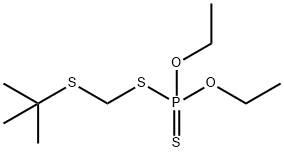
Terbufos
- CAS NO.:13071-79-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H21O2PS3
- Molecular Weight: 288.43
- MDL number: MFCD00055355
- EINECS: 235-963-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is Terbufos?
Chemical properties
Yellowish liquid. Soluble in alcohol, acetone.
Chemical properties
Terbufos is a colorless to pale yellow liquid.
The Uses of Terbufos
Terbufos is used to control soil pests in maize, sugar beet and vegetables and also nematodes in sugar beet and bananas.
The Uses of Terbufos
Soil insecticide.
Definition
ChEBI: Terbufos is an organic thiophosphate, an organothiophosphate insecticide and an organosulfur compound. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, an agrochemical and a nematicide.
General Description
Technical product is a clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid. Used as a soil insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzes under alkaline conditions [EPA, 1998]. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Organothiophosphates, such as Terbufos, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Terbufos decomposes in the presence of acids or bases .
Hazard
Moderate fire risk. Toxic by ingestion. Cholinesterase inhibitor. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Terbufos may be fatal if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. Repeated inhalation or skin contact may progressively increase susceptibility to poisoning.
Fire Hazard
This is a liquid organophosphorus pesticide. Fire may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Hydrolyzes under alkaline conditions.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Nematicide: This insecticide and nematicide is applied at planting time to corn, sugar beets, sorghum, maize, cotton, bananas and cabbage. It controls corn rootworms, wireworms, white grubs, maggots, billbugs and nematodes. Some above-ground pests can be controlled when soil has been treated with terbufos. Terbufos has no residential use. Not approved for use in EU countries. A U.S. EPA restricted use Pesticide (RUP).
Trade name
AC 921000®; ARAGRAN®; CONTRAVEN®; COUNTER®; COUNTER 15G SYSTEMIC INSECTICIDE®; PLYDOX®; TERBUROX®
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation or application of this organophosphate soil insecticide.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Oxidized in soil to its primary and secondary oxidation products, terbufos sul-
foxide and terbufos sulfone, respectively (Bowman and Sans, 1982; Chapman et al., 1982;
Wei, 1990). Both metabolites were formed due to micobial activity and chemical oxidation
(Chapman et al., 1982). Incubation of terbufos (5 μg/g) in a loamy sand containing
Nitrosomonas sp. and Nitrobacter sp. gave terbufos sulfoxide and terbufos sulfone as the
primary products. After 2 weeks, the sulfoxide increased the bacterial population >55%
and the sulfone increased the fungal population at least 66% (Tu, 1980). The half-life in
soil is 9–27 days (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Chemical/Physical. Terbufos and its degradation products terbufos sulfoxide and ter-
bufos sulfone followed first-order disappearance in natural, sterilized natural and distilled water at 20°C. In natural and distilled water, the sulfoxide and su
Metabolic pathway
Terbufos is the S-tertiary butyl homologue of phorate (the S-ethyl homolope). Consequently, the compound is more strongly sorbed to soils; however, the metabolism is essentially the same, with activation via thiooxidation and to a lesser degree oxidative desulfuration being the principal mechanisms. The metabolic routes for terbufos biotransformation have mainly been studied in soils where oxidation to the sulfoxide is rapid and further metabolism to the sulfone quite slow. In common with other phosphorodithioate insecticides, the phosphorodithioate moiety is excreted in mammalian urine as diethyl phosphate, O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate and O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate and in humans the concentrations of these metabolites have been found useful as indicators of exposure to the insecticide.
Metabolism
The metabolic routes of terbufos are essentially the same in plants, animals, and soils, involving the oxidation of the sulfide group into the sulfoxide, then sulfone, and oxidative desulfuration to the corresponding oxons, followed by hydrolysis to diethyl hydrogen phosphorodithioate, phosphorothioate, and phosphate. DT50 in soil is 9–27 d.
Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2783 Organophosphorus pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Terbufos is hydrolysed in strong alkalis (pH>9) and acids (pH﹤2) (PM). Terbufos disappeared rapidly when incubated in distilled water (pH 5.9), natural water (pH 8.7) and sterilised natural water (pH 8.75) with DT50 values of 3.3, 3.2 and 3.5 days, respectively. Terbufos was not converted into the sulfoxide (2) or the sulfone (3) under these conditions. The actual products of hydrolysis were not identified. Terbufos sulfoxide (2) and sulfone (3) were ten to one hundred times more stable than terbufos under the same conditions and there was evidence that, in contrast to terbufos, the hydrolysis was pH dependent (Bowman and Sans, 1982).
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is 1.6mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is 1.2–6.1 μg/L air. ADI is 0.2 μg/kg b.w.
Incompatibilities
Organophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Strong oxidizers may cause release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Organophosphates, in the presence of strong reducing agents, such as hydrides, may form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Keep away from alkaline materials.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Terbufos
| Melting point: | -29°C |
| Boiling point: | 69°C (0.01 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.105 |
| vapor pressure | 3.46×10-2 Pa (25 °C) |
| Flash point: | 88°C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless, pale |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Merck | 13,9233 |
| BRN | 1710115 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13071-79-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphorodithioic acid, s-[(tert-butylthio)methyl] o,o-diethyl ester(13071-79-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Terbufos (13071-79-9) |
Safety information for Terbufos
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Terbufos
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8