Tau-fluvalinate
- CAS NO.:102851-06-9
- Empirical Formula: C26H22ClF3N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 502.91
- MDL number: MFCD00871307
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
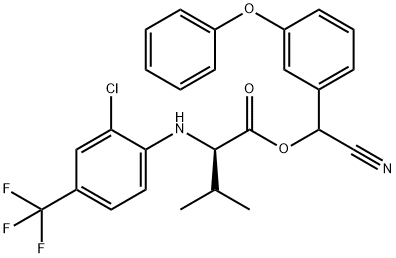
What is Tau-fluvalinate?
Description
Fluvalinate is a viscous, yellow oil in appearance. It is very soluble in organic solvents and aromatic hydrocarbons and insoluble in water. It is a synthetic pyrethroid. It is used as a broad-spectrum insecticide against moths, beetles, fleas, turf and ornamental insects, and other insect pests on cotton, cereal, grape, potato, fruit tree, vegetable, and plantation crops. It is available in emulsifiable concentrates, suspensions, and flowable formulations. Fluvalinate is a moderately toxic compound in the U.S. EPA toxicity class II. Some formulations may have the capacity to cause corrosion of the eyes. Pesticides containing fluvalinate must bear the signal word DANGER on the product label. Fluvalinate is classified as an RUP because of its high toxicity to fish and aquatic invertebrates.
Chemical properties
Yellow viscous liquid
Chemical properties
Fluvalinate is a viscous, yellow oil in appearance. It is very soluble in organic solvents and aromatic hydrocarbons and insoluble in water. Fluvalinate is a synthetic pyrethroid. It is used as a broad-spectrum insecticide against moths, beetles, and other insect pests on cotton, cereal, grape, potato, fruit tree, vegetable and plantation crops, fl eas, and turf and ornamental insects. It is available in emulsifi able concentrates, suspensions, and fl owable formulations. Fluvalinate is a moderately toxic compound in the US EPA toxicity class II. Some formulations may have the capacity to cause corrosion of the eyes. Pesticides containing fl uvalinate must bear the signal word DANGER on the product label. Fluvalinate is classifi ed as an RUP because of its high toxicity to fi sh and aquatic invertebrates.
Chemical properties
Yellow to yellow-amber, viscous oil. Sweet, weak odor.
The Uses of Tau-fluvalinate
Fluvalinate is used to control a wide range of insects and spider mites on fruit trees, vines, vegetables, cereals, cotton, tea, tobacco, ornamentals and other crops. It is also used for parasite control in bee hives.
Definition
ChEBI: The (2R) diastereomers of fluvalinate. A synthetic pyrethroid insecticide, it is used to control varroa mites in honey bee colonies.
Health Hazard
Exposures to fl uvalinate cause coughing, sneezing, throat irritation, itching, or burning sensations on the arms or face with or without a rash, headache, and nausea. Prolonged period of exposures to pyrethroids cause adverse effects on the CNS, liver, and kidneys. Fluvalinate is slightly toxic to birds.
Potential Exposure
Pyrethroid insecticide used as a broad spectrum insecticide to control moths, beetles and other pests on cereals, potatoes, fruit trees, vegetables, fleas, cot ton, turf and ornamentals. It is also used to control varroa mites in honey bees. Some applications may be classified as a United States Environmental Protection Agency Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Formerly used as an insec ticide. Production discontinued by Sandoz Agro, Inc. Incompatibilities: Corrosive to some metals. Keep away from strong oxidizers and alkaline materials. Decomposes in temperatures above 350℃ releasing toxic vapors of hydrogen chloride, nitrogen oxides, and hydrogen fluoride.
