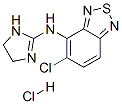
Tizanidine
- CAS NO.:51322-75-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H8ClN5S
- Molecular Weight: 253.71
- MDL number: MFCD00865192
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31

What is Tizanidine?
Absorption
This drug undergoes significant first-pass metabolism. After the administration of an oral dose, tizanidine is mostly absorbed. The absolute oral bioavailability of tizanidine is measured to be about 40% .
Effect of food on absorption
Food has been shown to increase absorption for both the tablets and capsules. The increase in absorption with the tablet (about 30%) was noticeably higher than the capsule (~10%). When the capsule and tablet were administered with food, the amount absorbed from the capsule was about 80% of the amount absorbed from the tablet . It is therefore advisable to take this drug with food for increased absorption, especially in tablet form.
Toxicity
LD50 information
Oral LD50 (rat): 414 mg/kg; Subcutaneous LD50 (rat): 282 mg/kg; Oral LD50 (mouse): 235 mg/kg
Use in pregnancy
Animal studies have determined that this drug causes fetal harm . Studies have not been performed in humans, and it is advisable to ensure that tizanidine use in pregnant women should be reserved for cases in which possible benefit clearly outweighs the possible risk to mother and unborn child .
Use in breastfeeding
In studies of rat models, this tizanidine was found excreted in the breastmilk with a milk-to-blood ratio of 1.8:1 . In young nursing rats, abnormal results were obtained in tests indicative of central nervous system function. Various developmental changes that may have been attributable to the drug were observed. It is unknown whether tizanidine is excreted in human milk. It is a lipid-soluble drug, however, and likely to be excreted into breast milk .
Carcinogenesis and mutagenesis
No signs of carcinogenicity were observed in two dietary studies performed in rodent models. Tizanidine was given to mice for 78 weeks at doses reaching a maximum 16 mg/kg (equivalent to twice the maximum recommended human dose). In addition, the drug was given to rats for 104 weeks at doses reaching 9 mg/kg (equivalent to 2.5 times the maximum recommended human dose). There was a lack of a statistically significant increase in the occurrence of tumors in either study group .
Tizanidine was not found to be mutagenic or clastogenic in several laboratory essays, including the bacterial Ames test, the mammalian gene mutation test, in addition to the chromosomal aberration test in Chinese hamster cells and several other assays .
Description
Tizanidine is a centrally-acting muscle relaxant useful in the treatment of muscle spasms and a variety of spastic conditions.
Originator
Sandoz (Switzerland)
The Uses of Tizanidine
Labeled Tizanidine, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Tizanidine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of Tizanidine
Tizanidine could have therapeutic use as a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor.
Background
Tizanidine is a fast-acting drug used for the management of muscle spasm, which may result from the effects of multiple sclerosis, stroke, an acquired brain injury, or a spinal cord injury . It may also be caused by musculoskeletal injury . Regardless of the cause, muscle spasticity can be an extremely painful and debilitating condition.
Initially approved by the FDA in 1996, tizanidine is an Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist reducing spasticity by the presynaptic inhibition of excitatory neurotransmitters that cause firing of neurons promoting muscle spasm .
Indications
Tizanidine is indicated for the relief of muscle spasticity, which can interfere with daily activities. The general recommendation is to reserve tizanidine use for periods of time when there is a particular need for relief, as it has a short duration of action .
Definition
ChEBI: 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole substituted at C-4 by a Delta1-imidazolin-2-ylamino group and at C-4 by a chloro group. It is an agonist at alpha2-adrenergic receptor sites.
Manufacturing Process
14 ml of benzoyl chloride are added to a solution of 11.5 g of ammonium thiocyanate in 150 ml of acetone in an ice bath and the mixture is then stirred for 10 min. This solution is heated to the boil at reflux together with 19 g of 4-amino-5-chloro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole. The solution is cooled to room temperature and diluted with a 4-fold quantity of water. The precipitate is filtered off and rapidly brought to a boil together with 150 ml of a 2 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and kept at the boil for 5 min. The solution is cooled to room temperature, is acidified weakly with glacial acetic acid, the precipitate is filtered off, washed with ether and recrystallized from methanol. The N-(5-chloro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-yl)thiourea, obtained and this is boiled for 1 h together with 9 g of methyl iodide in 150 ml of methanol. After concentrating by evaporation, crude S-methyl-N-(5-chloro-2,1,3- benzothiadiazol-4-yl)isothiuronium iodide is obtained. 9.8 g of S-methyl-N-(5- chloro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-yl)isothiuronium iodide are heated to the boil at reflux for 1 h together with 50 ml of methanol and 1.8 ml of ethylene diamine. The solvent is then removed by evaporation and the moist residue is boiled at reflux for 1 h together with 20 ml of n-amyl alcohol. The mixture is subsequently shaken with 50 ml of chloroform and 150 ml of water until all the material is dissolved. 40 ml of a 2 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution are added to the aqueous phase and extraction is effected with 200 ml of chloroform. The organic phase is dried and concentrated by evaporation. After recrystallizing the residue from methanol with the addition of some active charcoal, 4-(2-imidazolin-2-yl-amino)-5-chloro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole, having a melting point of 221-223°C, is obtained. The 4-(2-imidazolin-2-yl-amino)-5-chloro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole hydrochloride may be obtained by the teaction of 4-(2-imidazolin-2-yl-amino)-5-chloro- 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole with hydrochloric acid.
