Tetrabenazine
Synonym(s):9,10-Dimethoxy-1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-3-isobutyl-2H-benzo[a]quinolizin-2-one;Tetrabenazine, TBZ - CAS 58-46-8 - Calbiochem;VMAT2 Inhibitor, Xenazine
- CAS NO.:58-46-8
- Empirical Formula: C19H27NO3
- Molecular Weight: 317.42
- MDL number: MFCD00042740
- EINECS: 200-383-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
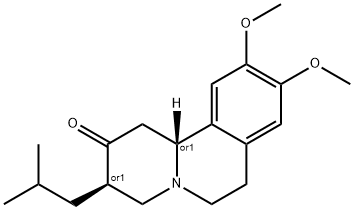
What is Tetrabenazine ?
Absorption
Following oral administration of tetrabenazine, the extent of absorption is at least 75%. After single oral doses ranging from 12.5 to 50 mg, plasma concentrations of tetrabenazine are generally below the limit of detection because of the rapid and extensive hepatic metabolism of tetrabenazine. Food does not affect the absorption of tetrabenazine. Cmax, oral = 4.8 ng/mL in HD or tardive dyskinesia patients; Tmax, oral = 69 min in HD or tardive dyskinesia patients
Toxicity
Dose-limiting adverse effects are sedation, parkinsonism, akathsia, and depression. LD50 oral, mouse: 550 mg/kg
Description
Tetrabenazine (58-46-8) is a potent inhibitor of the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT), IC50=3.2 nM1,2?with selectivity for VMAT2 over VMAT13. Promotes late stage differentiation of Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells into Neurog3-positive endocrine precursors.4
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Nitoman,Roche,UK,1960
The Uses of Tetrabenazine
Tetrabenazine has been used for dopamine uptake assays in mouse brain cells1. Tetrabenazine has also been used for non-specific binding assays in postnuclear supernatants derived from PC-12 and CV-1 cells2.
The Uses of Tetrabenazine
Dopamine depleting agent. An antidyskinetic; antipsychotic.
Indications
Treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders like chorea in Huntington's disease, hemiballismus, senile chorea, Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders, and tardive dyskinesia
Background
A drug formerly used as an antipsychotic but now used primarily in the symptomatic treatment of various hyperkinetic disorders. It is a monoamine depletor and used as symptomatic treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease. FDA approved on August 15, 2008.
What are the applications of Application
Tetrabenazine is a potent inhibitor of vesicular monoamine uptake
Definition
ChEBI: A benzoquinolizine that is 1,2,3,4,4a,9,10,10a-octahydrophenanthrene in which the carbon at position 10a is replaced by a nitrogen and which is substituted by an isobutyl group at position 2, an oxo group at position 3, and methoxy groups at positions 6 an 7.
Manufacturing Process
280 grams of 1-carbethoxymethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinoline, 150 grams of mono-isobutylmalonic acid dimethyl
ester and 35 grams of paraformaldehyde were refluxed for 24 hours in 1,000
ml of methanol. Upon cooling, 1-carbethoxymethyl-2-(2,2-dicarbomethoxy-4-
methyl-n-pentyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline crystallized;
MP after recrystallization from methanol, 94° to 96°C. The latter was
subjected to Dieckmann cyclization, hydrolysis and decarboxylation in the
following manner.
28 grams of sodium was dissolved in 650 ml of absolute ethanol, the solution
was concentrated to dryness, and the residue was mixed with 3,600 ml of
toluene and 451 grams of the intermediate prepared above. The mixture was
heated, and the methanol formed by condensation was distilled off until the
boiling point of toluene was reached. The mixture was thereupon refluxed for
2 hours, and then it was concentrated to dryness. The residue was dissolved
in 5,200 ml of 3 N hydrochloric acid and heated for 14 hours at 120°C,
thereby effecting hydrolysis and decarboxylation. The mixture was cooled,
washed with diethyl ether, decolorized with carbon, made alkaline and taken
up in diethyl ether. The process yields 2-oxo-3-isobutyl-9,10-dimethoxy-
1,2,3,4,6,7-hexahydro-11b-benzo[a]quinolizine; MP after recrystallization from
diisopropyl ether, 126° to 128°C.
