Sulfolane
Synonym(s):Sulfolane;Tetramethylene sulfone;Tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide;Tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide, Tetramethylene sulfone;Sulfolane in dimethyl sulfoxide
- CAS NO.:126-33-0
- Empirical Formula: C4H8O2S
- Molecular Weight: 120.17
- MDL number: MFCD00005484
- EINECS: 204-783-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-24 17:44:56
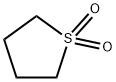
What is Sulfolane?
Description
Sulfolane, or more formally, tetrahydrothiophene-1,1-dioxide, has been used as an industrial solvent for almost 60 years. Its combination of a polar sulfone groups and a nonpolar hydrocarbon chain make it miscible with liquids ranging from water to hydrocarbons. Sulfolane is used for removing aromatics from saturated hydrocarbons and in liquid–vapor extractions such as the purification of natural gas.
Chemical properties
colourless crystals
Chemical properties
Sulfolane is a colorless oily liquid
The Uses of Sulfolane
Sulfolane is used in lithium-ion batteries.
The Uses of Sulfolane
Selective solvent for liquid-vapor extractions.
The Uses of Sulfolane
Process solvent for extractions of aromatics and for purification of acid gases.
Definition
ChEBI: Sulfolane is a member of the class of tetrahydrothiophenes that is tetrahydrothiophene in which the sulfur has been oxidised to give the corresponding sulfone. A colourless, high-boiling (285℃) liquid that is miscible with both water and hydrocarbons, it is used as an industrial solvent, particularly for the purification of hydrocarbon mixtures by liquid-vapour extraction. It has a role as a polar aprotic solvent. It is a sulfone and a member of tetrahydrothiophenes. It derives from a hydride of a tetrahydrothiophene.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 63, p. 2939, 1941 DOI: 10.1021/ja01856a021
General Description
Colorless oily liquid with a weak oily odor. Solidifies (freezing point is 79°) and sinks on first contact with water, then mixes with water. F.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Mixing Sulfolane in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid and oleum [NFPA 1991]. With nitrating agents (nitronium tetrafluoroborate in Sulfolane) very highly exothermic reactions are known to occur, [J. Org. Chem., 1978, 43, 4677].
Hazard
Combustible. Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Very mildly irritating to the eyes.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic, irritating gases may be generated in fires.
Industrial uses
Sulfolane is the most common commercially available sulfone solvent. The solvent,
also known as tetrahydrothiophene-1,1-dioxide, is a colorless, highly polar liquid
consisting of a fully hydrogenated five-member sulfur-carbon heterocyclic
thiophene ring. The solvent is available as both anhydrous sulfolane and as
sulfolane containing 3 wt% deionized water. Sulfolane is used as a reaction medium, as a solvent for a wide variety of organic chemicals and polymers, and as
an extraction solvent.
Sulfolane is a very high boiling point, colorless liquid with a very high
viscosity (10.3 centipoises) and medium surface tension value (35.5 dynes/cm).Sulfolane is miscible with water and many organic solvents.
Sulfolane is used to separate aromatic hydrocarbons
from aliphatic hydrocarbons. The extraction process first developed by Shell Oil in
1959 and which is referred to as the "Sulfolane" process is used worldwide. The
solvency of sulfolane for certain fatty acids and fatty acid esters is the basis for
upgrading animal and vegetable fatty acids used in food products, paints, plastics,
resins, and soaps.
Sulfolane is used to remove acidic components like
hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide from gas feed stocks. Sulfolane is used as a
polymerization solvent for the production of polysulfones, polysiloxanes,
polyphenylene ethers, and other polymers. Sulfolane is said to increase the
reaction rates, afford easier polymer purification, and improved thermal stability.
Sulfolane is a solvent for dissolving a variety of polymers for use in the fiberspinning
process.Cellulose and cellulose ester polymers can be plasticized with
sulfolane to give improved flexibility and other physical property improvements.
Other application areas that have used sulfolane include electronic and electrical
uses, textile dye uses, curing of polysulfide sealant, and as a catalyst in certain
synthetic reactions.
Potential Exposure
Sulfolane is used primarily as a process solvent for extraction of aromatics and for purification of acid gases. Used as a curing agent for epoxy resins, in medicine ash an antibacterial; fractionation of wood tars, tall oil, and other fatty acids; a component of hydraulic fluid; in textile finishing.
Carcinogenicity
Sulfolane was not mutagenic in bacterial assays with or without metabolic activation.
Shipping
UN3334 Aviation regulated liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material. Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
prepared commercially by a Diels-Alder reaction of between 1,3-butadiene and sulfur dioxide, followed by Raney nickel hydrogenation. The principal impurities are water, 3-sulfolene, 2-sulfolene and 2-isopropyl sulfolanyl ether. It is dried by passage through a column of molecular sieves. Distil it under reduced pressure through a column packed with stainless steel helices. Again dry it with molecular sieves and distil. [Cram et al. J Am Chem Soc 83 3678 1961, Coetzee Pure Appl Chem 49 211 1977.] Alternatively, it is stirred at 50o, and small portions of solid KMnO4 are added until the colour persists during 1hour. Dropwise addition of MeOH then destroys the excess KMnO4; the solution is filtered, freed from potassium ions by passage through an ion-exchange column and dried under vacuum. It has also been distilled in a vacuum from KOH pellets. It is hygroscopic. [See Sacco et al. J Phys Chem 80 749 1976, J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 73 1936 1977, 74 2070 1978, Trans Faraday Soc 62 2738 1966.] Coetzee has reviewed the methods of purification of sulfolane, and also the removal of impurities. [Coetzee in Recommended Methods of Purification of Solvents and Tests for Impurities, Coetzee Ed. Pergamon Press, 1982, Beilstein 17 I 5, 17 III/IV 37, 17/1 V 39.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Contact with nitronium tetrafluoroborate(1-) is potentially explosive.
Properties of Sulfolane
| Melting point: | 20-26 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 104 °C/0.2 mmHg (lit.)
285 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.261 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.01 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 330 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | >=100g/l soluble |
| form | Liquid After Melting |
| color | Clear yellow |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| FreezingPoint | 26℃ |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8955 |
| BRN | 107765 |
| Dielectric constant | 44.0 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 126-33-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiophene, tetrahydro-, 1,1-dioxide(126-33-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulfolane (126-33-0) |
Safety information for Sulfolane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sulfolane
| InChIKey | HXJUTPCZVOIRIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Sulfolane manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Sulfolane 98%View Details
Sulfolane 98%View Details
126-33-0 -
 Sulpholane CAS 126-33-0View Details
Sulpholane CAS 126-33-0View Details
126-33-0 -
 Tetramethylene Sulfone CASView Details
Tetramethylene Sulfone CASView Details -
 Sulpholane Anhydrous pure CAS 126-33-0View Details
Sulpholane Anhydrous pure CAS 126-33-0View Details
126-33-0 -
 Tetramethylene Sulfone CASView Details
Tetramethylene Sulfone CASView Details -
 SULFOLANE ANHYDROUS(126-33-0)View Details
SULFOLANE ANHYDROUS(126-33-0)View Details
126-33-0 -
 Industrial 99.5% Sulfolane Anhydrous SolventView Details
Industrial 99.5% Sulfolane Anhydrous SolventView Details
126-33-0 -
 CHINA SULFOLANE, For Industrial, Grade: TechnicalView Details
CHINA SULFOLANE, For Industrial, Grade: TechnicalView Details
126-33-0
