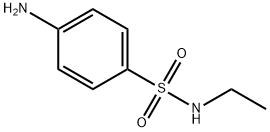
Sulfacytine
- CAS NO.:17784-12-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H14N4O3S
- Molecular Weight: 294.33
- MDL number: MFCD00057425
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
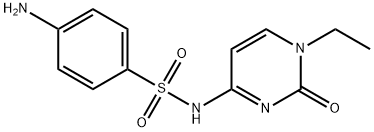
What is Sulfacytine?
Absorption
Well absorbed following oral administration.
Originator
Renoquid,Glenwood,US,1975
The Uses of Sulfacytine
Sulfacytine is a soluble short-acting sulfonamide. Sulfacytine is used as an oral antibiotic.
The Uses of Sulfacytine
Antibacterial.
Background
Sulfacytine is a short-acting sulfonamide. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections.
Sulfacytine is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. It inhibits bacterial synthesis of of dihydrofolic acid by preventing the condensation of the pteridine with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid.
Indications
Used orally in the treatment of acute urinary tract infections.
Definition
ChEBI: Sulfacytine is a member of benzenes and a sulfonamide.
Manufacturing Process
The N-(N-acetylsulfanilyl)-1-ethylcytosine used as a starting material is
prepared as follows: To a solution of 333 grams of 3-(ethylamino)propionitrile
in 1,697.3 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid is added 275 grams of potassium
cyanate, the resulting solution is concentrated under reduced pressure to a
syrup, and the syrup is heated at 90° to 100°C for 6 hours and then
evaporated to dryness at 90° to 100°C under reduced pressure. The residue is
extracted with 1,600 ml of hot absolute ethanol, and the extract is
concentrated to 500 ml and chilled. The crystalline 1-(2-cyanoethyl)-1-
ethylurea obtained is isolated, washed with cold absolute ethanol, and dried,
melting point 88° to 91°C. This intermediate (58.7 grams) is added to a
solution of 11.5 grams of sodium in 500 ml of methanol and the resulting
solution is heated under reflux for 30 minutes. After cooling, the mixture,
containing 1-ethyl-5,6-dihydrocytosine, is treated with a slight excess of
gaseous hydrogen bromide and evaporated to dryness. The residue is
extracted, first with 500 ml, then with 100 ml of hot isopropyl alcohol, the
extracts are combined and chilled, and the crystalline 1-ethyl-5,6-dihydrocytosine hydrobromide obtained is isolated and dried, MP 167.5° to
169.5°C. This salt (88.8 grams) is dissolved in 200 ml of nitrobenzene at
174°C, 22.6 ml of bromine is added over a period of 8 minutes, and the
mixture is kept at 170° to 175°C until hydrogen bromide evolution ceases
(about 15 minutes). Upon cooling, there is obtained crude 1-ethylcytosine
hydrobromide, which is isolated, washed with ether, and dried, MP 170° to
187°C.
This salt is heated at 90° to 100°C with 70 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide and
60 ml of piperidine, and the resulting solution is chilled to give 1-
ethylcytosine, MP 238° to 243°C. A mixture of 10.5 grams of 1-ethylcytosine,
18.6 grams of N-acetylsulfanilyl chloride, and 50 ml of pyridine is stirred at
room temperature for 2 days. The precipitated solid is removed by filtration,
and the filtrate is evaporated at 60°C under reduced pressure to a syrup. The
syrup is triturated with 0.25N hydrochloric acid, and the solid N-(N-acetylsulfanilyl)-
1-ethylcytosine obtained is isolated and dried. This solid is suitable
for use without further purification.
A solution of 65 grams of N-(N-acetylsulfanilyl)-1-ethylcytosine in 380 ml of 2
N aqueous sodium hydroxide is heated under reflux for 1 hour. Upon cooling,
the solution is treated with charcoal, purified by filtration, and acidified with
acetic acid. The solid N-sulfanilyl-1-ethylcytosine that precipitates is isolated,
washed with water, and dried, MP 166.5° to 168°C following successive
crystallizations from butyl alcohol and from methanol.
brand name
Renoquid (Glenwood).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfacytine is a short-acting sulfonamide. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections. Their antibacterial action is inhibited by pus.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Sulfacytine
| Melting point: | 166.5-168°; mp 104° |
| Boiling point: | 496.8±47.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 6.9(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Sulfacytine
Computed Descriptors for Sulfacytine
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5