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
General Description
A cell permeable benzoquinolizine based compound that acts as a monoamine-depleting agent by blocking the activity vesicular monoamine transporter 2. Promotes late-stage differentiation of Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells into Neurog3 (Ngn3)-positive endocrine precursors without increasing their proliferation. Increases the number of insulin expressing cells in a dose dependent manner (EC50 = 220 nM) and this effect is significantly enhanced when cells are simultaneously treated with dibutyryl cAMP. Embryonic stem cells treated with TBZ and/or dibutyryl cAMP and then grafted into kidney capsule of AKITA mice reduce hyperglycemia, improve fasting blood glucose levels, and show an increase in plasma C-peptide levels.
Biological Activity
Potent inhibitor of vesicular monoamine uptake; depletes stores of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenalin. Binds with high affinity (IC 50 = 3.2 nM) to vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) in chromaffin granule membranes and displays higher affinity for VMAT2 than VMAT1. Also reported to block dopamine receptors. Causes behavioral depression; inhibits locomotor activity and produces hypothermia upon systemic administration in rats and mice.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Primary TargetVMAT2
Pharmacokinetics
Prolongation of the QTc interval has been observed at doses of 50 mg. In rats, it has been observed that tetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues such as the eyes and skin. After a single oral dose of radiolabeled tetrabenazine, radioactivity was still detected in eye and fur at 21 days post dosing.
Metabolism
Tetrabenazine is hepatically metabolized. Carbonyl reductase in the liver is responsible for the formation of two major active metabolites: α-dihydrotetrabenazine (α-HTBZ) and β-dihydrotetrabenazine (β-HTBZ). α-HTBZ is further metabolized into 9-desmethyl-α-DHTBZ, a minor metabolite by CYP2D6 and with some contribution of CYP1A2. β-HTBZ is metabolized to another major circulating metabolite, 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ, by CYP2D6. The Tmax of this metabolite is 2 hours post-administration of tetrabenazine.
Storage
+4°C
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from MeOH. The hydrochloride has m 208-210o, and the oxime has m 158o (from EtOH). [Beilstein 21 III/IV 6488.]
Properties of Tetrabenazine
| Melting point: | 128-130?C |
| Boiling point: | 456.71°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.12 |
| refractive index | 1.5180 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >10mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 6.46±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Merck | 14,9182 |
| BRN | 40090 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 1 week. |
Safety information for Tetrabenazine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Tetrabenazine
| InChIKey | MKJIEFSOBYUXJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Tetrabenazine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![2H-BENZO[A]QUINOLIZIN-2-ONE, 1,3,4,6,7,11B-HEXAHYDRO-9,10-DIMETHOXY-3-(2-METHYLPROPYL)-, (3S,11BS)-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/1026016-84-1.gif)

You may like
-
 58-46-8 Tetrabenazine 99%View Details
58-46-8 Tetrabenazine 99%View Details
58-46-8 -
 58-46-8 99%View Details
58-46-8 99%View Details
58-46-8 -
 Tetrabenazine 98%View Details
Tetrabenazine 98%View Details
58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 -
 58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 98%View Details
58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 98%View Details
58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 -
 58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 Tetrabenazine 99%View Details
58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 Tetrabenazine 99%View Details
58-46-8 / 718635-93-9 -
 Tetrabenazine 95% CAS 58-46-8View Details
Tetrabenazine 95% CAS 58-46-8View Details
58-46-8 -
 Tetrabenazine CAS 58-46-8View Details
Tetrabenazine CAS 58-46-8View Details
58-46-8 -
 Tetrabenazine, TBZ CAS 58-46-8View Details
Tetrabenazine, TBZ CAS 58-46-8View Details
58-46-8