brand name
SIRDALUD
Therapeutic Function
Muscle relaxant, Spasmolytic
Mechanism of action
Tizanidine is a centrally active muscle relaxant analogue of clonidine that is approved for use in reducing spasticity associated with cerebral or spinal cord injury. Its mechanism of action for reducing spasticity suggests presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons at the α2-adrenergic receptor sites, reducing the release of excitatory amino acids and inhibiting facilitatory ceruleospinal pathways, thus resulting in a reduction in spasticity. Tizanidine only has a small fraction of the antihypertensive action of clonidine, presumably because of action at a selective subgroup of α2C-adrenoceptors, which appear to be responsible for the analgesic and antispasmodic activity of imidazoline α2-agonists(20).
Pharmacokinetics
A note on spasticity
Spasticity is an increase in muscle accompanied by uncontrolled, repetitive contractions of skeletal muscles which are involuntary.
The patient suffering from muscle spasticity may have reduced mobility and high levels of pain, contributing to poor quality of life and problems performing activities of personal hygiene and care .
General effects
Tizanidine is a rapidly acting drug used for the relief of muscle spasticity when it is required for performing specific activities. It acts as an agonist at Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor sites and relieves symptoms of muscle spasticity, allowing the continuation of normal daily activities. In animal models, tizanidine has not been shown to exert direct effects on skeletal muscle fibers or the neuromuscular junction, and has shown no significant effect on monosynaptic spinal reflexes (consisting of the communication between only 1 sensory neuron and 1 motor neuron) . The frequency of muscle spasm and clonus are shown to be decreased by tizanidine . Tizanidine shows a stronger action on polysynaptic reflexes, which involve several interneurons (relay neurons) communicating with motor neurons stimulating muscle movement .
Effects on blood pressure and heart rate
This drug decreases heart rate and blood pressure in humans . Despite this, rebound hypertension and tachycardia along with increased spasticity can occur when tizanidine is abruptly discontinued .
Clinical Use
Tizanidine is a centrally acting adrenergic α2 receptor agonist used to treat chronic muscle spasticity conditions, such as multiple sclerosis.
Side Effects
Postulated mechanisms include α2 receptor-mediated decreased release of norepinephrine and serotonin from spinal interneurons. Tizanidine is structurally related to the α2 agonist clonidine that is used to treat hypertension; however, the blood pressure–lowering potency of tizanidine is approximately 10 to 20% that of clonidine. Nevertheless, patients may experience hypotension with tizanidine, together with muscle weakness, that may result in dizziness and falls in mobile patients. Tizanidine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; however, the estimated bioavailability is only 10 to 15% because of extensive first-pass metabolism, mainly by CYP1A2, which results in oxidative degradation of the imidazoline ring and hydroxylation of the aromatic system. Elevated liver enzyme values are not frequent with tizanidine use. Hepatic injury and death because of liver failure have been reported, however, and this complication should be considered in view of its marginal antispasmodic efficacy. Other frequently reported side effects of tizanidine are drowsiness and dry mouth. Clonidine also has been used to treat spasticity; however, even less high-quality clinical study data are available for this agent.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: enhanced muscle relaxant effect
with procainamide.
Antibacterials: concentration increased by
ciprofloxacin - avoid; concentration possibly
increased by norfloxacin; concentration possibly
reduced by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: concentration increased by
fluvoxamine - avoid.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Oral contraceptives: clearance of tizanidine reduced
by 50
%.
Metabolism
About 95% of the ingested dose of tizanidine is metabolized. The main enzyme involved in the hepatic metabolism of tizanidine is CYP1A2 .
Metabolism
Tizanidine undergoes rapid and extensive first pass metabolism in the liver mainly via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP1A2. The metabolites (mainly inactive) constitute 70
% of the administered dose and are excreted via the renal route.
Properties of Tizanidine
| Melting point: | 221-223° |
| Boiling point: | 391.2±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.82±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: ~29 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 7.48±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51322-75-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tizanidine(51322-75-9) |
Safety information for Tizanidine
Computed Descriptors for Tizanidine
Tizanidine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 51322-75-9 TIZANIDINE HCL 2% GRANULES 98%View Details
51322-75-9 TIZANIDINE HCL 2% GRANULES 98%View Details
51322-75-9 -
 TIZANIDINE HCL 99%View Details
TIZANIDINE HCL 99%View Details -
 Tizanidine 98%View Details
Tizanidine 98%View Details
51322-75-9 -
 Tizanidine 51322-75-9 98%View Details
Tizanidine 51322-75-9 98%View Details
51322-75-9 -
 Tizanidine API PowderView Details
Tizanidine API PowderView Details
51322-75-9 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
