Esfenvalerate
- CAS NO.:66230-04-4
- Empirical Formula: C25H22ClNO3
- Molecular Weight: 419.91
- MDL number: MFCD00203302
- EINECS: 613-911-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 16:22:15
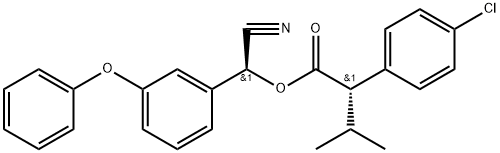
What is Esfenvalerate?
Chemical properties
Viscous yellow or amber liquid or white or amber crystalline solid.
The Uses of Esfenvalerate
Esfenvalerate is the most potent insecticidal isomer of Fenvalerate (F279450), a pyrethroid insecticide used to control insects from food crops, animal feed and cotton products.
The Uses of Esfenvalerate
Insecticide.
The Uses of Esfenvalerate
Esfenvalerate possesses a broad range of insecticidal activity and it is used on cotton, fruit, vegetables and other crops.
Definition
ChEBI: Esfenvalerate is a fenvalerate. It has a role as a pyrethroid ester insecticide and an agrochemical.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Esfenvalerate is a synthetic insecticide used to control a wide range of pests such as moths, flies, beetles, and other insects. It is used on vegetable crops (soya beans, sugar cane), tree fruit, cotton, maize, sorghum and nut crops, and non-crop lands. It also is used on a wide variety of household pests. It is usually mixed with a wide variety of other types of pesticides such as carbamate compounds or organophosphates and has the naturally occurring compound fenvalerate for use in the U.S. Esfenvalerate is almost identical to fenvalerate. Much of the data for fenvalerate is applicable to the pesticide esfenvalerate because the two compounds contain the same components. The only differences in the two products are the relative proportions of the four separate constituents (isomers). Esfenvalerate has become the preferred compound because it requires lower application rates than fenvalerate, is less chronically toxic, and is a more powerful insecticide.
Trade name
AMERICARE®; ASANA®; ASANA-XL®; ASANA® DPX-YB656-84; ENFORCER®; EVERCIDE®; HALMARK®; OMS-3023®; S-1844®; S-5602 ALPHA®; SUMI-ALFA®; SUMI-ALPHA®; SS-PYDRIN®; SUMICIDIN A-ALPHA®
Potential Exposure
Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid Insecticide used to control wide range of pests such as moths, flies, beetles, and other insects. It is used on vegetable crops (soya beans, sugar cane), tree fruit, cotton, maize, sorghum and nut crops, and noncrop lands. It also isused on a wide variety of household pests. It is usually mixed with a wide variety of other types of pesticides such as carbamate compounds or organophosphates and has the naturally occurring compound fenvalerate for use in the United States Esfenvalerate is almost identical to fenvalerate. Much of the data for fenvalerate is applicable to the pesticide esfenvalerate (E:0207) because the two compounds contain the same components. The only differences in the two products are the relative proportions of the four separate constituents (isomers). Esfenvalerate has become the preferred compound because it requires lower applications rates than fenvalerate, is less chronically toxic, and is a more powerful insecticide. A United States Environmental Protection Agency Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Incompatibilities: Oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); strong acids. Moisture may cause hydrolysis/ decomposition.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. May hydrolyze in aqueous solutions forming acetic acid and other compounds.
Metabolic pathway
Esfenvalerate is the 2SαS-isomer of fenvalerate (which is racemic). It possesses some small differences in physical properties when compared with the racemate. Overall, the degradation and metabolism of the two compounds are very similar. Reference should be made to the fenvalerate entry. An important exception, which is discussed fully in the latter entry, is that esfenvalerate does not form the cholesterol ester conjugate that has been shown to be responsible for granulomatous changes in several tissues on repeated dosing of fenvalerate.
Shipping
UN3349 Pyrethroid pesticide, solid toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous material. UN3352 Pyrethroid pesticide, liquid toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Degradation
Esfenvalerate is hydrolysed in aqueous alkali to its constituent acid and alcohol; the latter decomposes to 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde and cyanide ion as described for fenvalerate and cypermethrin. Photodecomposition occurs as for fenvalerate.
Incompatibilities
Oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); strong acids. Moisture may cause hydrolysis/ decomposition.
Waste Disposal
Incineration would be an effective disposal procedure where permitted. If an efficient incinerator is not available, the product should be mixed with large amounts of combustible material and contact with the smoke should be avoided. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers
Properties of Esfenvalerate
| Melting point: | 59°C |
| Boiling point: | 151-167°C |
| alpha | D25 -15.0° (c = 2.0 in CH3OH) |
| Density | d2323 1.163 |
| vapor pressure | 2×10-7 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (238.15 mM; Need ultrasonic) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 0.002 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to light yellow |
| BRN | 4275674 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 66230-04-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro-«alpha»-(1-methylethyl)-, cyano (3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl ester,(s-(r*,r*))-(66230-04-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Esfenvalerate (66230-04-4) |
Safety information for Esfenvalerate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Esfenvalerate
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Esfenvalerate CAS 66230-04-4View Details
Esfenvalerate CAS 66230-04-4View Details
66230-04-4 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
