed by autoxidation.
On an industrial scale, cinnamaldehyde is prepared almost exclusively by
alkaline condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde. Self-condensation of
acetaldehyde can be avoided by using an excess of benzaldehyde and by slowly
adding acetaldehyde.
Cinnamaldehyde is used in many compositions for creating spicy and oriental
notes (e.g., soap perfumes). It is the main component of artificial cinnamon oil. In
addition, it is an important intermediate in the synthesis of cinnamic alcohol and
dihydrocinnamic alcohol.
The Uses of trans-Cinnamaldehyde
trans-Cinnamaldehyde is used in the flavor and perfume industry. It is also used in medicine. It reacts with glutathione to get an adduct 1'-(glutathion-S-yl)-dihydrocinnamaldehyde. It is used to prepare cinnamylidene-bisacetamide by reacting with acetamide. Further, it inhibits xanthine oxidase.
The Uses of trans-Cinnamaldehyde
Buildingblock - Cinnamaldehyde is an unsaturated aldehyde so it can easily react to many different compounds to be used in a wide range of fragrance compositions. It is also a building block for several agrochemicals (miticides) or for derivatives like cinnamic alcohol, 3-phenylpropanol, cinnamonitrile, 3-phenylpropionylaldehyde (fragrances and as an alternative to enalapril, lisinopril and ramipril).
Indications
Cinnamaldehyde is approved by the FDA for use within allergenic epicutaneous patch tests which are indicated for use as an aid in the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) in persons 6 years of age and older.
Background
Cinnamaldehyde is a naturally occurring flavonoid that gives the spice cinnamon its flavour and odour. It occurs naturally in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum such as camphor and cassia.
Sensitivity to cinnamaldehyde may be identified with a clinical patch test.
Definition
ChEBI: The E (trans) stereoisomer of cinnamaldehyde, the parent of the class of cinnamaldehydes.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Chemistry Letters, 12, p. 1207, 1983
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 93, p. 2080, 1971 DOI: 10.1021/ja00737a057
Tetrahedron Letters, 18, p. 1215, 1977
General Description
Clear yellow liquid with an odor of cinnamon and a sweet taste.
Air & Water Reactions
May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air and light. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
trans-Cinnamaldehyde is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases. trans-Cinnamaldehyde can also react with sodium hydroxide.
Fire Hazard
trans-Cinnamaldehyde is combustible.
Potential Exposure
Botanical fungicide and insecticide. Used as an antifungal agent, corn rootworm attractant, and dog and cat repellent. Can be used on soil casing for mushrooms, row crops, turf, and all food commodities. Not listed for use in EU countries.
Metabolism
Not Available
Shipping
UN1989 Aldehydes, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid
Incompatibilities
Aldehydes are frequently involved in selfcondensation or polymerization reactions. These reactions are exothermic; they are often catalyzed by acid. Aldehydes are readily oxidized to give carboxylic acids. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of aldehydes with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Aldehydes can react with air to give first peroxo acids, and ultimately carboxylic acids. These autoxidation reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by the products of the reaction). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) to shipments of aldehydes retards autoxidation. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, ketones, azo dyes, caustics, boranes, hydrazines
Waste Disposal
Incineration. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers.
Properties of trans-Cinnamaldehyde
| Melting point: | −9-−4 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 250-252 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.05 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.6 (vs air) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2286 | CINNAMALDEHYDE |
| Flash point: | 160 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| appearance | yellow oily liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear yellow |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. sweet spice candy cinnamon red hots warm |
| Water Solubility | 1.1 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2297 |
| JECFA Number | 656 |
| BRN | 1071571 |
| Dielectric constant | 16.899999999999999 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 14371-10-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cinnamaldehyde, (E)-(14371-10-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | trans-Cinnamaldehyde (14371-10-9) |
Safety information for trans-Cinnamaldehyde
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for trans-Cinnamaldehyde
trans-Cinnamaldehyde manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Anand Agencies
ASM Organics
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 trans-Cinnamaldehyde, 98% CAS 14371-10-9View Details
trans-Cinnamaldehyde, 98% CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 trans-Cinnamaldehyde 98% (GC) CAS 14371-10-9View Details
trans-Cinnamaldehyde 98% (GC) CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
trans-Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
Cinnamaldehyde CAS 14371-10-9View Details
14371-10-9 -
 14371-10-9 trans-Cinnamaldehyde, 98% 99%View Details
14371-10-9 trans-Cinnamaldehyde, 98% 99%View Details
14371-10-9 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1