Metabolic pathway
The information reported below is derived from studies on fluvalinate, the racemic m-valinate (CASRN 69409-94-5). This has been superseded by the D-isomer. Evidence is given below to show that the results derived from fluvalinate are relevant to tau-fluvalinate. The chemical and photochemical degradation of fluvalinate and its degradation in soils have been reported. Information on metabolism in plants, rats, monkeys, cows and chickens is also published. The metabolism of fluvalinate is dominated by hydrolysis followed by oxidation and conjugation of the metabolites. Novel bile acid conjugates are highlighted. All quantitative data reported below are for the lower of usually two doses.
storage
Fluvalinate should be kept stored only in its original container at a temperature not exceeding 40°C. It should be kept away from food, drink, and animal feedstuffs.
Shipping
UN2902 Pesticides, liquid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Fluvalinate is readily hydrolysed under basic conditions. Half-lives at pH
5, 7 and 9 were 48,38.5 and 1.1 days, respectively (PM). A value of a few
minutes would be expected at pH 12.
The compound is very sensitive to photodegradation. [14C-trifluoro-
methyl]Fluvalinate and [14C-benzyl]fluvalinateh ave been studied in solution
(water and methanol) and as thin films on soils and glass (Quistad
and Staiger, 1984). Its half-life in sunlight under these conditions is about
1 day, but in dilute aqueous solution it can be as short as 10 minutes (PM).
The only sigruficant product retaining the ester structure (up to 18% yield)
was the amide (7). Its formation was non-photochemical and was directly
related to the temperature of the system. A minor product which retained
both portions of the molecule was the COTelimination product (12).
Under aqueous conditions 7 was a minor product and 12 was not
detected.
2-Chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)aniline( 3) was the major product derived
from the acid moiety on a thin film on glass and under aqueous conditions
(up to 40% and l8%, respectively). On soil surfaces the major products
were the amide (7) and the anilino acid, N-(2-chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-ptolyl)-
D-valinate (2), and 35% remained bound. This residue may have
arisen via the formation of aniline (3) (which was trapped as a volatile
product from the glass surface). The formation of 2 and 7 were considered
to be largely non-photochemical because they were also found under dark
conditions. The dicarboxylic acid (11) was found as a 1% metabolite on
soil surface photolysis.
The 3-phenoxybenzyl (3PB) portion (the alcohol moiety) was seen
under all conditions as 3PBA aldehyde (5) and its oxidation product 3PBA
(6) (together 40-50% of the applied radioactivity). The cyanohydrin (4)
was also detected and this was probably a primary product. Also detected
in 341% yields were the formanilide (8), (3-phenoxyphenyl)acetonitrile
(9) and the oxamic acid (10). These products are illustrated in Scheme 1.
Waste Disposal
Incineration would be an effective disposal procedure where permitted. If an efficient incinerator is not available, the product should be mixed with large amounts of combustible material and contact with the smoke should be avoided. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers.
Precautions
Occupational workers should avoid contact of fl uvalinate with the skin and eyes and avoid breathing contaminated fumes. Wear suitable protective clothing, nitrile rubber gloves, and safety glasses or a face shield. Fluvalinate is an RUP and should be used, handled, and/or purchased only by certifi ed applicators.
Properties of Tau-fluvalinate
| Boiling point: | 450°C |
| Density | 1.2900 |
| vapor pressure | 9×10-11 Pa (25 °C) |
| Flash point: | 90 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMF: 10 mg/ml,DMSO: 10 mg/ml,Ethanol: 10 mg/ml |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 0.001 mg l-1 (20 °C) |
| pka | -1.16±0.50(Predicted) |
| BRN | 8092907 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 102851-06-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tau-fluvalinate (102851-06-9) |
Safety information for Tau-fluvalinate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Tau-fluvalinate
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
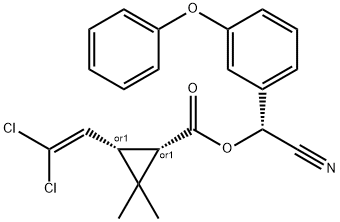
 τ-Fluvalinate CAS 102851-06-9View Details
τ-Fluvalinate CAS 102851-06-9View Details
102851-06-9 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1